Waste Management
Introduction to Waste Management
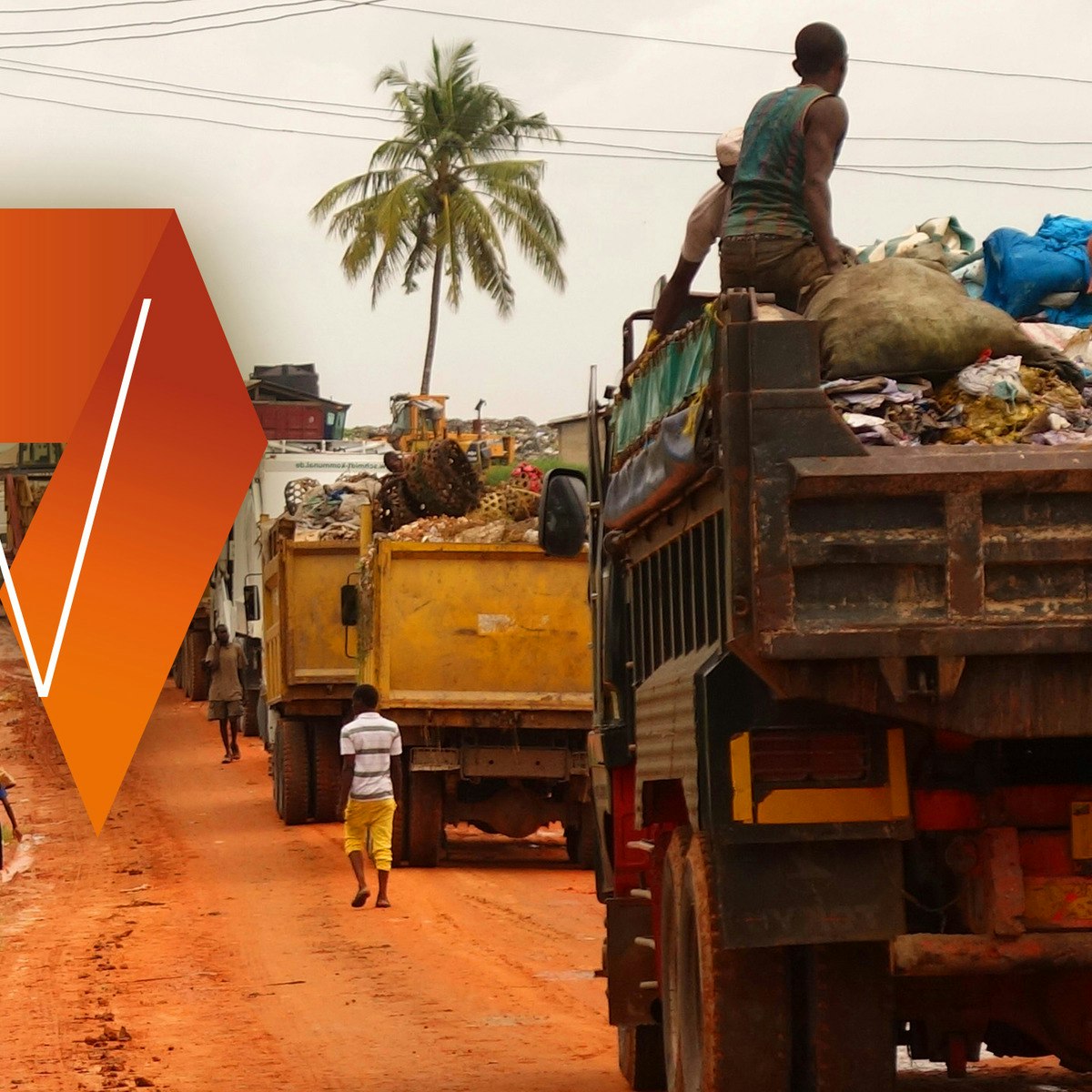
Waste management encompasses the various processes and actions required to handle waste from its creation to its final disposal. The primary aim is to reduce the adverse effects of waste on human health, the environment, and aesthetics. This involves a multidisciplinary approach that integrates principles from engineering, economics, urban planning, and social sciences to minimize overall wastage. Waste management is a critical aspect of modern society, addressing the byproducts of human activity, including industrial, commercial, and household refuse.
Working in waste management can be engaging due to its direct impact on environmental sustainability and public health. Professionals in this field often find satisfaction in developing and implementing strategies that protect natural resources and improve the quality of life in communities. The field is also dynamic, constantly evolving with new technologies and approaches to make waste handling more efficient and environmentally sound. This continuous innovation offers exciting opportunities for those interested in problem-solving and contributing to a greener future.
Historical Evolution of Waste Management
The story of waste management is as old as civilization itself. As societies have grown and changed, so too have their methods of dealing with refuse. Understanding this history provides valuable context for current practices and the ongoing evolution of the field.
From Ancient Practices to Early Urbanization
Early human settlements generated relatively small amounts of waste, primarily organic materials that could decompose naturally. Archaeological evidence from ancient civilizations, such as the Minoans in Crete, reveals the first recorded landfill, where refuse was dumped into large pits. Around 2000 B.C. in China, simple methods of composting and recycling, particularly of bronze, were already in use. In ancient Athens, around 500 B.C., a law mandated that garbage be dumped at least one mile from the city, indicating an early awareness of the need for organized disposal. Similarly, ancient Rome had systems for waste removal, though often rudimentary and focused on major public events.
With the rise of urbanization, particularly in ancient cities, waste started to accumulate in streets and public areas. While some early laws prohibited indiscriminate dumping, organized collection was not widespread. After the fall of Rome, municipal sanitation and waste collection declined throughout the Middle Ages. Waste was often thrown into streets or carted by scavengers to dumps outside city walls. Some medieval German cities required wagons bringing produce into the city to also carry waste out, and Spanish copper mines practiced a form of recycling by using scrap iron.
These early efforts, though often insufficient by modern standards, laid the groundwork for more systematic approaches to waste management as populations grew and the impacts of unmanaged waste became more apparent.
The Impact of Industrialization and Early Modern Practices
The Industrial Revolution, beginning in the late 18th century, brought about unprecedented levels of production and consumption, and with it, a dramatic increase in the volume and complexity of waste. Urban areas, particularly in industrializing nations like England, saw a rapid deterioration in sanitation. This era marked a turning point, as the sheer quantity of waste necessitated more organized systems. The late 18th century saw the emergence of the 'dust-yards' system in London, an early attempt at organized solid waste management.
In the 19th century, growing awareness of the links between sanitation and public health, spurred by reports like Edwin Chadwick's on sanitary conditions in England, led to important legislative actions. The Nuisance Removal and Disease Prevention Act of 1846 in England was a significant step. The first refuse incinerator was constructed in Nottingham, England, in 1874. Across the Atlantic, American cities also began to grapple with mounting waste. In 1757, Benjamin Franklin initiated the first street cleaning service in Philadelphia and encouraged residents to dig pits for waste disposal. By the late 19th century, watertight garbage cans were introduced in the U.S., and sturdier vehicles began to be used for collection. New York City established public-sector garbage management in 1895, and by the turn of the 20th century, some major American cities were incinerating solid waste.
Technological advancements continued into the early 20th century with the development of garbage grinders and compaction trucks. However, open dumping and improper incineration remained common, leading to increasing pollution and public health concerns. This period set the stage for more sophisticated and environmentally conscious waste management strategies in the decades to come.
Key 20th-Century Regulatory Milestones and the Shift Towards Sustainability
The mid-20th century marked a critical juncture as the environmental and public health consequences of inadequate waste disposal became undeniable. This realization spurred significant regulatory and technological shifts. A pivotal development was the move away from open dumping towards the use of sanitary landfills, designed to be more controlled and reduce pollution. Many countries began to categorize waste into hazardous and nonhazardous types, establishing separate regulations for their disposal.
Key legislative actions in the latter half of the 20th century further shaped modern waste management. For instance, the Clean Air Act of 1963 in the United States was a precursor to broader environmental regulation. The Solid Waste Disposal Act of 1965 authorized federal research into resource recovery and landfill practices. A landmark moment was the founding of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 1970, tasked with regulating environmental safety. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) of 1976 provided a comprehensive framework for managing solid and hazardous waste, emphasizing recycling and conservation.
Alongside these regulatory efforts, there was a growing movement towards what is now known as the circular economy. This model emphasizes keeping materials in use for as long as possible, extracting maximum value, and then recovering and regenerating products and materials at the end of their service life. This represented a significant departure from the traditional linear "take-make-dispose" model. The focus began to shift from mere disposal to waste reduction, reuse, and recycling, laying the foundation for the more sustainable practices prioritized today.
For those interested in delving deeper into the evolution of waste management and the foundational principles that guide current practices, exploring online courses can be highly beneficial. These resources often cover the historical context that has shaped the field.
Understanding the historical context can be further enriched by comprehensive texts on the subject.
Key Concepts and Terminology in Waste Management
Navigating the field of waste management requires familiarity with its core concepts and terminology. These ideas form the bedrock of how professionals approach the challenges of managing our discards responsibly and sustainably.
The Waste Hierarchy: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
At the forefront of waste management philosophy is the waste hierarchy, often depicted as an inverted pyramid. This model prioritizes waste prevention strategies, with disposal as the least favored option. The primary goal is to extract the maximum practical benefits from products and generate the minimum amount of waste.
The most preferred approach, at the top of the hierarchy, is reduction. This involves minimizing the amount of waste generated in the first place. Think of it like this: if you use a reusable water bottle instead of buying single-use plastic bottles, you're reducing waste before it even starts. Businesses can reduce waste by designing products with less packaging or making them more durable so they last longer.
Next comes reuse. This means using items multiple times for their original purpose or a new purpose without significantly altering their form. An example is refilling a glass jar, donating old clothes, or using an old tire as a garden planter. Reusing items extends their life and delays the need to discard them.
Following reuse is recycling, which includes composting. Recycling involves processing used materials into new products to prevent waste of potentially useful materials, reduce the consumption of fresh raw materials, reduce energy usage, and decrease air and water pollution. When you sort your paper, plastic, and glass for collection, those materials can be transformed. Composting is a form of recycling for organic waste like food scraps and yard trimmings, turning them into nutrient-rich soil amendment.
Further down the hierarchy are material recovery and waste-to-energy processes, such as incineration with energy recovery. The least desirable option, at the bottom of the pyramid, is disposal, typically in landfills or through incineration without energy recovery. The waste hierarchy provides a clear framework for making sustainable choices in managing waste.
These foundational courses can help build a solid understanding of waste management principles, including the crucial waste hierarchy.
Landfills vs. Incineration: Understanding the Trade-offs
When waste cannot be prevented, reused, or recycled, disposal becomes necessary. Two common methods are landfills and incineration, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making informed decisions about waste management strategies.
Landfills are engineered sites where non-hazardous solid waste is spread in layers, compacted, and covered with soil or other materials. Modern sanitary landfills are designed to minimize environmental impact by including liners to prevent groundwater contamination from leachate (liquid that has passed through waste) and systems to collect methane gas produced during decomposition. Advantages: Landfills can accommodate large volumes of waste and are often a relatively less expensive disposal option in the short term, especially in areas with ample land. Disadvantages: Landfills require significant land area. Even with modern designs, there's a risk of soil and water pollution. Decomposition of organic waste in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Landfills can also lead to odor issues and decreased property values nearby.
Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of waste materials at high temperatures. This process converts waste into ash, flue gas, and heat. The volume of solid waste is significantly reduced (typically by 80-90%). If the heat generated is used to produce electricity or for industrial heating, it's often referred to as a waste-to-energy (WtE) plant. Advantages: Incineration drastically reduces waste volume, extending the life of landfills. WtE plants can recover energy from waste, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Modern incinerators are equipped with pollution control systems to minimize harmful emissions. Disadvantages: Incineration facilities are expensive to build and operate. The process can release pollutants into the air, including dioxins and heavy metals, if not properly controlled, potentially impacting public health. The ash produced from incineration can be hazardous and requires careful disposal, often in specialized landfills. There's also a concern that over-reliance on incineration might disincentivize waste reduction and recycling efforts.
The choice between landfilling and incineration, or a combination of both, depends on various factors including local geography, waste composition, economic considerations, environmental regulations, and public acceptance. Often, an integrated approach that prioritizes the waste hierarchy is the most sustainable solution.
For those seeking in-depth knowledge about waste treatment methods, these resources can be valuable.
Lifecycle Assessment (LCA) Principles
Lifecycle Assessment, or LCA, is a systematic method for evaluating the environmental impacts of a product, process, or service throughout its entire life cycle. This "cradle-to-grave" (or sometimes "cradle-to-cradle" if recycling or reuse is involved) approach considers all stages, from raw material extraction and processing, manufacturing, transportation, and distribution, through to use, reuse, maintenance, recycling, and final disposal.
The core idea of LCA is to identify and quantify the environmental burdens associated with each stage. These burdens can include energy consumption, raw material depletion, air and water emissions, and waste generation. By understanding these impacts, decision-makers can identify opportunities for improvement, compare different products or processes, and make more environmentally informed choices.
For example, an LCA of a plastic water bottle would look at the energy and materials used to extract oil, process it into plastic, manufacture the bottle, transport it to a bottling plant, fill it, distribute it to stores, the consumer's use of it, and finally, whether it's landfilled, incinerated, or recycled. This comprehensive view helps to avoid "burden shifting," where solving an environmental problem in one stage of the life cycle inadvertently creates a new problem in another stage.
In waste management, LCA is a valuable tool for comparing different waste treatment options (e.g., landfilling vs. incineration vs. recycling for a particular waste stream) and for guiding policy decisions aimed at minimizing the overall environmental footprint of waste.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is an environmental policy approach in which a producer’s responsibility for a product is extended to the post-consumer stage of a product’s life cycle. This means that companies that manufacture, import, or sell certain products are financially or physically responsible for their collection, recycling, or disposal at the end of their useful life.
Imagine you buy a new television. Under an EPR scheme, the company that made or sold that TV might be required to contribute to a system that ensures old TVs are collected and properly recycled, rather than just ending up in a landfill. The goal of EPR is to provide incentives for producers to design products that are more environmentally friendly – for example, easier to recycle, made with fewer hazardous materials, or more durable.
EPR programs can take various forms. Some involve producers paying fees that fund municipal recycling programs. Others require producers to set up their own take-back and recycling systems. Common product categories covered by EPR schemes include packaging, electronics (e-waste), batteries, tires, and vehicles. By shifting some of the waste management burden (and cost) from municipalities and taxpayers to producers, EPR aims to encourage more sustainable product design and increase recycling rates.
Circular Economy Fundamentals
The circular economy is an economic system aimed at eliminating waste and promoting the continual use of resources. Unlike the traditional linear economy model of "take-make-dispose," a circular economy is regenerative by design. The core principles are to design out waste and pollution, keep products and materials in use at their highest value for as long as possible, and regenerate natural systems.
Think of it like nature, where everything is a nutrient for something else. In a circular economy, materials are seen as valuable resources to be kept in circulation. This involves strategies like:
- Designing for Durability and Repair: Making products that last longer and are easier to fix.
- Reuse and Sharing Models: Encouraging the reuse of products (e.g., refillable containers) and developing sharing platforms (e.g., tool libraries, car sharing).
- Remanufacturing and Refurbishment: Taking old products, repairing or rebuilding them, and returning them to a like-new condition.
- Recycling: Processing used materials into new raw materials for manufacturing. This is often seen as a last resort within the circularity principles, with preference given to strategies that maintain more of the product's original value.
- Using Renewable Resources: Shifting towards renewable energy and materials.
The circular economy offers significant benefits, including reduced environmental impact, conservation of resources, economic growth through new business opportunities, and increased resilience against resource scarcity. It requires a systemic shift in how we design, produce, consume, and manage materials.
These courses offer a great introduction to the principles of a circular economy and how it relates to sustainable waste management.
For further reading on the interconnectedness of circular economy principles and practical waste management, consider these books.
Current Global Trends and Innovations
The field of waste management is not static; it's continually evolving in response to environmental pressures, technological advancements, and changing societal expectations. Several key trends and innovations are shaping the future of how we handle waste globally.
Zero-Waste City Initiatives
Around the world, a growing number of municipalities are embracing the ambitious goal of becoming "zero-waste cities." This doesn't necessarily mean producing absolutely no waste, but rather aiming to divert a very high percentage (often 90% or more) of waste from landfills and incinerators through comprehensive strategies that prioritize waste prevention, reuse, recycling, and composting.
Zero-waste initiatives often involve a multi-pronged approach. This can include widespread public education campaigns to encourage source separation of recyclables and organics, implementing pay-as-you-throw systems where households are charged based on the amount of trash they produce, banning single-use plastics, establishing robust composting infrastructure for food and yard waste, and supporting businesses in adopting circular economy practices. The philosophy emphasizes that reducing, reusing, and recycling creates significantly more jobs than disposal and helps build more equitable communities.
Cities pursuing zero waste often report benefits beyond just waste diversion, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions, conservation of resources, cleaner communities, and economic development through new "green" jobs. While achieving true zero waste is a significant challenge, these initiatives represent a paradigm shift in how communities view and manage their resources.
Plastic Waste Reduction Technologies
Plastic pollution is a major global environmental concern, and significant research and development are focused on new technologies to reduce and manage plastic waste. These innovations span the entire lifecycle of plastics, from production to disposal and recycling.
One area of advancement is in chemical recycling technologies like pyrolysis, gasification, and depolymerization. Pyrolysis uses heat in the absence of oxygen to break down plastics into oil and gas, which can then be used to create new plastics or fuels. Gasification converts plastics into a synthetic gas (syngas) that can be used for energy or chemical production. Depolymerization breaks plastics back down into their original monomer building blocks, allowing for the creation of virgin-quality recycled plastics. These technologies offer potential solutions for plastics that are difficult to recycle through traditional mechanical methods.
Biotechnological approaches are also emerging, such as the use of enzymes to break down plastics into their constituent parts, which can then be used to create new materials. Innovations in mechanical recycling are also improving sorting capabilities, for instance, using AI-powered optical sorters to more accurately separate different types of plastics from mixed waste streams. Furthermore, there's ongoing research into developing new types of biodegradable and compostable plastics, as well as innovative product designs that use less plastic or make plastic products easier to recycle.
For those interested in the cutting edge of resource management, these courses explore some of the latest thinking and technologies.
Waste-to-Energy (WtE) Advancements
Waste-to-Energy (WtE) technologies play a role in integrated waste management systems by recovering energy from waste that cannot be readily recycled. Traditional WtE primarily involves incineration, where waste is burned to produce steam that drives turbines to generate electricity. However, advancements are making these processes more efficient and environmentally sound.
Modern WtE facilities incorporate sophisticated air pollution control systems to capture and neutralize harmful emissions like dioxins, furans, and heavy metals. There's also a focus on improving energy efficiency, maximizing the amount of electricity or heat generated per ton of waste. Beyond conventional incineration, other thermal technologies like gasification and pyrolysis (also relevant to plastics, as mentioned earlier) are being adapted for mixed municipal solid waste. These processes can convert waste into syngas or bio-oil, which can then be used to generate energy or as chemical feedstocks, sometimes with higher efficiencies and potentially lower emissions than direct incineration.
Anaerobic digestion is another important WtE technology, particularly for organic waste streams like food scraps and agricultural waste. This biological process uses microorganisms in an oxygen-free environment to break down organic matter, producing biogas (primarily methane and carbon dioxide) which can be captured and used to generate electricity or heat, or upgraded to biomethane for injection into natural gas grids. The solid and liquid residues from anaerobic digestion, known as digestate, can be used as a soil conditioner and fertilizer.
AI-Driven Sorting Systems
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly being integrated into waste management, particularly in sorting facilities. Traditional material recovery facilities (MRFs) rely on a combination of mechanical sorters (like screens and magnets) and manual labor to separate recyclables from mixed waste. AI-powered systems are enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of this process.
These advanced systems often use a combination of computer vision, machine learning, and robotics. High-resolution cameras identify different types of materials (e.g., specific types of plastics, paper grades, metals) as they move along conveyor belts. The AI algorithms, trained on vast datasets of images, can recognize and classify these items with high speed and precision. Robotic arms, guided by the AI, then pick and sort the identified materials into appropriate bins.
The benefits of AI-driven sorting include higher recovery rates for valuable materials, improved purity of sorted recyclables (which increases their market value), reduced reliance on manual sorting (which can be a physically demanding and sometimes hazardous job), and the ability to adapt to changes in the waste stream more quickly. Some systems can even provide valuable data on the composition of incoming waste, helping municipalities and businesses to better understand waste generation patterns and optimize their collection and recycling programs. As AI technology continues to develop, its role in creating smarter and more efficient waste management systems is expected to grow.
Consider exploring these related topics to broaden your understanding of the technological and systemic shifts in environmental management.
Formal Education Pathways
A career in waste management often benefits from a solid educational foundation. Formal education can provide the theoretical knowledge, technical skills, and critical thinking abilities necessary to address the complex challenges in this field. Various academic routes can lead to a fulfilling career in managing our world's waste.
Relevant Undergraduate Degrees
Several undergraduate degrees can provide a strong foundation for a career in waste management. One of the most direct routes is a bachelor's degree in Environmental Science. This interdisciplinary field explores the interactions between humans and the environment, covering topics like ecology, chemistry, geology, and policy, all of which are relevant to understanding waste generation, impacts, and management strategies.
Engineering disciplines are also highly applicable. A degree in Environmental Engineering specifically focuses on applying scientific and engineering principles to improve and protect environmental quality, with waste management being a core component. Civil Engineering programs often include specializations or coursework in environmental areas, including solid waste system design and landfill engineering. Chemical Engineering can be relevant for understanding waste treatment processes, particularly for hazardous waste or advanced recycling technologies. Mechanical Engineering skills are valuable in designing and operating waste processing machinery and facilities.
Other relevant degrees might include Geology (for understanding landfill siting and groundwater protection), Biology or Biochemistry (for understanding organic waste decomposition and bioremediation), or even Public Policy or Urban Planning with an environmental focus, for those interested in the regulatory and societal aspects of waste management. The key is to choose a program that offers a strong scientific or technical base, along with opportunities to study environmental issues and solutions.
These courses can provide an initial look into environmental science and sustainable practices, which are core to waste management.
Specialized Graduate Programs
For those seeking advanced knowledge or specialized roles in waste management, pursuing a graduate degree can be a significant advantage. Master's (M.S. or M.Eng.) and doctoral (Ph.D.) programs offer opportunities for in-depth study and research.
Many universities offer specialized Master's programs in Waste Management, Environmental Engineering with a waste focus, or Sustainability. These programs typically delve deeper into topics like advanced waste treatment technologies, landfill design and operation, hazardous waste management, recycling systems, lifecycle assessment, circular economy principles, and environmental policy and regulation. A Master's degree can open doors to more senior technical roles, research positions, policy development, and consultancy.
A Ph.D. is generally geared towards those interested in academic research, leading cutting-edge R&D in industry or government, or high-level policy and advisory roles. Doctoral research in waste management can focus on a wide array of topics, from developing novel recycling processes to analyzing the economic and social impacts of waste policies.
When considering graduate programs, look for institutions with strong research programs in waste management, experienced faculty, and connections to industry or governmental agencies. Some programs may also offer opportunities for internships or collaborative projects, providing valuable practical experience.
Certifications and Professional Development
Beyond formal degrees, professional certifications can enhance credentials and demonstrate specialized expertise in waste management. Several organizations offer well-recognized certifications for waste management professionals.
In North America, the Solid Waste Association of North America (SWANA) offers a range of certifications covering areas like landfill operations, recycling systems, composting programs, and integrated solid waste management. These certifications often require a combination of education, experience, and passing an exam, and they are widely respected in the industry.
Similarly, the Chartered Institution of Wastes Management (CIWM), based in the UK but with international reach, offers Chartered Waste Manager status, which is a globally recognized professional qualification. Achieving chartered status typically involves demonstrating a high level of competence and commitment to professional development.
Many other national and international organizations provide specialized training and certification programs. Continuing professional development (CPD) is also crucial in this rapidly evolving field. Attending workshops, conferences, and webinars, and staying updated on new technologies and regulations are essential for career growth and maintaining expertise.
These courses are excellent for professionals looking to update their knowledge on current environmental standards and circular economy practices.
Further your understanding with these key texts on solid and hazardous waste management.
Research Opportunities in Waste Valorization
Waste valorization, the process of converting waste materials into higher-value products, is a rapidly growing area of research and innovation within the broader field of waste management. This field is driven by the principles of the circular economy, aiming to move beyond simple disposal or basic recycling towards creating new materials, chemicals, fuels, and energy from waste streams.
Research opportunities in waste valorization are abundant and diverse. Scientists and engineers are exploring novel thermal, chemical, and biological processes to break down and transform various types of waste. This includes developing more efficient methods for converting plastic waste into new polymers or chemical feedstocks, transforming organic waste (like food scraps or agricultural residues) into biofuels, bioplastics, or valuable biochemicals, and extracting precious metals or other useful materials from electronic waste (e-waste).
Universities with strong environmental engineering, chemical engineering, materials science, and biotechnology programs are often at the forefront of this research. Opportunities exist for undergraduate research projects, master's theses, and doctoral dissertations focused on specific aspects of waste valorization. Funding for such research often comes from government agencies, industry partnerships, and private foundations focused on sustainability and innovation. A career in research in this area can be highly rewarding, contributing directly to the development of technologies that can transform waste from a problem into a valuable resource.
Online and Self-Directed Learning
The digital age has revolutionized access to education, and waste management is no exception. Online courses and self-directed learning offer flexible and accessible pathways for individuals looking to enter the field, supplement existing knowledge, or pivot their careers. These avenues are particularly valuable for international learners or those who need to balance studies with work or other commitments.
Feasibility of Remote Waste Management Education
Learning about waste management remotely is entirely feasible and increasingly common. Many universities and professional organizations now offer a wide array of online courses, certificates, and even full degree programs related to environmental science, sustainability, and waste management. These programs can cover theoretical foundations, policy and regulation, technological advancements, and practical management strategies.
Online learning platforms provide access to lectures, reading materials, interactive assignments, and discussion forums, allowing learners to engage with content and peers from anywhere in the world. While some highly specialized technical roles might still require hands-on laboratory or field experience, a significant portion of the knowledge base in waste management can be effectively acquired through remote study. For instance, understanding the principles of the waste hierarchy, lifecycle assessment, circular economy models, or the regulatory landscape can all be thoroughly explored online. Furthermore, many online courses incorporate case studies and virtual simulations to provide practical context.
OpenCourser itself is a testament to the power of online learning, offering a vast catalog to explore courses in Environmental Sciences and related fields. The platform makes it easy to find and compare options, helping learners tailor their educational journey to their specific interests and career goals.
These courses are specifically designed for online learning and cover crucial aspects of modern waste management and circular economy principles.
Project-Based Learning Strategies
One of the most effective ways to solidify knowledge gained through online courses and self-directed study is through project-based learning. This approach involves applying theoretical concepts to real-world or simulated waste management challenges. Engaging in projects helps develop practical skills, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities – all highly valued by employers.
For instance, a learner could undertake a project to analyze the waste stream of their own household or a local business, identifying opportunities for waste reduction and improved recycling. They might research and propose a composting initiative for their community, or develop a hypothetical plan for managing a specific type of waste, like electronic waste or construction debris, in their region. Another project could involve conducting a mini-lifecycle assessment for a common product to understand its environmental footprint.
These projects don't necessarily require formal institutional backing. Many can be done independently or in small, self-organized groups. The key is to define a clear objective, gather relevant information (often available through online research, local government resources, or by observation), apply learned principles, and document the process and findings. Such projects can form the basis of a strong portfolio, showcasing initiative and practical application of knowledge to potential employers.
Virtual Simulations for Logistics Planning
The logistics of waste collection, transportation, and processing are complex and critical to efficient waste management. Virtual simulations are emerging as powerful tools for learning and practicing logistics planning without the need for real-world physical infrastructure or the risks associated with operational changes.
Simulation software can model various aspects of waste management logistics. For example, learners can experiment with different collection routes to optimize fuel efficiency and time, design the layout of a material recovery facility (MRF) to maximize throughput and sorting efficiency, or simulate the impact of different fleet sizes or vehicle types on operational costs and service levels. These tools can incorporate variables like population density, waste generation rates, traffic patterns, and facility capacities to create realistic scenarios.
While access to sophisticated commercial simulation software might be limited for individual learners, some online courses or open-source tools may offer simplified versions or case studies based on simulation outputs. Even conceptualizing and mapping out logistics flows for a hypothetical waste management system can be a valuable learning exercise, honing analytical and planning skills relevant to the field.
Open-Source Waste Data Analysis Tools
Data analysis plays an increasingly important role in modern waste management, helping to identify trends, optimize operations, and measure the effectiveness of different programs. Fortunately, a growing number of open-source tools and publicly available datasets can be utilized for self-directed learning and projects in waste data analysis.
Open-source software like R and Python (with libraries such as Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib) are powerful tools for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and visualization. Many governmental agencies, research institutions, and international organizations publish waste-related data, such as waste generation rates, recycling rates, landfill capacity, and waste composition studies. Learners can access this data and use open-source tools to explore trends, create informative charts and graphs, and even build simple predictive models.
For example, one could analyze publicly available data on municipal solid waste generation in their region over several years to identify patterns or assess the impact of a new recycling program. This type of hands-on data analysis helps develop quantitative skills that are highly valuable in many waste management roles, from operational management to policy development. Engaging with these tools and datasets allows learners to build a practical understanding of how data can inform decision-making in the sector.
To get started with the analytical side of waste management, understanding data handling is key. Consider exploring courses related to data analysis and visualization, which can be found on platforms like OpenCourser by searching for relevant terms.
Career Progression in Waste Management
A career in waste management offers diverse pathways for growth and development, from entry-level positions to executive leadership and specialized consultancy. The field is dynamic, with opportunities spanning public and private sectors, and even entrepreneurial ventures. Understanding the potential career trajectories can help individuals plan their professional journey in this impactful industry.
Entry-Level Roles
For individuals starting their careers in waste management, several entry-level roles provide valuable experience and a foothold in the industry. A Waste Auditor, for example, might be involved in assessing waste streams for businesses or municipalities to identify types and quantities of waste generated, often as a first step towards developing reduction and recycling programs. Compliance Officers or Environmental Technicians may focus on ensuring that waste handling and disposal activities adhere to local, state, and federal regulations. This can involve site inspections, sample collection, and report writing.
Other entry points can include roles in recycling coordination, public education and outreach (helping to promote waste reduction and recycling programs within communities), or as an assistant in a waste treatment facility or landfill operation. These positions often require a foundational understanding of environmental principles and regulations, good communication skills, and attention to detail. A bachelor's degree in environmental science, engineering, or a related field is often beneficial, though some roles may be accessible with an associate's degree or relevant certifications combined with practical experience.
These roles offer a practical introduction to the field, allowing individuals to learn the operational and regulatory aspects of waste management firsthand. They also provide a base from which to specialize or move into more senior positions with experience and further education or training.
Gaining foundational knowledge through online courses can be a great way to prepare for entry-level positions. Consider these options to start building your expertise:
Mid-Career Paths
With a few years of experience and potentially further education or certifications, professionals in waste management can progress to a variety of mid-career roles with increased responsibility and specialization. Facility Managers oversee the operations of landfills, transfer stations, material recovery facilities (MRFs), or waste-to-energy plants. This involves managing staff, budgets, equipment, and ensuring compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
Policy Advisors or Environmental Planners work on developing and implementing waste management strategies and policies, often for government agencies or large corporations. This can involve researching best practices, analyzing data, drafting regulations, and engaging with stakeholders. Those with strong technical expertise might become Environmental Consultants, advising clients on waste reduction, recycling programs, regulatory compliance, or site remediation.
Other mid-career paths include roles in hazardous waste management, specializing in the safe handling, treatment, and disposal of dangerous materials. Project Manager positions are also common, leading specific waste management projects such as the development of new facilities or the implementation of large-scale recycling programs. These roles typically require a combination of technical knowledge, management skills, and a proven ability to deliver results.
For those in or aspiring to mid-career roles, specialized knowledge in areas like hazardous waste or advanced recycling can be beneficial. Relevant books can provide deep insights:
You may also find these careers of interest if you are looking at mid-career paths in or related to waste management:
Executive Leadership Trajectories
For individuals with significant experience, a strong track record of success, and often advanced degrees (such as an MBA or a Master's in Environmental Management or Engineering), executive leadership positions in waste management become attainable. These roles involve setting strategic direction, managing large teams and budgets, and representing the organization at a high level.
Positions such as Director of Waste Management for a city or county, Vice President of Operations for a private waste services company, or Chief Sustainability Officer for a corporation with significant waste footprints fall into this category. These leaders are responsible for long-term planning, innovation, ensuring regulatory compliance on a broad scale, and often engaging with policymakers and the public. They need strong leadership, strategic thinking, financial acumen, and a deep understanding of the technical, economic, and social aspects of waste management.
The path to executive leadership often involves progressing through various mid-career roles, demonstrating increasing levels of responsibility and impact. Networking, continuous learning, and developing a broad understanding of the entire waste management ecosystem are crucial for those aspiring to these top-tier positions.
Entrepreneurship in Waste Tech Startups
The waste management sector, particularly with the rise of the circular economy and the urgent need for sustainable solutions, is ripe for innovation and entrepreneurship. This has led to a growing number of "waste tech" startups developing new technologies, services, and business models to address waste challenges.
Entrepreneurs in this space might focus on developing advanced sorting technologies using AI and robotics, creating novel chemical recycling processes for hard-to-recycle plastics, designing innovative products from waste materials, or building platforms to facilitate waste reduction and reuse. Other startups might offer specialized consulting services, develop software for optimizing waste collection logistics, or create new models for community-based composting or recycling initiatives. According to Grand View Research, the global waste management market is substantial and expected to grow, indicating significant opportunities.
Launching a waste tech startup requires not only a good idea but also business acumen, access to funding, and the ability to navigate a complex regulatory environment. However, for those with an innovative spirit and a passion for sustainability, entrepreneurship offers a path to make a significant impact and potentially achieve substantial financial success. Many universities and incubators offer support programs for environmentally focused startups, providing mentorship, resources, and networking opportunities.
Global Mobility Opportunities
Waste management is a global challenge, and the skills and expertise developed in this field are often transferable across borders. This can create opportunities for professionals to work in different countries and cultural contexts, contributing to sustainable waste practices worldwide.
International development organizations, multinational corporations with global sustainability goals, and environmental consulting firms with international clients often seek individuals with waste management expertise. There may be opportunities to work on projects in developing countries, helping to establish basic waste infrastructure and improve public health, or to advise governments on policy development. In more developed nations, there might be roles in implementing advanced waste treatment technologies or circular economy initiatives.
Working internationally requires adaptability, cross-cultural communication skills, and often proficiency in other languages. However, it can also be an incredibly enriching experience, offering a broader perspective on global environmental challenges and solutions. Professionals considering global mobility should research the specific needs and regulatory environments of different regions and seek out organizations with an international focus.
Understanding international waste management practices can be enhanced with these courses:
Challenges in Modern Waste Management
Despite significant advancements, the field of waste management faces numerous complex challenges. These issues require ongoing attention, innovation, and collaboration from professionals, policymakers, and the public to ensure that waste is managed in an environmentally sound, socially equitable, and economically viable manner.
Environmental Justice and Waste Colonialism
A critical challenge in waste management is ensuring environmental justice. Historically, and even today, waste disposal facilities such as landfills and incinerators have often been disproportionately sited in or near low-income communities and communities of color. These communities bear a greater burden of the negative environmental and health impacts associated with waste, including air and water pollution, odor, and decreased property values. This unequal distribution of environmental burdens is a core concern of the environmental justice movement.
On an international scale, the concept of "waste colonialism" or "toxic trade" refers to the practice of developed countries exporting their waste, particularly hazardous waste or difficult-to-recycle materials, to developing countries. These recipient countries often lack the infrastructure and regulatory framework to manage this waste safely, leading to significant environmental degradation and health risks for their populations. Addressing these challenges requires policies that ensure equitable siting of waste facilities, robust international agreements to control transboundary waste shipments, and a commitment to reducing waste generation at its source so there is less to manage overall.
Understanding the broader societal impacts is crucial. Courses focusing on sustainability and public health can provide context.
Plastic Recycling Economic Viability
While recycling is a key component of sustainable waste management, the economic viability of plastic recycling, in particular, faces persistent challenges. The cost of collecting, sorting, and processing post-consumer plastic can be higher than the cost of producing new (virgin) plastic, especially when oil prices are low (as virgin plastic is derived from petroleum). This economic disparity can make it difficult for recycling businesses to compete and remain profitable.
Several factors contribute to this challenge. Contamination of recyclable plastics with food residues or non-recyclable materials can reduce their value and increase processing costs. The wide variety of plastic types, many of which are not easily recyclable together, complicates sorting. Furthermore, the global market for recycled plastics can be volatile, influenced by international trade policies and demand from manufacturers. There are also technical limitations; some plastics degrade in quality each time they are recycled, limiting their applications.
Efforts to improve the economic viability of plastic recycling include investing in advanced sorting technologies, developing new chemical recycling processes that can handle mixed or contaminated plastics, creating stronger domestic markets for recycled materials through procurement policies and industry commitments, and implementing policies like Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) to shift some of the financial burden of recycling onto producers.
Cross-Border Waste Trafficking
Cross-border waste trafficking, or the illegal international trade in waste, is a significant global problem. This illicit activity often involves the shipment of hazardous waste or mixed municipal waste, falsely declared as non-hazardous or recyclable materials, from developed countries to developing nations that lack the capacity for environmentally sound management. This practice is driven by the high cost of legitimate disposal in developed countries and the potential for profit by unscrupulous operators.
The consequences of illegal waste trafficking are severe. It can lead to serious environmental pollution in recipient countries, including contamination of soil, water, and air, and pose significant health risks to communities living near dumping sites. It also undermines legitimate recycling and waste management industries and can be linked to other forms of organized crime. International agreements like the Basel Convention aim to control the transboundary movement of hazardous wastes and their disposal, but enforcement remains a major challenge.
Combating cross-border waste trafficking requires stronger international cooperation, enhanced monitoring and enforcement at ports and borders, stricter penalties for illegal dumping, and greater transparency in the global waste trade. Promoting waste reduction and developing adequate domestic recycling and disposal capacity in all countries are also crucial long-term solutions.
Workforce Safety in Hazardous Waste Handling
Protecting the health and safety of workers involved in waste management, particularly those handling hazardous waste, is a paramount concern. Workers in this sector can be exposed to a wide range of risks, including chemical exposures, biological hazards, physical injuries from machinery or heavy lifting, and respiratory problems from dust and fumes.
Hazardous waste, by its nature, poses acute and chronic health risks. This can include materials that are toxic, corrosive, flammable, or infectious. Workers at hazardous waste treatment facilities, those involved in cleaning up contaminated sites, or even those at municipal facilities who inadvertently handle improperly disposed of hazardous materials, require specialized training, appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and strict adherence to safety protocols.
Ensuring workforce safety involves comprehensive risk assessments, engineering controls to minimize exposures (e.g., ventilation systems, enclosed processes), robust training programs on safe handling procedures and emergency response, provision and proper use of PPE (such as respirators, gloves, and protective clothing), and regular health monitoring for workers. Regulatory oversight and strong enforcement of occupational health and safety standards are also critical to protecting this essential workforce.
For those managing or working in roles involving hazardous materials, specific training is essential. Consider these courses and resources:
Future Outlook and Sustainability Goals
The future of waste management is intrinsically linked to global sustainability goals and the ongoing transition towards a more circular economy. As societies grapple with resource scarcity, climate change, and environmental degradation, the impetus to manage waste more effectively and view it as a resource will only intensify. Several key trends and goals are shaping this future landscape.
UN Sustainable Development Goals Alignment
The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a global blueprint for a more sustainable future, and several SDGs are directly or indirectly related to waste management. For example, SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) includes a target to reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management. SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) aims to substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse by 2030.
Other relevant SDGs include SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being), as poor waste management has significant public health impacts; SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), which is threatened by improper waste disposal; and SDG 14 (Life Below Water) and SDG 15 (Life on Land), both impacted by pollution from mismanaged waste. Aligning waste management practices with these global goals requires integrated strategies that address the entire lifecycle of materials, promote resource efficiency, and minimize environmental pollution. This often involves collaboration between governments, businesses, and civil society.
Exploring courses on broader sustainability topics can provide context on how waste management fits into global efforts.
Carbon Credit Systems for Waste Reduction
Carbon credit systems, also known as emissions trading or cap-and-trade systems, are market-based mechanisms designed to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. In the context of waste management, these systems can create financial incentives for projects that reduce or avoid GHG emissions associated with waste.
For example, landfill gas capture projects that collect and either flare or use methane (a potent GHG) for energy generation can earn carbon credits. Similarly, composting projects that divert organic waste from landfills (where it would produce methane anaerobically) can also generate credits. Waste-to-energy projects that displace fossil fuel-based power generation may also be eligible. These credits can then be sold to entities that need to offset their own emissions, providing an additional revenue stream for waste reduction and resource recovery initiatives.
While carbon credit systems can help finance environmentally beneficial waste management projects, their effectiveness depends on robust methodologies for quantifying emission reductions, clear regulatory frameworks, and transparent market operations. As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, the role of carbon markets in incentivizing sustainable waste management practices is likely to grow.
Biodegradable Material Innovation Timelines
The development and adoption of innovative biodegradable materials are seen as a potential pathway to reduce the environmental impact of certain types of waste, particularly single-use plastics and packaging. Biodegradable materials are designed to break down into natural substances (like water, carbon dioxide, and biomass) through the action of microorganisms under specific environmental conditions.
Research in this area is rapidly advancing, with new bio-based polymers and compostable materials emerging. However, the timeline for widespread adoption and the actual environmental benefits depend on several factors. These include the performance characteristics of these materials (e.g., durability, barrier properties), their cost-competitiveness with conventional plastics, the availability of appropriate composting or degradation infrastructure, and clear labeling and consumer understanding to ensure proper disposal. Not all "biodegradable" materials break down in all environments (e.g., some require industrial composting facilities, not backyard compost piles or marine environments).
While innovation continues, it's crucial to remember that biodegradable materials are not a silver bullet for the plastic waste problem. They are best suited for specific applications where collection and proper end-of-life management can be ensured. The focus on the broader waste hierarchy – reduce, reuse, recycle – remains paramount even as new material technologies develop.
Predictions for Regulatory Tightening
The global trend is towards increasingly stringent regulations governing waste management. This is driven by growing public awareness of environmental issues, international commitments like the SDGs, and the recognition that current waste generation and disposal practices are often unsustainable.
Predictions for future regulatory tightening include stricter targets for waste diversion from landfills, mandatory recycling and composting programs, bans or levies on single-use plastics and other problematic materials, and expanded Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes covering more product categories. There is also likely to be increased regulatory focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the waste sector, managing hazardous waste more effectively, and tackling issues like microplastic pollution and marine litter.
For waste management professionals and businesses, staying ahead of these regulatory trends will be crucial. This requires continuous monitoring of policy developments, investing in compliant technologies and practices, and proactively adopting more sustainable approaches to waste management. The move towards a circular economy will likely be further embedded in future regulations, encouraging businesses to design products for durability, repairability, and recyclability.
Understanding environmental policy is key to anticipating regulatory changes.
Frequently Asked Questions (Career Focus)
Embarking on or transitioning into a career in waste management often comes with many questions. This section aims to address some common queries to help you gauge if this field aligns with your aspirations and skills.
Is waste management a growing field?
Yes, waste management is generally considered a growing field. Several factors contribute to this growth. Increasing global population and urbanization lead to greater waste generation. Heightened environmental awareness and stricter regulations worldwide are driving demand for more sophisticated and sustainable waste management solutions. The shift towards a circular economy, which emphasizes resource recovery and waste minimization, is also creating new roles and opportunities. Reports indicate significant job growth projections in the sector, particularly in areas related to recycling, waste-to-energy, and sustainable materials management. For instance, the Chartered Institution of Wastes Management (CIWM) estimated that 240,000 new waste and recycling roles could be created by 2040 in the UK alone.
What technical skills are most valued?
A diverse range of technical skills is valued in the waste management sector. For engineering roles, skills in environmental engineering, civil engineering, chemical engineering, or mechanical engineering are crucial, including knowledge of landfill design, waste treatment processes, and equipment operation. Scientific aptitude, including knowledge of chemistry, biology, geology, and environmental science, is important for understanding waste composition, decomposition processes, and environmental impacts. Data analysis skills are increasingly important for tracking waste streams, optimizing collection routes, and evaluating program effectiveness. Familiarity with relevant software, such as GIS for site selection and route planning, CAD for facility design, or specialized waste management and route optimization software, is also beneficial. Knowledge of environmental regulations and compliance procedures is essential for many roles. Additionally, skills related to specific technologies like recycling processes, composting, anaerobic digestion, or waste-to-energy systems are in demand.
How transferable are waste management skills across industries?
Many skills developed in a waste management career are highly transferable to other industries. Project management skills, for instance, are universally valuable. Experience in regulatory compliance and environmental health and safety (EHS) is sought after in manufacturing, construction, energy, and consulting sectors. Data analysis and logistics planning skills gained in optimizing waste collection and processing can be applied in supply chain management, transportation, and urban planning.
Communication and stakeholder engagement skills, often honed through public outreach or policy work in waste management, are transferable to roles in public relations, corporate social responsibility, and community development. Technical expertise in areas like chemical processes or environmental remediation can be relevant in the chemical industry, environmental consulting, or land development. The growing emphasis on sustainability across all sectors means that experience in resource efficiency and circular economy principles, core to modern waste management, is increasingly valued by a wide range of employers.
Do roles require fieldwork or lab experience?
The need for fieldwork or lab experience in waste management varies significantly depending on the specific role. Environmental scientists, geologists, and hydrogeologists involved in landfill monitoring, site assessment, or remediation often spend considerable time in the field collecting samples, conducting tests, and overseeing operations. Waste auditors and compliance inspectors also perform fieldwork.
Lab experience is crucial for environmental chemists or technicians who analyze waste samples, water quality, or air emissions. Researchers developing new waste treatment technologies or valorization processes will typically work extensively in laboratory settings. However, many other roles in waste management are primarily office-based. These include positions in policy development, planning, data analysis, public education, management, and consulting. Some roles, like facility management, may involve a mix of office work and on-site supervision.
What are common entry points for non-STEM backgrounds?
While many roles in waste management benefit from a STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) background, there are also entry points for individuals with non-STEM degrees. Strong communication skills can lead to roles in public education, community outreach, and customer service for waste management companies or municipalities. Individuals with backgrounds in business administration, finance, or economics might find opportunities in the management, financial analysis, or business development aspects of waste services.
Policy-focused roles, such as working for environmental advocacy groups or in government agencies on waste policy, can be accessible to those with degrees in public administration, political science, or law. Marketing and sales positions also exist within private waste management firms. Furthermore, roles in logistics and transportation coordination may prioritize organizational and planning skills over a specific STEM degree. While some technical understanding of waste issues is always helpful, many organizations value diverse skill sets and provide on-the-job training for specific knowledge.
If you're looking to explore different career options within or related to environmental services, browsing career profiles can be very insightful. OpenCourser’s Career Development section can be a useful starting point.
How does automation threaten/create jobs in the sector?
Automation, including AI-driven sorting and robotics, is transforming the waste management sector, leading to both job displacement and job creation. Routine, manual tasks, particularly in waste sorting and some aspects of collection, are increasingly being automated. This can reduce the need for manual sorters in material recovery facilities (MRFs) and potentially some collection driver roles in the long term.
However, automation also creates new job opportunities. There is a growing demand for skilled technicians to install, maintain, and repair automated systems and robotic equipment. Professionals with expertise in data science, AI, and software development are needed to design, implement, and manage these advanced technologies. Furthermore, as automation improves the efficiency and economic viability of recycling and resource recovery, it can lead to growth in these sub-sectors, potentially creating more jobs in areas like processing higher-value recycled materials or developing new products from recovered resources. The shift is generally from physically demanding, repetitive labor towards more skilled, technical, and analytical roles.
Pursuing a career in waste management offers a chance to contribute to a more sustainable and healthy planet. While it presents unique challenges, the field is dynamic, growing, and provides diverse opportunities for individuals with various skills and backgrounds. With a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation, a career in waste management can be both rewarding and impactful.