GIS Manager
GIS Manager: Charting the Course with Spatial Data
A Geographic Information System (GIS) Manager oversees the systems and strategies related to spatial data within an organization. At its core, GIS involves capturing, storing, analyzing, managing, and presenting data linked to locations on Earth. Think of it as layering different types of information onto a map to understand patterns, relationships, and trends. A GIS Manager ensures these powerful tools are used effectively to support decision-making and operational efficiency.
Working as a GIS Manager can be deeply engaging. You might find excitement in leading a team to solve complex spatial problems, such as optimizing delivery routes for a logistics company or identifying areas most vulnerable to climate change impacts for a government agency. The role often involves blending technical expertise with strategic planning, offering a unique mix of hands-on involvement and high-level oversight that drives tangible results across various industries.
Introduction to GIS Management
What is GIS?
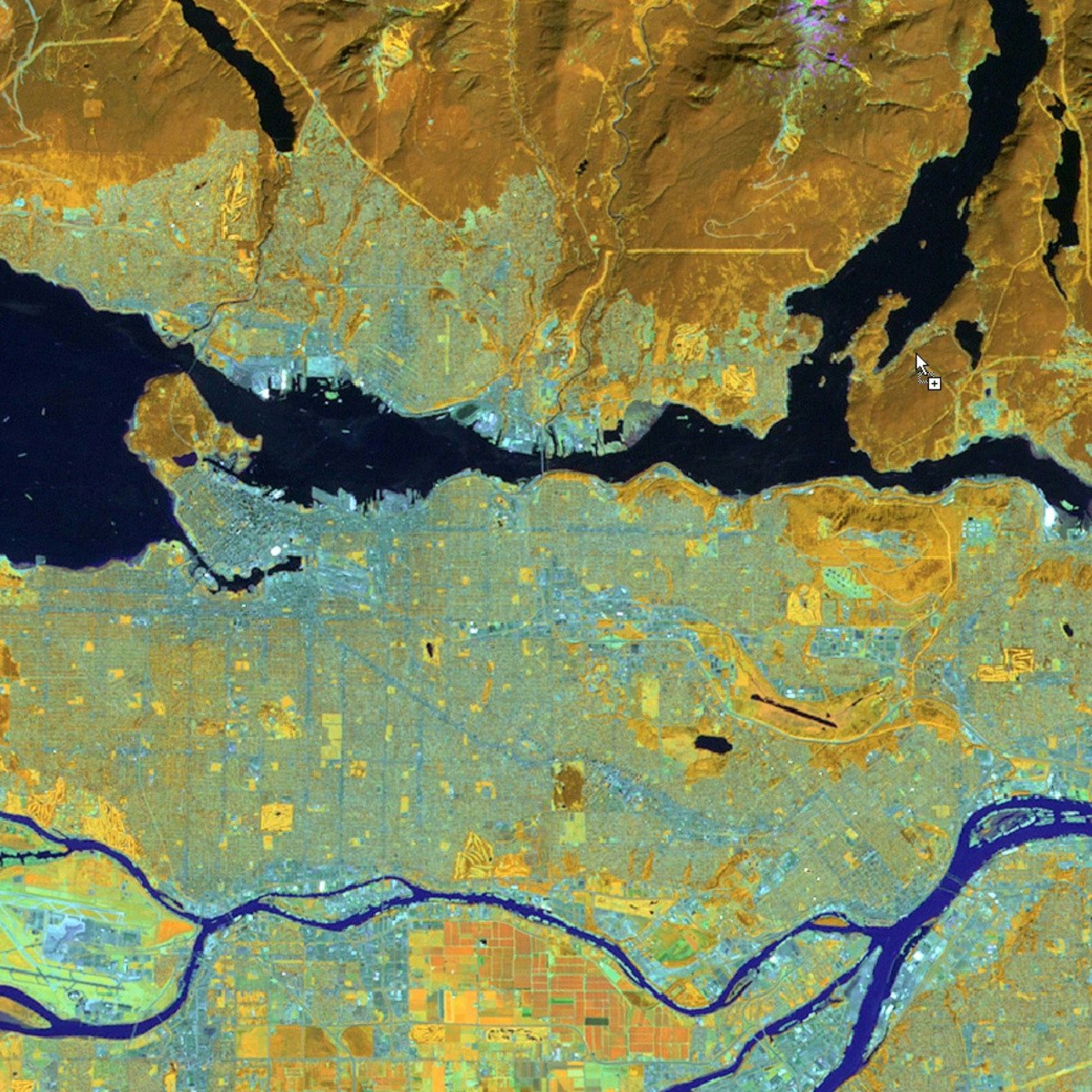
Geographic Information Systems, or GIS, are sophisticated computer systems designed to work with data tied to specific locations on the Earth's surface. This "spatial" or "geospatial" data can range from street addresses and administrative boundaries to elevation levels and satellite imagery. GIS allows users to visualize this data on maps, perform complex analyses, and reveal insights that might be hidden in traditional spreadsheets or databases.
The core functions of GIS include data capture (like digitizing maps or using GPS), data management (storing and organizing large spatial datasets), spatial analysis (querying data based on location, identifying patterns, modeling scenarios), and visualization (creating informative maps and graphics). These capabilities make GIS a powerful tool for understanding our world.
Ultimately, GIS helps organizations answer questions involving "where." Where are resources located? Where are customers concentrated? Where should new infrastructure be built? By providing spatial context, GIS supports better planning, resource allocation, and informed decision-making across countless fields.
A Brief History of GIS
The roots of GIS trace back to the mid-20th century, spurred by advances in computing and the need for better methods to manage geographic information, particularly in fields like urban planning and natural resource management. Early developments, like Canada's Geographic Information System in the 1960s, demonstrated the potential of computer-aided mapping and spatial analysis, though these systems were complex and expensive.
The advent of personal computers and more affordable software in the 1980s and 1990s democratized GIS technology. Companies like Esri emerged, providing software like ArcGIS that became industry standards. Open-source alternatives like QGIS later offered powerful, free tools, further expanding access.
Today, GIS is integrated with cloud computing, mobile technology, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT). This evolution allows for real-time data analysis, web-based mapping accessible to anyone, and sophisticated predictive modeling, making GIS more pervasive and impactful than ever before.
This foundational text explores the science and systems behind modern GIS.
Another excellent resource covers the fundamental principles of GIS.
Why Spatial Data Matters
In today's data-driven world, understanding the "where" aspect is crucial. Spatial data provides context that non-spatial data lacks. Knowing not just *what* happened, but *where* it happened, unlocks deeper understanding and enables more effective actions. From planning emergency response routes to analyzing market demographics, location is often a key factor.
Industries increasingly rely on spatial data for efficiency and insight. Logistics companies optimize routes, retailers select store locations, environmental agencies monitor changes, and cities plan infrastructure development—all using GIS. The ability to visualize and analyze information geographically leads to better resource management, risk assessment, and strategic planning.
As technology generates more location-aware data (from smartphones, sensors, satellites), the importance of skilled professionals who can manage and interpret this information grows. GIS Managers play a vital role in harnessing the power of spatial data to address complex challenges and drive innovation.
These courses offer introductions to mapping and spatial analysis fundamentals.
Role of a GIS Manager
Core Responsibilities
A GIS Manager wears many hats, blending technical expertise with leadership and strategic planning. Key responsibilities often include overseeing the organization's GIS infrastructure, managing geospatial databases, and ensuring data quality and security. They lead a team of GIS analysts, technicians, and specialists, assigning tasks, providing guidance, and fostering professional development.
Beyond technical oversight, the GIS Manager develops and implements the organization's geospatial strategy. This involves understanding organizational goals and identifying how GIS can support them, proposing new projects, managing budgets for GIS operations, and advocating for the value of spatial technology across departments.
Stakeholder management is also crucial. The GIS Manager often acts as a liaison between the technical GIS team and other departments or external clients, translating complex spatial concepts into understandable terms and ensuring GIS solutions meet user needs effectively.
Industries and Applications
GIS Managers are employed across a wide spectrum of industries, reflecting the versatility of geospatial technology. Government agencies at all levels (local, state, federal) are major employers, using GIS for urban planning, infrastructure management, public safety, environmental protection, and election administration.
In the private sector, utilities (water, gas, electric) rely heavily on GIS for network management and maintenance. Engineering and environmental consulting firms use GIS for site assessments, impact studies, and infrastructure design. Logistics and transportation companies optimize routing and fleet management, while retail businesses use GIS for market analysis and site selection.
Other significant sectors include natural resource management (forestry, agriculture, mining), real estate, telecommunications, and increasingly, technology companies developing location-based services. The specific applications vary, but the core need for managing and interpreting spatial data remains consistent.
This book provides a look into how GIS is applied in planning contexts.
Daily Tasks vs. Strategic Goals
The day-to-day work of a GIS Manager can be varied. It might involve troubleshooting technical issues with GIS software or databases, meeting with team members to review project progress, coordinating data collection efforts, or preparing reports and presentations for stakeholders. Ensuring the smooth operation of GIS systems and responding to immediate user needs are ongoing tasks.
However, a significant portion of the role focuses on longer-term strategic objectives. This includes planning for system upgrades or migrations, evaluating new geospatial technologies, developing standards and best practices for data management, aligning GIS initiatives with broader organizational strategy, and securing funding for future projects.
Balancing these operational demands with strategic vision is a key challenge and defining characteristic of the GIS Manager role. Effective managers must be adept at both managing current resources and planning for the future use of geospatial technology within their organization.
Formal Education Pathways
Relevant Degree Programs
A bachelor's degree is typically the minimum educational requirement for entering the GIS field, and often a prerequisite for management roles. Degrees in Geography, Geographic Information Science (GIS), or Cartography provide the most direct foundation, covering core concepts of spatial analysis, map design, and GIS software.
However, professionals also enter the field from related disciplines. Degrees in Computer Science offer strong technical skills applicable to GIS software development and database management. Environmental Science, Urban Planning, Geology, Civil Engineering, and Surveying degrees often include GIS coursework and provide valuable domain expertise for specific applications.
Regardless of the specific major, coursework in statistics, database management, programming, and project management complements a GIS-focused education and prepares individuals for the multifaceted demands of a management role.
This foundational text is often used in university GIS programs.
Advanced Studies and Specializations
For those seeking deeper expertise or aiming for leadership roles, a master's degree specializing in GIS, Geoinformatics, Geospatial Intelligence, or a related field can be highly beneficial. Graduate programs often offer advanced coursework in spatial statistics, remote sensing, database administration, web GIS development, and GIS project management.
A master's degree can provide a competitive edge in the job market and may be required for certain research or high-level management positions. Some programs also offer opportunities for specialized research or internships, providing practical experience and networking opportunities.
Doctoral programs (Ph.D.) are typically pursued by those interested in academic research, teaching at the university level, or leading cutting-edge research and development in government or private industry. While not usually required for a GIS Manager role, a Ph.D. signifies the highest level of expertise in the field.
Professional Certifications
Professional certifications serve as a valuable credential, validating an individual's knowledge, skills, and experience in the GIS field. The most widely recognized vendor-neutral certification is the GIS Professional (GISP) offered by the GIS Certification Institute (GISCI). Achieving GISP status typically requires a combination of education, experience, and contributions to the profession, along with passing an exam.
Software vendors, particularly Esri, also offer technical certifications focused on their specific products (e.g., ArcGIS Desktop, ArcGIS Enterprise). These certifications demonstrate proficiency with widely used industry tools and can be beneficial for roles requiring deep expertise in a particular software ecosystem.
While certifications may not always be mandatory, they can enhance credibility, demonstrate commitment to professional development, and potentially improve job prospects or salary negotiations, especially when combined with practical experience and formal education.
Online Learning and Skill Development
Prioritizing Core Technical Skills
Online learning offers a flexible and accessible way to build the technical foundation needed for a GIS career. Prioritize mastering core GIS software packages like ArcGIS and QGIS. Develop strong skills in spatial analysis techniques, understanding how to manipulate and query geographic data to answer specific questions.
Database management is another critical area. Learn SQL for querying databases and understand spatial database concepts, possibly exploring platforms like PostGIS. Programming skills, especially in Python, are increasingly valuable for automating tasks, performing complex analyses (using libraries like ArcPy or GeoPandas), and customizing GIS workflows.
Familiarity with web mapping technologies (Leaflet, Mapbox GL JS, Esri's JavaScript API) and concepts of web GIS is also becoming essential as more applications move online. Online courses provide structured paths to acquire these diverse technical competencies.
These courses provide introductions to essential software and programming skills for GIS professionals.
This book provides practical guidance on scripting for a leading GIS platform.
Project-Based Learning Strategies
Theoretical knowledge is important, but practical application solidifies skills and demonstrates capability to potential employers. Seek online courses that incorporate hands-on exercises and capstone projects. Building a portfolio of projects showcasing your abilities in data analysis, map creation, and problem-solving is crucial, especially for career changers or those new to the field.
Look for opportunities to apply your learning to real-world scenarios or datasets. You could volunteer your GIS skills for a local non-profit, contribute to open-source mapping projects (like OpenStreetMap), or develop a personal project based on publicly available data relevant to your interests (e.g., analyzing local crime patterns, mapping environmental hazards).
Platforms like OpenCourser can help you find courses with strong project components. You can save courses to a list and compare syllabi to identify those emphasizing practical application. Document your projects clearly, explaining the problem, methods, tools used, and outcomes.
This capstone course focuses entirely on applying GIS skills through a self-directed project.
This book offers tutorials for learning core GIS software through practical exercises.
Balancing Online and Hands-On Experience
Online courses are excellent for acquiring foundational knowledge and specific technical skills efficiently. They allow you to learn at your own pace and often provide access to cutting-edge topics. However, complementing online learning with hands-on experience is vital for career growth, particularly towards a management role.
Seek internships, entry-level positions (like GIS Technician), or volunteer opportunities to gain practical experience in an organizational setting. This exposure helps you understand real-world workflows, data challenges, team dynamics, and the practical constraints of implementing GIS solutions. It also provides valuable networking opportunities.
For professionals already working in a related field, look for opportunities to incorporate GIS into your current role or collaborate on projects with the GIS team. This gradual integration can build relevant experience. Remember, the path to GIS Manager often involves demonstrating not just technical skill, but also project management capabilities and an understanding of how GIS fits within the larger organizational context, which often comes from practical immersion.
Consider exploring OpenCourser's Geography or Data Science categories for a wide range of courses to build your skills.
GIS Manager Career Progression Path
Entry-Level Roles
Most GIS careers begin in technical, hands-on roles. Common entry-level positions include GIS Technician, GIS Specialist, or GIS Analyst. A GIS Technician often focuses on data creation, data entry, digitizing, and producing maps based on established procedures.
A GIS Specialist or GIS Analyst typically has broader responsibilities, including performing spatial analysis, managing databases, developing GIS applications, and supporting GIS users. These roles require a stronger understanding of GIS principles and software capabilities.
Experience in these positions builds foundational technical skills, familiarity with different types of geospatial data and projects, and an understanding of how GIS is applied within an organization. This practical grounding is essential before moving towards management.
Transitioning to Management
Moving from a technical role to a GIS Manager position usually requires several years of experience and demonstrated leadership potential. Mid-career roles like Senior GIS Analyst, GIS Coordinator, or GIS Project Manager often serve as stepping stones. These positions involve more complex projects, mentoring junior staff, and increased responsibility for project planning and execution.
The transition involves shifting focus from primarily technical tasks to overseeing projects, managing resources (people, budget, technology), and aligning GIS activities with organizational goals. Developing strong communication, leadership, problem-solving, and project management skills becomes paramount.
This transition might be facilitated by taking on lead roles within projects, pursuing additional training in management or leadership, seeking mentorship from existing managers, and actively demonstrating an understanding of the strategic value of GIS.
Advanced Leadership Opportunities
Beyond the GIS Manager role, experienced professionals may advance to higher-level leadership positions. Titles like Director of Geospatial Technology, Director of GIS Services, or Chief Geospatial Officer reflect broader strategic responsibilities, often overseeing multiple teams or the entire geospatial function within a large organization or government agency.
In some cases, individuals with strong technical and strategic backgrounds might move into roles like Chief Data Officer or Director of Analytics, where geospatial data is a key component of a larger data strategy. These advanced positions require a deep understanding of both the technology and the business or mission it supports, combined with exceptional leadership and strategic planning abilities.
Career progression often depends on the size and structure of the organization, individual performance, continuous learning, and the ability to demonstrate the strategic impact of geospatial information and technology.
Technical Skills and Tools
GIS Software Proficiency
Mastery of core GIS software is fundamental. The ArcGIS platform by Esri is the dominant commercial software suite, widely used in government and industry. Proficiency typically includes ArcGIS Pro for desktop analysis and mapping, ArcGIS Online for web GIS and collaboration, and potentially ArcGIS Enterprise for managing larger, on-premises systems.
QGIS is the leading open-source GIS software, offering powerful capabilities comparable to commercial options at no cost. Familiarity with QGIS is increasingly valuable, especially in academia, non-profits, and organizations seeking flexible, cost-effective solutions. Experience with both ArcGIS and QGIS broadens opportunities.
Depending on the industry, specialized software may also be relevant, such as ERDAS IMAGINE or ENVI for advanced remote sensing analysis, or AutoCAD Map 3D for integration with engineering workflows.
These resources can help you learn key GIS software platforms.
Database Management
GIS deals with large volumes of data, making database management skills essential. Understanding relational database concepts and proficiency in Structured Query Language (SQL) are critical for querying, manipulating, and managing attribute data linked to geographic features.
Experience with spatial database extensions is particularly important for storing and querying geographic data types efficiently. PostGIS, an extension for the open-source PostgreSQL database, is widely used. Esri's geodatabase format, particularly enterprise geodatabases built on systems like SQL Server, Oracle, or PostgreSQL, is also prevalent in ArcGIS environments.
A GIS Manager often oversees the design, implementation, and maintenance of these spatial databases, ensuring data integrity, security, and performance.
These courses provide insights into managing enterprise-level GIS, often involving complex database setups.
Programming and Automation
Programming skills significantly enhance efficiency and capability in GIS. Python has become the de facto scripting language for GIS automation and analysis. Libraries like ArcPy (for ArcGIS) and PyQGIS (for QGIS), along with general geospatial libraries like GDAL/OGR, Shapely, and GeoPandas, allow users to automate repetitive tasks, perform complex analyses, and build custom tools.
For web GIS development, knowledge of JavaScript and relevant mapping libraries (Leaflet, OpenLayers, Mapbox GL JS, Esri JavaScript API) is essential for creating interactive web maps and applications. Some roles, particularly those involving heavy statistical analysis, may also utilize R with its spatial packages.
While not all GIS professionals need to be expert programmers, a foundational understanding of scripting and automation is increasingly expected, especially at the management level where optimizing workflows is key.
These courses focus on developing web GIS applications and using scripting.
These books cover geospatial analysis using programming languages.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
GIS in Emergency Management
GIS plays a critical role in all phases of emergency and disaster management. Before an event, GIS is used for risk assessment (mapping flood plains, earthquake fault lines, wildfire risk zones) and planning (designing evacuation routes, siting shelters, allocating resources). This proactive analysis helps communities prepare and mitigate potential impacts.
During a disaster, GIS provides situational awareness by mapping the extent of the event, tracking response team locations, identifying affected populations, and visualizing infrastructure damage in near real-time. This information is crucial for coordinating effective response efforts.
After an event, GIS supports recovery by mapping damage assessments, managing debris removal logistics, planning reconstruction efforts, and analyzing the effectiveness of the response to inform future preparedness.
This book touches upon crime analysis, another public safety application of GIS.
Analytics for Retail and Logistics
The retail and logistics sectors leverage GIS extensively for spatial analytics to gain a competitive edge. Retailers use GIS to analyze demographic data, competitor locations, and traffic patterns to identify optimal locations for new stores (site selection). They also analyze customer data geographically to understand market penetration and tailor marketing campaigns.
Logistics companies rely heavily on GIS for route optimization, minimizing travel time and fuel costs for deliveries and service calls. GIS helps manage vehicle fleets, track shipments in real-time, and plan efficient distribution networks. Warehouse location analysis also benefits from considering proximity to suppliers, customers, and transportation hubs.
These applications demonstrate how understanding spatial relationships directly translates into improved efficiency, reduced costs, and better business decisions.
Environmental Science and Monitoring
GIS is an indispensable tool in environmental science and natural resource management. It's used to map ecosystems, monitor changes in land cover (like deforestation or urbanization) using satellite imagery, and model the spread of pollutants in air or water.
Environmental impact assessments heavily rely on GIS to analyze the potential effects of proposed development projects on surrounding habitats, water resources, and sensitive species. Conservation organizations use GIS to identify priority areas for protection, manage parks and reserves, and track wildlife populations.
In agriculture, precision farming uses GIS and GPS technology to manage fields more effectively, optimizing irrigation and fertilizer application based on spatial variations in soil conditions. GIS helps manage resources sustainably and understand complex environmental processes.
Emerging Trends in GIS Management
Integrating AI and Machine Learning
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) is transforming geospatial analysis. These technologies enable more sophisticated pattern recognition, predictive modeling, and automation within GIS workflows. Examples include automatically extracting building footprints or road networks from satellite imagery, predicting urban growth patterns, or identifying optimal locations based on complex spatial factors.
ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of spatial and non-spatial data to uncover subtle relationships and make predictions with greater accuracy than traditional methods. GIS Managers need to understand the potential and limitations of these techniques to leverage them effectively.
Staying updated requires exploring how AI/ML can enhance spatial analysis and decision-making within their specific organizational context.
This course explores the intersection of machine learning and GIS.
Cloud-Based GIS Platforms
The shift towards cloud computing is significantly impacting GIS. Cloud-based platforms like ArcGIS Online, Google Earth Engine, and others offer scalable infrastructure, easier data sharing and collaboration, and access to powerful processing capabilities without requiring significant on-premises hardware investments.
Cloud GIS facilitates the development of web and mobile applications, making spatial data and tools accessible to a wider range of users, often through simple browser interfaces. This democratization of GIS requires managers to adapt their strategies for data management, security, and application deployment in a cloud environment.
Understanding cloud architecture, service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), and the cost implications of cloud deployment is becoming increasingly important for effective GIS management.
This course introduces concepts relevant to advanced computational GIS, often leveraging cloud infrastructure.
Ethical Considerations and Data Privacy
As geospatial data becomes more ubiquitous, particularly from personal devices and sensors, ethical considerations and data privacy are paramount concerns. GIS Managers must navigate the complexities of collecting, storing, and using location data responsibly.
Issues include ensuring data anonymization where appropriate, complying with privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA, addressing potential biases in spatial algorithms, and considering the implications of location data monetization. Transparency in how location data is used and securing consent are critical.
Managers need to establish clear policies and best practices for ethical data handling within their teams and ensure that GIS applications respect individual privacy while still delivering valuable insights.
Challenges in GIS Management
Data Security and Privacy
Protecting sensitive geospatial data from unauthorized access or breaches is a primary challenge. This includes implementing robust security measures for databases and servers, managing user permissions effectively, and ensuring compliance with organizational and regulatory data security standards.
Privacy concerns, especially with detailed location data about individuals, require careful management. GIS Managers must ensure that data collection, analysis, and sharing practices adhere to privacy laws and ethical guidelines. Balancing the utility of detailed spatial data with the need to protect individual privacy is an ongoing challenge.
Developing clear data governance policies and training staff on security and privacy best practices are essential components of mitigating these risks.
Managing Technology Evolution
The rapid pace of technological change in the geospatial field presents both opportunities and challenges. GIS Managers must constantly evaluate new software, hardware, and data sources (like drones or new satellite sensors) to determine their potential value to the organization.
Balancing the adoption of new technologies with the need to maintain and support existing legacy systems can be difficult. Decisions about system upgrades or migrations require careful planning, budget justification, and managing the transition process to minimize disruption.
Staying current requires continuous learning and strategic foresight to ensure the organization's GIS capabilities remain effective and aligned with evolving needs and possibilities.
Fostering Collaboration and Buy-in
GIS often serves multiple departments within an organization, requiring effective cross-departmental collaboration. A GIS Manager must often bridge communication gaps, understand the needs of different user groups, and promote the value of geospatial thinking across the organization.
Gaining buy-in for GIS initiatives and securing adequate resources can be challenging. This requires demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of GIS projects, communicating successes effectively, and building strong relationships with stakeholders at various levels.
Overcoming organizational silos and fostering a culture where spatial data is seen as a valuable enterprise asset, rather than just a tool for a specific department, is a key leadership challenge for GIS Managers.
Global Job Market and Opportunities
Demand Across Sectors and Regions
The demand for skilled GIS professionals, including managers, remains strong globally, though it varies by region and sector. Government agencies consistently employ a large number of GIS professionals for public administration, infrastructure, and environmental management. The private sector demand is growing, particularly in utilities, engineering, consulting, logistics, and technology.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment for related occupations like Cartographers and Photogrammetrists is projected to grow, driven by the increasing use of spatial data across industries. Growth areas often include urban and regional planning, environmental management, and location-based services.
Regional hotspots often correlate with government centers, technology hubs, or areas with significant activity in natural resources or infrastructure development. Understanding local market needs is key for job seekers.
Remote Work and Flexibility
The GIS field has seen an increase in remote work opportunities, particularly for analyst and developer roles that primarily involve working with digital data and software. Cloud-based GIS platforms and collaboration tools have further enabled distributed teams.
While many technical tasks can be performed remotely, GIS Manager positions may require more on-site presence due to leadership responsibilities, team oversight, and stakeholder interaction needs. However, hybrid arrangements are becoming more common, offering greater flexibility.
The feasibility of remote work often depends on the specific organization's culture, security requirements, and the nature of the projects being managed.
Salary Expectations
Salaries for GIS Managers vary based on factors like geographic location, industry, years of experience, level of education, certifications, and the size and complexity of the team and systems being managed. Generally, GIS management roles offer competitive compensation reflecting the blend of technical expertise and leadership skills required.
As reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for cartographers and photogrammetrists was $74,900 in May 2023, though managers typically earn significantly more. Salary survey data from organizations like URISA or general salary comparison websites can provide more specific benchmarks.
Advanced degrees, certifications like the GISP, specialized technical skills (e.g., programming, enterprise database management), and experience in high-demand sectors can positively influence earning potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I become a GIS Manager without a geography degree?
Yes, it is possible. While a geography or GIS degree provides a strong foundation, individuals with degrees in related fields like computer science, environmental science, urban planning, engineering, or even business can transition into GIS management, especially if they acquire relevant technical skills and experience.
Often, extensive practical experience, demonstrated expertise in GIS software and principles, strong project management skills, and leadership qualities are more critical than the specific undergraduate major, particularly later in one's career.
Supplementing a non-geography degree with GIS-focused coursework, certifications, and hands-on projects is crucial for building the necessary qualifications.
What soft skills are most valued?
Beyond technical proficiency, several soft skills are crucial for GIS Managers. Strong communication skills are essential for explaining complex spatial concepts to non-technical audiences, collaborating with other departments, and leading a team. Leadership abilities are needed to guide, motivate, and develop GIS staff.
Problem-solving skills are vital for tackling technical challenges and finding innovative spatial solutions to organizational problems. Project management skills are necessary for planning, executing, and monitoring GIS projects, managing budgets, and meeting deadlines.
Strategic thinking helps align GIS initiatives with broader organizational goals and anticipate future needs. Adaptability is also key in a rapidly evolving technological field.
How does GIS management differ from data science?
While both fields involve data analysis, GIS management specifically focuses on *spatial* data and its applications. GIS Managers oversee systems, teams, and strategies centered around geographic information. Their work inherently involves mapping, spatial analysis techniques (like proximity analysis, network analysis, geostatistics), and managing geospatial databases.
Data Science is a broader field focused on extracting knowledge and insights from data in various forms, often using statistical modeling, machine learning, and programming. While data scientists may work with spatial data (leading to the emerging field of Geospatial Data Science), their scope is generally wider and less focused on cartographic representation or traditional GIS workflows.
A GIS Manager's role typically involves more operational oversight of GIS infrastructure and personnel compared to a data scientist who might be more focused on specific analytical modeling tasks.
Is coding mandatory for GIS professionals?
While not strictly mandatory for every single GIS role, coding skills (especially Python) are increasingly valuable and often expected, particularly for analyst, developer, and management positions. Coding allows for automation of repetitive tasks, customization of workflows, implementation of complex analyses, and development of web applications, significantly enhancing productivity and capability.
For a GIS Manager, understanding the principles of programming and automation is important for overseeing technical staff, evaluating project feasibility, and making strategic decisions about technology adoption. While they may not code daily, familiarity helps manage resources effectively.
Entry-level technician roles might require less coding, but acquiring scripting skills generally opens more doors for career advancement in the field.
What industries hire the most GIS Managers?
Government agencies (federal, state, county, municipal) are traditionally among the largest employers of GIS professionals, including managers, due to the wide use of GIS in public administration, planning, and infrastructure management.
Other major employers include utility companies (electric, water, gas, telecom), engineering and environmental consulting firms, natural resource management organizations, and increasingly, technology companies involved in mapping, logistics, or location-based services.
Sectors like transportation, retail, real estate, agriculture, and public health also employ GIS Managers, reflecting the broad applicability of geospatial technology.
How stable is this career amid automation trends?
The GIS field is generally considered stable, as the need for spatial data analysis and management continues to grow across industries. While automation, AI, and ML are changing *how* some GIS tasks are performed (automating feature extraction, improving predictive models), they also create new opportunities and increase the demand for skilled professionals who can manage and interpret these complex systems.
The role of the GIS Manager is evolving towards more strategic oversight, data governance, integration of new technologies, and ensuring GIS delivers business value, rather than solely focusing on routine technical tasks. Adaptability and continuous learning are key to remaining relevant.
While specific tasks might be automated, the fundamental need for experts who understand spatial principles, manage complex geospatial projects, and lead teams is likely to persist and evolve.
Embarking on a career as a GIS Manager involves a blend of technical mastery, strategic thinking, and leadership. It's a dynamic field where you can leverage the power of location to solve real-world problems across diverse industries. Whether you're starting your educational journey, considering a career change, or looking to advance within the field, resources like OpenCourser can help you find the online courses and information needed to navigate your path in the exciting world of geospatial technology.