Greenhouse Gases
Introduction to Greenhouse Gases
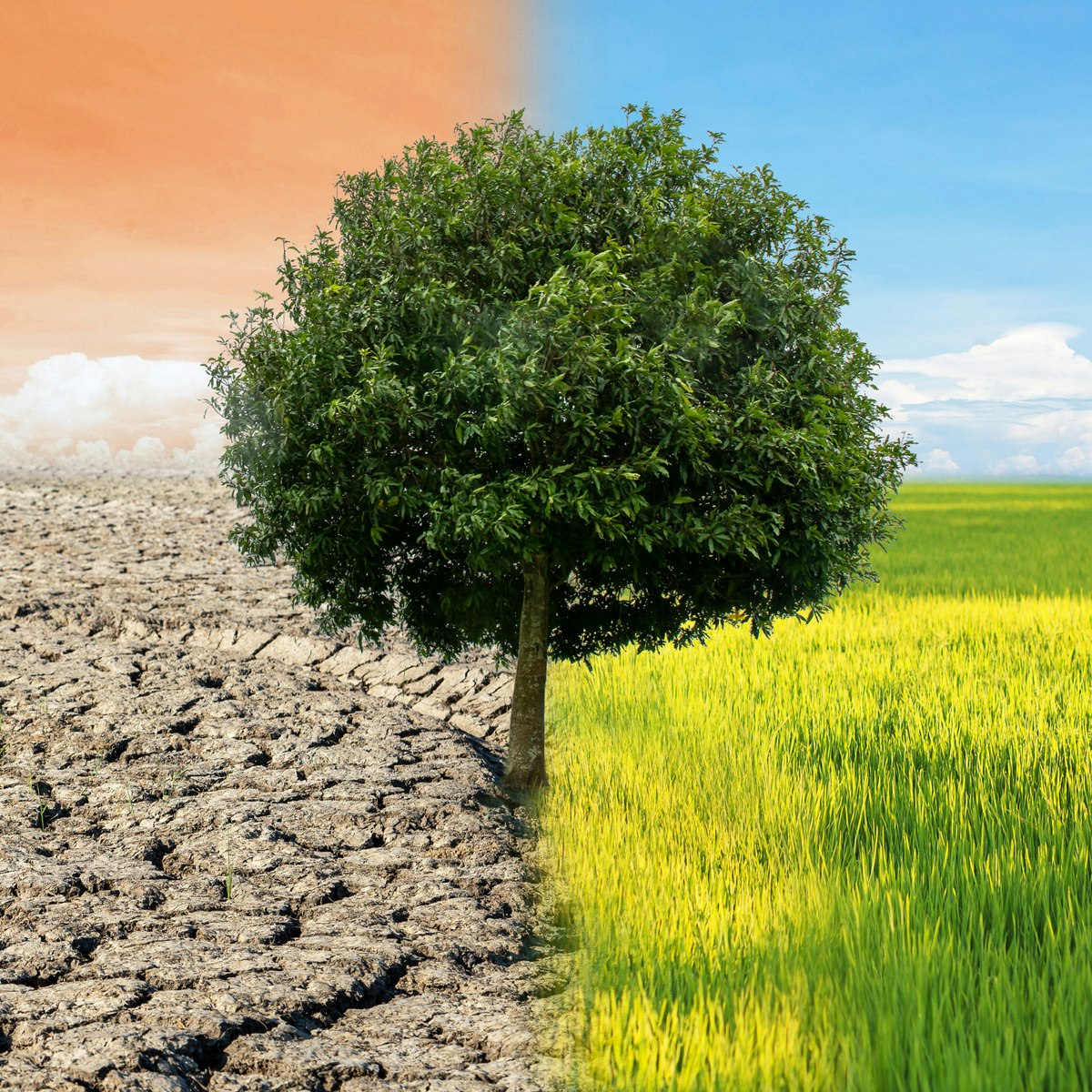
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are a category of gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat. They function somewhat like the glass roof of a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass through and warm the planet's surface, but then preventing some of the resulting heat from escaping back into space. This natural process, known as the greenhouse effect, is crucial for life on Earth as we know it, maintaining an average global temperature that can support ecosystems. Without this effect, Earth's average temperature would be significantly colder, making it inhospitable for most life forms.
Understanding greenhouse gases opens doors to fascinating and critical areas of study and work. Delving into this topic allows individuals to contribute to comprehending and addressing one of the most significant global challenges: climate change. Professionals in this field might find themselves analyzing complex data to model future climate scenarios, developing innovative technologies to reduce emissions, or crafting policies that guide societies towards a more sustainable future. The interdisciplinary nature of this field means that it draws on and contributes to environmental science, economics, policy, engineering, and international relations, offering diverse and impactful career paths.
For those embarking on a journey to understand or work with greenhouse gases, the path can be both intellectually stimulating and deeply rewarding. It's a field that directly impacts the well-being of our planet and future generations. Whether you are a student exploring career options, a professional considering a pivot, or simply a curious individual, the study of greenhouse gases offers a chance to engage with pressing global issues and potentially contribute to meaningful solutions. OpenCourser offers a vast library of Climate Science courses and Environmental Science courses to help you get started.
The Science of Greenhouse Gases
The science behind greenhouse gases is fundamental to understanding their role in Earth's climate. This section will explore the mechanisms of the greenhouse effect, identify the key greenhouse gases, differentiate between natural and human-caused sources, and introduce important metrics used to quantify their impact.
Mechanisms of the Greenhouse Effect
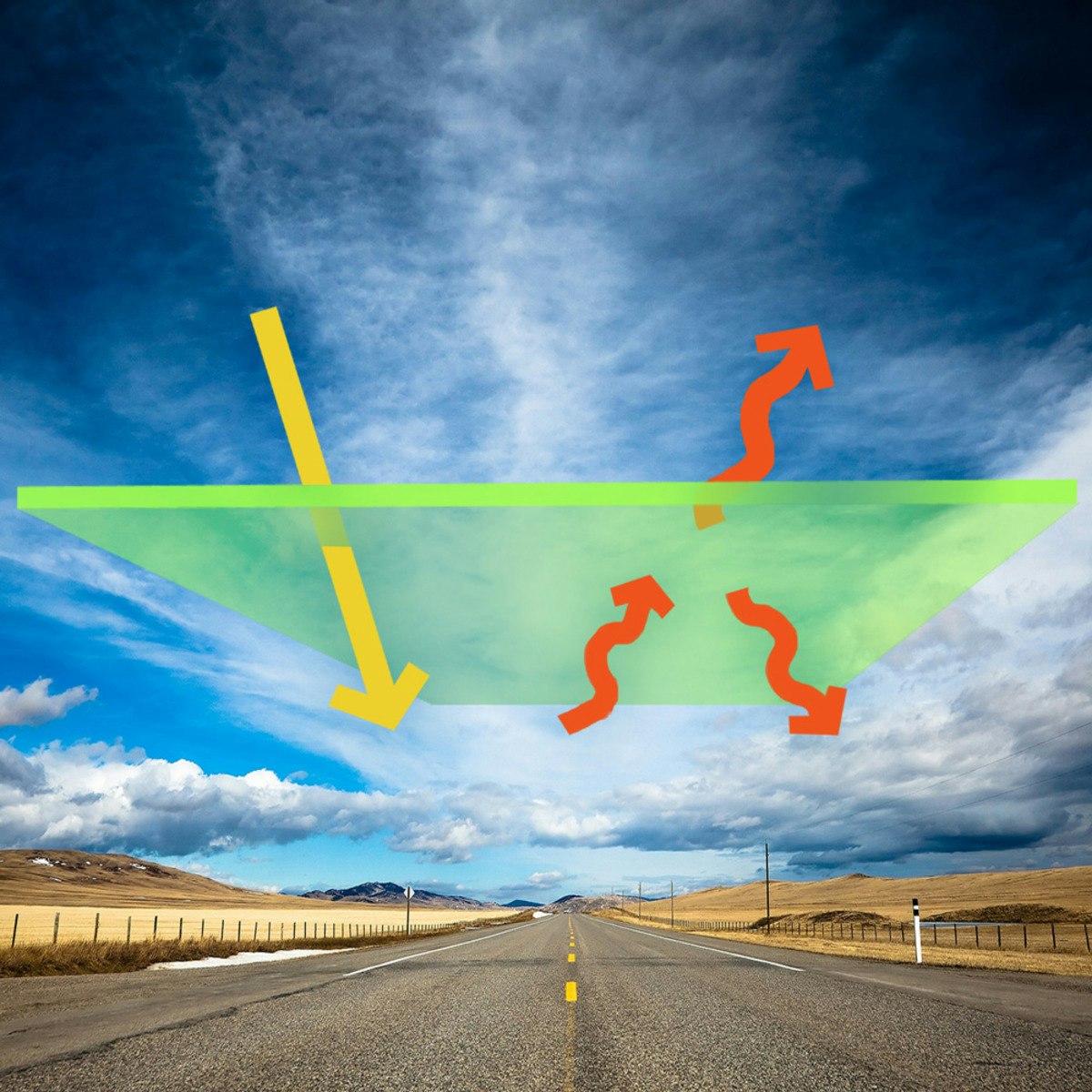
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface. When the sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space, and the rest is absorbed by the land and oceans, heating the Earth. The warmed Earth then radiates heat (infrared radiation) back towards space. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb some of this outgoing infrared radiation and re-emit it in all directions, including back towards the Earth's surface. This trapping of heat keeps the planet warmer than it would be otherwise.
Think of it like a blanket. Just as a blanket traps your body heat to keep you warm, greenhouse gases trap some of the Earth's heat, keeping the planet at a habitable temperature. Without this natural greenhouse effect, Earth's average temperature would be about -18°C (0°F) instead of the current average of 15°C (59°F). This natural warming is essential for life on Earth.
However, human activities, particularly since the Industrial Revolution, have significantly increased the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This increase enhances the natural greenhouse effect, leading to what is often called the "enhanced greenhouse effect" or global warming. More greenhouse gases mean more heat is trapped, causing the Earth's average temperature to rise.
The following courses offer a deeper dive into the science of climate change and the greenhouse effect.
Key GHGs: CO₂, Methane, Nitrous Oxide, Fluorinated Gases
Several different gases contribute to the greenhouse effect. The most significant ones, both naturally occurring and those increased by human activity, include carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), nitrous oxide (N₂O), and fluorinated gases.
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities. It enters the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste, trees and other biological materials, and also as a result of certain chemical reactions, such as in the manufacture of cement. Natural sources include respiration and volcanic eruptions. CO₂ is removed from the atmosphere when it is absorbed by plants as part of the biological carbon cycle.
Methane (CH₄) is emitted during the production and transport of coal, natural gas, and oil. Methane emissions also result from livestock and other agricultural practices, land use, and by the decay of organic waste in municipal solid waste landfills. While methane stays in the atmosphere for a shorter time than CO₂, it is much more efficient at trapping radiation.
Nitrous oxide (N₂O) is emitted during agricultural and industrial activities, combustion of fossil fuels and solid waste, as well as during treatment of wastewater.
Fluorinated gases, such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF₃), are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that are emitted from a variety of industrial processes. Fluorinated gases are sometimes used as substitutes for ozone-depleting substances. While they are typically emitted in smaller quantities, they are potent greenhouse gases, sometimes referred to as high-GWP (Global Warming Potential) gases because they trap substantially more heat than CO₂.
Water vapor is also a significant greenhouse gas, but its concentration in the atmosphere is primarily controlled by temperature rather than direct human emissions, so it acts more as a climate feedback.
These courses provide comprehensive explanations of different greenhouse gases and their impacts.
To understand the fundamental science of climate, consider the following book.
Natural vs. Anthropogenic Sources
Greenhouse gases originate from both natural processes and human activities (anthropogenic sources). Natural sources have always been part of Earth's climate system, maintaining the natural greenhouse effect that keeps the planet habitable.
Natural sources of greenhouse gases include volcanic eruptions, which release CO₂ and other gases; decomposition of organic matter by microbes, which produces methane and CO₂; respiration by plants and animals, which releases CO₂; and evaporation from oceans and other bodies of water, which adds water vapor to the atmosphere. Wildfires also release CO₂ and other GHGs naturally, although their frequency and intensity can be influenced by human activity and climate change.
Anthropogenic sources, on the other hand, are those resulting from human activities. Since the Industrial Revolution began around 1750, human activities have dramatically increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The primary anthropogenic source is the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy and transportation, which releases large amounts of CO₂. Deforestation and other land-use changes also contribute significantly to CO₂ emissions, as forests that store carbon are cleared. Agricultural activities are major sources of methane (from livestock digestion and rice cultivation) and nitrous oxide (from the use of fertilizers). Industrial processes can release various greenhouse gases, including fluorinated gases. Waste decomposition in landfills is another source of methane.
The increase in atmospheric concentrations of GHGs due to human activities is the primary driver of recent climate change.
Quantitative Metrics (e.g., Global Warming Potential)
To compare the impact of different greenhouse gases on global warming, scientists use a metric called Global Warming Potential (GWP). GWP is a measure of how much energy the emissions of 1 ton of a gas will absorb over a given period, typically 100 years, relative to the emissions of 1 ton of carbon dioxide (CO₂). By definition, CO₂ has a GWP of 1.
Gases with a higher GWP absorb more energy per ton emitted than gases with a lower GWP, and thus contribute more to warming Earth for a given mass. For example, methane (CH₄) has a GWP of about 30 over 100 years, meaning that emitting one ton of methane has the same warming impact as emitting about 30 tons of CO₂ over that century. Nitrous oxide (N₂O) has a GWP of 273 over 100 years. Fluorinated gases can have GWPs in the thousands or even tens of thousands.
The GWP value depends on the gas's ability to absorb energy (its radiative efficiency) and its atmospheric lifetime—how long it stays in the atmosphere before being removed by natural processes. Some gases are very effective at trapping heat but have short lifetimes, while others trap less heat but persist for much longer. The choice of time horizon (e.g., 20 years, 100 years, or 500 years) can affect the GWP value. A 100-year time horizon is commonly used in policy and reporting.
Another important metric is carbon dioxide equivalent (CO₂e). This converts emissions of various greenhouse gases into a common unit by multiplying the amount of each gas by its GWP. This allows for the aggregation and comparison of emissions from different sources and gases, providing a comprehensive picture of their total warming impact.
This course offers insights into modeling climate change, which involves these quantitative metrics.
Historical Context and Evolution
Understanding the current state of greenhouse gases and their impact requires looking back at their historical levels, the scientific journey of discovery, the evolution of international policy responses, and advancements in our ability to measure these crucial atmospheric components.
Pre-industrial vs. Post-industrial GHG Levels
The period before the widespread industrialization that began around 1750 is often referred to as the "pre-industrial" era. During this time, atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases were relatively stable and lower than today, maintained by natural cycles. For instance, atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO₂) levels were around 280 parts per million (ppm).
Since the Industrial Revolution, human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and land-use changes, have led to a dramatic increase in GHG concentrations. By 2023, atmospheric CO₂ concentrations had risen to over 419 ppm, an increase of more than 40% from pre-industrial levels. Some sources indicate CO2 levels are now 50% higher than pre-industrial times. Methane (CH₄) concentrations have more than doubled, increasing from approximately 722 parts per billion (ppb) in the 18th century to 1,922 ppb in 2023. Nitrous oxide (N₂O) concentrations have risen by about 20%, from a pre-industrial level of 270 ppb to 337 ppb in 2023. These increases are unprecedented in at least the last 800,000 years, according to data from ice cores.
This significant and rapid rise in post-industrial GHG levels is the primary driver of the observed warming of the climate system. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) uses pre-industrial levels as a baseline to assess the extent of human-induced climate change and to set targets for limiting global warming.
Milestones in Climate Science Discovery
The understanding of greenhouse gases and their effect on climate has evolved over nearly two centuries of scientific inquiry. In the 1820s, Joseph Fourier first proposed that Earth's atmosphere trapped heat, similar to a "hothouse." In the 1850s and 1860s, John Tyndall identified that certain gases, including water vapor and carbon dioxide, were strong absorbers of infrared radiation, suggesting they played a role in Earth's temperature.
Svante Arrhenius, in 1896, was the first to quantitatively estimate the warming effect of increasing atmospheric CO₂ due to industrial coal burning, predicting that a doubling of CO₂ could lead to a significant temperature rise. Guy Callendar, in the 1930s, compiled temperature records and CO₂ measurements, arguing that global temperatures were already rising due to fossil fuel combustion. However, these ideas were not widely accepted until more robust data became available.
A crucial milestone was the establishment of continuous atmospheric CO₂ monitoring at Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii by Charles David Keeling starting in 1958. The resulting "Keeling Curve" provided clear evidence of a steady increase in atmospheric CO₂, directly linking it to human emissions. Throughout the latter half of the 20th century and into the 21st, advances in climate modeling, paleoclimatology (the study of past climates using ice cores, tree rings, etc.), and satellite observations have further solidified the scientific understanding of the link between rising GHG concentrations and global warming. The establishment of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has been pivotal in synthesizing and assessing scientific knowledge on climate change for policymakers and the public.
Policy Developments (e.g., Kyoto Protocol, Paris Agreement)
Growing scientific understanding of the risks posed by increasing greenhouse gas emissions spurred international efforts to address climate change through policy. A significant early step was the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), an international treaty adopted at the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro. The UNFCCC established a framework for international cooperation to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system.
The Kyoto Protocol, adopted in 1997 and entering into force in 2005, was the first legally binding treaty to commit industrialized nations to limit and reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. It set specific, differentiated emission reduction targets for these countries relative to their 1990 levels. However, the Kyoto Protocol did not compel developing countries, including major emerging economies like China and India, to take on binding reduction targets, and the United States never ratified it.
The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015 under the UNFCCC, marked a new phase in global climate action. Unlike the Kyoto Protocol, it calls on all countries—both developed and developing—to make commitments to reduce their emissions and to strengthen these commitments over time. Countries submit their own nationally determined contributions (NDCs), outlining their climate action plans. The central aim of the Paris Agreement is to keep the global average temperature rise this century well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase even further to 1.5 degrees Celsius. It also aims to strengthen the ability of countries to deal with the impacts of climate change and to make finance flows consistent with a pathway towards low greenhouse gas emissions and climate-resilient development.
These books provide further details on climate change policy and legal frameworks.
Technological Advancements in Measurement
The ability to accurately measure greenhouse gas concentrations and emissions has been critical to understanding climate change and informing policy. Early measurements, like those by Keeling, relied on ground-based observatories using precise analytical instruments. Over time, the network of ground-based monitoring stations has expanded globally, providing more comprehensive data on atmospheric composition.
Significant advancements have come from satellite remote sensing. Satellites equipped with specialized sensors can now measure the concentrations of various greenhouse gases, such as CO₂ and methane, over large areas of the globe and at different altitudes in the atmosphere. These space-based observations provide a global perspective that complements ground-based measurements and helps identify emission sources and sinks more effectively.
Improvements in analytical techniques, such as spectroscopy and gas chromatography, have increased the accuracy and precision of GHG measurements. The use of isotopic analysis helps differentiate between natural and anthropogenic sources of gases like CO₂ and methane. Furthermore, sophisticated atmospheric transport models, combined with measurement data, allow scientists to estimate emissions at regional and national scales and to verify self-reported emissions data from countries and industries.
Technological advancements also extend to monitoring emissions from specific sources, such as industrial facilities, landfills, and agricultural operations, using techniques like eddy covariance flux towers, aircraft-based sensors, and drone-mounted instruments. These ongoing developments in measurement technology are crucial for tracking progress towards emission reduction targets and for refining our understanding of the complex carbon cycle.
Current Trends and Market Implications
The global focus on greenhouse gases is not just an environmental issue; it has profound economic and market implications. This section explores current emission trends by sector, the rise of carbon markets, corporate responses through ESG initiatives, and the burgeoning field of green technologies.
GHG Emissions by Sector (Energy, Agriculture, etc.)
Globally, greenhouse gas emissions originate from several key economic sectors. The energy sector is by far the largest contributor, responsible for approximately 75.7% of worldwide emissions. This includes emissions from electricity and heat production (around 29.7%), transportation (around 13.7%), manufacturing and construction (around 12.7%), and direct fuel use in buildings (around 6.6%). Fugitive emissions, which are leaks during fossil fuel extraction and transport, also fall under this category.
Agriculture, Forestry, and Other Land Use (AFOLU) is the second-largest emitting sector, accounting for roughly 22% of global emissions when considering activities like deforestation and livestock cultivation. Agricultural soils and livestock, particularly methane from enteric fermentation in cattle, are significant sources.
Industry, excluding energy used for manufacturing (which is counted in the energy sector), contributes about 24% of global emissions (or 6.5% if only direct process emissions like those from cement and chemical production are considered, depending on accounting methods). The waste sector, primarily through methane emissions from landfills and wastewater, accounts for a smaller but still significant portion of global GHGs. Direct emissions from buildings (e.g., from burning fuels for heating and cooking) contribute around 6% globally. It's important to note that these percentages can vary by country and region, reflecting different economic structures and energy sources. For instance, in some countries, land-use change and agriculture might be the dominant sources, while in highly industrialized nations, energy and industry take precedence.
Data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) shows that in the United States in 2022, the transportation sector was the largest source of direct GHG emissions, followed by electricity generation and industry.
Carbon Markets and Pricing Mechanisms
Carbon markets and carbon pricing are economic tools designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by making polluting activities more expensive. Carbon pricing assigns a monetary value to carbon emissions, creating a financial incentive for emitters to reduce their output.
There are two main types of carbon pricing mechanisms:
- Carbon Taxes: This is a direct price on GHG emissions, where the government sets a price per ton of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO₂e) emitted. Companies and industries then pay this tax based on their emissions, encouraging them to invest in cleaner technologies and processes to reduce their tax burden.
- Emissions Trading Systems (ETS), also known as Cap-and-Trade Systems: In an ETS, a government sets an overall limit (a "cap") on total emissions from a specific group of emitters (e.g., power plants, industrial facilities). This cap is gradually lowered over time. Emitters receive or buy emission allowances (permits to emit a certain amount of GHGs) within this cap. Companies that reduce their emissions below their allowance can sell their surplus allowances to those who exceed their limits. This creates a "carbon market" where allowances are traded, and the price of an allowance is determined by supply and demand.
Voluntary carbon markets also exist, where companies, organizations, or individuals voluntarily purchase carbon credits to offset their emissions. These credits are generated by projects that reduce or remove greenhouse gases from the atmosphere, such as reforestation projects or renewable energy installations. According to the World Bank, in 2024, carbon pricing instruments covered approximately 24% of global emissions, with revenues exceeding $100 billion in 2023. International agreements like Article 6 of the Paris Agreement also aim to facilitate international carbon markets to help countries achieve their emission reduction targets more cost-effectively.
Understanding the intricacies of energy markets and carbon pricing is crucial in this evolving landscape.
Corporate ESG Initiatives
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria are a set of standards for a company’s operations that socially conscious investors use to screen potential investments. The "Environmental" aspect of ESG specifically addresses a company's impact on the natural world, including its greenhouse gas emissions, energy efficiency, waste management, and efforts to mitigate climate change.
Increasingly, companies are adopting robust ESG initiatives in response to pressure from investors, consumers, employees, and regulators. Regarding greenhouse gases, corporate ESG strategies often involve:
- Measuring and reporting GHG emissions: Companies are more frequently calculating their carbon footprint across their operations (Scope 1 and 2 emissions) and often their value chains (Scope 3 emissions).
- Setting emission reduction targets: Many corporations are setting ambitious targets to reduce their GHG emissions, sometimes aligned with scientific goals like those of the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), which promotes pathways consistent with limiting global warming to 1.5°C or well below 2°C.
- Investing in renewable energy and energy efficiency: Companies are transitioning to renewable energy sources for their electricity needs and implementing measures to improve energy efficiency in their buildings and processes.
- Engaging with suppliers: Recognizing that a significant portion of their carbon footprint may lie in their supply chains, companies are working with suppliers to reduce emissions.
- Developing low-carbon products and services: Innovation is leading to new products and services that have a lower carbon footprint or help customers reduce their own emissions.
Strong ESG performance, particularly in managing and reducing GHG emissions, is increasingly seen as an indicator of a company's long-term resilience, operational efficiency, and ability to manage climate-related risks and opportunities.
Emerging Technologies (Carbon Capture, Renewable Energy)
Technological innovation plays a vital role in addressing the challenge of greenhouse gas emissions. Two key areas of development are carbon capture technologies and renewable energy.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) refers to a suite of technologies designed to capture CO₂ emissions from large point sources, such as power plants and industrial facilities, or directly from the atmosphere (Direct Air Capture - DAC). Once captured, the CO₂ can be compressed and transported to be stored in deep geological formations (storage) or used to create valuable products (utilization), such as fuels, chemicals, or building materials. While CCUS technologies hold promise for decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors, their widespread deployment faces challenges related to cost, energy requirements, and long-term storage security.
Renewable energy technologies are central to transitioning away from fossil fuels, the largest source of GHG emissions. These include:
- Solar power: Photovoltaic (PV) panels and concentrated solar power (CSP) systems convert sunlight into electricity. The cost of solar PV has fallen dramatically in recent decades, making it increasingly competitive with fossil fuels.
- Wind power: Wind turbines convert wind energy into electricity. Wind power is another rapidly growing renewable energy source, both onshore and offshore.
- Hydropower: Utilizes the energy of flowing water to generate electricity.
- Geothermal energy: Taps into the Earth's internal heat for electricity generation and direct heating.
- Bioenergy: Derived from organic materials (biomass), which can be burned to produce heat and electricity or converted into biofuels. Sustainable sourcing of biomass is crucial to ensure genuine climate benefits.
This course explores technologies aimed at mitigating climate change, including carbon capture.
For those interested in the specifics of energy resources, including shale gas, the following book may be of interest.
Greenhouse Gases in Career Pathways
The increasing global focus on understanding, mitigating, and adapting to the impacts of greenhouse gases has created a diverse and expanding range of career opportunities. Professionals in this field work across various industries, applying scientific, technical, policy, and analytical skills to address climate change challenges.
Key Industries: Environmental Consulting, Policy, Cleantech
Several key industries are at the forefront of addressing greenhouse gas issues and offer significant career opportunities:
Environmental Consulting: Environmental consulting firms play a crucial role in helping businesses, governments, and other organizations understand and manage their environmental impact, including GHG emissions. Consultants may conduct GHG inventories, develop emission reduction strategies, assess climate risks, ensure regulatory compliance, and advise on sustainability initiatives. The environmental consulting market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental regulations and corporate sustainability efforts. Mordor Intelligence projects the market to reach USD 62.25 billion by 2030, up from an estimated USD 46.50 billion in 2025. Another report by The Insight Partners suggests the market could reach $77.35 billion by 2031.
Policy and Governance: Governments at local, national, and international levels require professionals to develop, implement, and enforce policies related to greenhouse gas reduction and climate change adaptation. This includes roles in regulatory agencies, legislative bodies, and international organizations. Policy analysts, climate advisors, and program managers work on issues such as emissions trading schemes, renewable energy mandates, energy efficiency standards, and climate finance.
Cleantech (Clean Technology): The cleantech sector encompasses a broad range of industries developing and deploying technologies that reduce negative environmental impacts, including those that lower GHG emissions. This includes renewable energy (solar, wind, etc.), energy storage, electric vehicles, sustainable transportation, green buildings, energy efficiency solutions, carbon capture technologies, and sustainable agriculture. This sector is characterized by innovation and rapid growth, offering roles for engineers, scientists, project developers, financial analysts, and marketing professionals.
Other industries with growing needs for GHG expertise include finance (for ESG investing and climate risk assessment), manufacturing (for sustainable production), agriculture (for climate-smart practices), and education/research.
Entry-Level Roles (e.g., Sustainability Analyst)
For individuals starting their careers in the field of greenhouse gases, several entry-level roles provide a solid foundation and opportunities for growth. A common entry point is the role of a Sustainability Analyst or Environmental Analyst. In these positions, individuals typically support senior staff by collecting and analyzing environmental data, including GHG emissions data; preparing reports; researching environmental regulations and best practices; and assisting with sustainability assessments or audits. These roles often require a bachelor's degree in environmental science, engineering, sustainability studies, or a related field, along with strong analytical and communication skills.
Other entry-level positions can include:
- Environmental Technician: Involves fieldwork, sampling, and monitoring of environmental conditions, potentially including air quality and emissions.
- Junior Policy Researcher: Assisting with research and analysis to support the development of climate and energy policies.
- Project Assistant/Coordinator (Cleantech): Supporting the development and implementation of renewable energy or energy efficiency projects.
- ESG Data Analyst: Collecting and analyzing data related to corporate environmental, social, and governance performance.
These roles provide valuable experience in understanding the practical aspects of GHG management, policy implementation, or technology deployment. They also offer opportunities to develop specialized skills and knowledge that can lead to more advanced positions. Many employers in this field look for candidates who are passionate about environmental issues and possess a proactive learning attitude. Internships and volunteer work can be very beneficial for gaining initial experience and making connections in the industry.
Advanced Careers (Climate Modeler, Carbon Auditor)
With experience and often advanced education (such as a Master's or Ph.D.), professionals can move into more specialized and senior roles related to greenhouse gases. These positions typically require a deeper level of expertise and responsibility.
Climate Modeler: Climate modelers use complex computer simulations to understand the climate system, project future climate change scenarios based on different GHG emission pathways, and assess the potential impacts of climate change. This role requires strong quantitative skills, a deep understanding of atmospheric science and physics, and proficiency in programming and data analysis. Climate modelers often work in research institutions, government agencies, or specialized consulting firms.
Carbon Auditor: Carbon auditors are responsible for verifying and validating greenhouse gas emissions data reported by organizations. This is a critical role in ensuring the accuracy and credibility of emissions reporting, particularly for companies participating in mandatory emissions trading schemes or voluntary carbon offset programs. Carbon auditors need a thorough understanding of GHG accounting standards (e.g., the GHG Protocol), auditing procedures, and relevant regulations. Certification as a GHG verifier or auditor is often required.
Other advanced career paths include:
- Senior Environmental Consultant/Manager: Leading complex environmental projects, managing teams, and providing high-level strategic advice to clients on GHG reduction and climate strategy.
- Climate Change Policy Director: Developing and advocating for climate policies at a senior level in government, NGOs, or industry associations.
- Renewable Energy Project Developer/Manager: Overseeing the entire lifecycle of large-scale renewable energy projects, from site selection and financing to construction and operation.
- Chief Sustainability Officer (CSO): A corporate leadership role responsible for developing and implementing the company's overall sustainability strategy, including GHG emission reduction targets and ESG reporting.
- Climate Scientist/Researcher: Conducting original research to advance the understanding of climate change, its impacts, and potential solutions. This often involves working at universities or government research labs.
Interdisciplinary Skills (Data Analysis, Regulatory Knowledge)
Success in careers related to greenhouse gases often requires a blend of technical, analytical, and soft skills, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of the field. Data analysis skills are increasingly crucial. Professionals need to be able to collect, manage, analyze, and interpret large datasets related to emissions, energy consumption, climate projections, and environmental impacts. Proficiency in spreadsheet software like Excel, statistical software, and potentially programming languages like Python or R for data analysis and visualization is highly valuable.
A strong understanding of regulatory knowledge is also essential. This includes familiarity with international climate agreements (like the Paris Agreement), national and regional environmental laws, emissions reporting requirements, carbon pricing mechanisms, and industry-specific regulations. The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, so a commitment to continuous learning is important.
Other valuable interdisciplinary skills include:
- Communication skills: The ability to clearly and effectively communicate complex scientific or technical information to diverse audiences, including policymakers, business leaders, and the public, both verbally and in writing.
- Problem-solving and critical thinking: Developing innovative solutions to complex environmental challenges and critically evaluating information and strategies.
- Project management: Planning, executing, and managing projects effectively, whether they are research projects, policy initiatives, or technology deployments.
- Understanding of economics and finance: Particularly for roles related to carbon markets, ESG investing, and the economic impacts of climate change and mitigation policies.
- Systems thinking: Understanding how different components of the climate system, economy, and society interact.
- Collaboration and teamwork: Climate change is a complex issue that requires working effectively with people from diverse backgrounds and disciplines.
Consider these courses to build foundational knowledge relevant to careers focusing on greenhouse gases and climate solutions.
Formal Education Pathways
A strong educational foundation is typically essential for those aspiring to build a career focused on greenhouse gases and climate change. Formal education provides the necessary scientific understanding, analytical skills, and specialized knowledge required in this complex and evolving field.
Relevant Undergraduate Majors (Environmental Science, Engineering)
Several undergraduate majors can provide an excellent foundation for a career related to greenhouse gases. Environmental Science is a popular and direct choice. This interdisciplinary field integrates principles from biology, chemistry, geology, and physics to study environmental systems and address environmental problems, including climate change and GHG emissions. Students learn about atmospheric science, ecology, environmental policy, and data analysis.
Engineering disciplines also offer strong pathways. Environmental Engineering focuses on applying engineering principles to protect and improve the environment, including designing solutions for pollution control, waste management, and renewable energy systems. Other relevant engineering fields include Chemical Engineering (for understanding industrial processes and developing cleaner technologies), Mechanical Engineering (for designing energy-efficient systems and renewable energy technologies), and Civil Engineering (for sustainable infrastructure and green building design).
Other undergraduate majors that can lead to careers in this area include:
- Atmospheric Science/Meteorology: For those interested in the physical science of climate and weather.
- Chemistry or Physics: Providing a strong fundamental science background applicable to climate research or technology development.
- Geology/Earth Sciences: For understanding Earth's climate history, carbon cycles, and potential for geological carbon storage.
- Ecology or Biology: Focusing on the impacts of climate change on ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Economics or Public Policy: With a specialization in environmental economics or policy, for careers in carbon markets, climate policy analysis, or sustainability consulting.
- Sustainability Studies: An emerging interdisciplinary field that directly addresses issues of sustainability, including climate change mitigation and adaptation.
Graduate Programs and Research Opportunities
For many specialized roles and for those interested in research or academic careers, a graduate degree (Master's or Ph.D.) is often necessary. Graduate programs allow for deeper specialization in areas related to greenhouse gases and climate change.
Relevant Master's programs include:
- Master of Science (M.S.) in Environmental Science, Atmospheric Science, Climate Science, or Environmental Engineering: These programs provide advanced scientific and technical training.
- Master of Public Policy (M.P.P.) or Master of Public Administration (M.P.A.) with a focus on Environmental Policy or Energy Policy: For careers in government, NGOs, or policy consulting.
- Master of Business Administration (M.B.A.) with a concentration in Sustainability or Sustainable Business: For leadership roles in corporate sustainability or cleantech ventures.
- Specialized Master's degrees in areas like Renewable Energy, Carbon Management, or Climate Change Adaptation.
A Ph.D. is typically required for independent research positions in academia or government research labs, and for some high-level expert roles in consulting or industry. Ph.D. research can focus on a vast array of topics, such as advancing climate models, developing new carbon capture technologies, understanding the impacts of GHGs on specific ecosystems, or analyzing the effectiveness of different climate policies.
Many universities host research centers and institutes dedicated to climate change and sustainability, offering numerous research opportunities for graduate students. These can involve laboratory work, fieldwork, computational modeling, and policy analysis. Securing research assistantships or fellowships can provide valuable experience and financial support during graduate studies.
This book delves into regional impacts and vulnerabilities related to climate change, a common area of graduate-level research.
Certifications (e.g., GHG Inventory Management)
In addition to formal degrees, professional certifications can enhance career prospects and demonstrate specialized expertise in areas related to greenhouse gas management. These certifications are often targeted at specific skills or knowledge areas valued by employers.
One notable area for certification is Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Inventory Management or Accounting. Professionals with these certifications are qualified to quantify and report GHG emissions for organizations according to established protocols like the GHG Protocol Corporate Standard. This is crucial for regulatory compliance, participation in carbon markets, and corporate sustainability reporting. Several organizations offer training and certification programs in GHG accounting and verification.
Other relevant certifications might include:
- LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) credentials: For professionals involved in green building design, construction, and operation.
- Certified Energy Manager (CEM): For individuals specializing in energy efficiency and energy management.
- Project Management Professional (PMP): While not specific to GHGs, this certification is valuable for managing complex environmental or cleantech projects.
- Sustainability-focused certifications: Various organizations offer certifications related to broader sustainability practices and reporting (e.g., GRI - Global Reporting Initiative).
Fieldwork and Laboratory Skill Development
For many scientific and technical roles related to greenhouse gases, practical skills gained through fieldwork and laboratory experience are essential. These hands-on experiences complement theoretical knowledge and prepare individuals for the challenges of real-world environmental assessment and research.
Fieldwork may involve:
- Atmospheric Monitoring: Collecting air samples for GHG analysis, operating and maintaining air quality monitoring equipment, and taking meteorological measurements.
- Ecological Assessments: Studying the impacts of climate change on ecosystems, which might involve vegetation surveys, soil sampling, and wildlife observation.
- Environmental Site Assessments: Investigating sites for potential contamination or assessing environmental impacts of projects, which can include measuring emissions from specific sources.
- Oceanographic Research: Collecting water samples, deploying sensors, and studying ocean chemistry and circulation, which are crucial for understanding the ocean's role as a carbon sink.
Laboratory skills are vital for analyzing samples and conducting experiments. This can include:
- Chemical Analysis: Using techniques like gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and spectroscopy to measure concentrations of greenhouse gases and related compounds in air, water, or soil samples.
- Isotope Analysis: Determining the isotopic composition of GHGs to trace their sources and understand biogeochemical cycles.
- Microbiological Techniques: Studying microbial processes involved in GHG production or consumption (e.g., methane production in wetlands or nitrous oxide emissions from soils).
- Experimental Design and Execution: Designing and conducting controlled experiments to investigate specific aspects of climate science or GHG mitigation technologies.
Online and Independent Learning
Beyond formal degree programs, online courses and independent study offer flexible and accessible pathways to gain knowledge and skills related to greenhouse gases. These resources can be invaluable for self-directed learners, professionals looking to upskill or pivot careers, and students seeking to supplement their formal education.
OpenCourser is a valuable resource for finding relevant online learning opportunities. With a comprehensive catalog of courses from various providers, learners can easily browse through thousands of courses, save interesting options to a list using the "Save to List" feature, compare syllabi, and read summarized reviews to find the perfect online course. The "Career Center" section on OpenCourser course pages can also help learners discover potential career paths related to their studies.
Core Topics for Self-Study (Climate Science Basics, Carbon Accounting)
For individuals new to the field or looking to build a foundational understanding through self-study, several core topics are essential.
Climate Science Basics: This includes understanding the Earth's climate system, the natural greenhouse effect, the different types of greenhouse gases and their properties (including their Global Warming Potentials), the carbon cycle, and the evidence for human-caused climate change. Key concepts include radiative forcing, climate feedbacks, and the observed and projected impacts of climate change (e.g., rising temperatures, sea-level rise, extreme weather events). Many introductory online courses and reputable websites (like those from NASA, NOAA, and the EPA) offer excellent resources on these topics.
Carbon Accounting and Management: This involves learning how to quantify greenhouse gas emissions from various sources (e.g., organizations, projects, products). Key frameworks include the GHG Protocol standards. Understanding emission scopes (Scope 1, 2, and 3), data collection methods, emission factors, and reporting practices is crucial. This knowledge is valuable for roles in corporate sustainability, environmental consulting, and regulatory compliance.
Other important areas for self-study include:
- Energy Systems and Renewable Energy: Learning about different energy sources, the transition to renewable energy technologies (solar, wind, etc.), and energy efficiency measures.
- Climate Policy and Governance: Understanding international agreements like the Paris Agreement, national climate policies, carbon pricing mechanisms (carbon taxes, emissions trading systems), and the role of different stakeholders.
- Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability: Exploring how different sectors and regions are affected by climate change and what measures can be taken to adapt and build resilience.
These courses offer a solid introduction to climate science and related issues, suitable for self-study.
This book provides a broad overview of global warming, a key aspect of climate science.
Project-Based Learning Opportunities
Project-based learning is an excellent way to apply theoretical knowledge gained from online courses or independent study and to develop practical skills. Engaging in projects can make learning more tangible and can also result in valuable additions to a portfolio.
Some examples of project-based learning opportunities related to greenhouse gases include:
- Conducting a Personal or Household Carbon Footprint Analysis: Use online calculators and research to estimate your own GHG emissions from energy use, transportation, food choices, and waste. Develop a plan to reduce your footprint.
- Analyzing Local Climate Data: Access publicly available weather and climate data for your region. Analyze trends in temperature, precipitation, or extreme weather events and try to relate them to broader climate change information.
- Researching a Local Renewable Energy Project: Investigate a solar, wind, or other renewable energy project in your community. Learn about its development, technology, economic viability, and environmental benefits.
- Developing a Mock GHG Inventory for a Small Organization: Using the GHG Protocol or similar guidelines, try to create a simplified GHG inventory for a hypothetical small business or a real one if you have access to data (with permission).
- Creating Educational Materials: Develop a presentation, infographic, or short video explaining a key concept related to greenhouse gases or climate change for a specific audience (e.g., K-12 students, community members).
- Participating in Citizen Science Projects: Many organizations run citizen science projects related to climate change, such as tracking changes in plant and animal behavior or monitoring local environmental conditions.
Integration with Formal Education
Online courses and independent learning can effectively supplement and enhance formal education in several ways. For students enrolled in undergraduate or graduate programs, these resources can:
- Provide foundational knowledge: If a student is new to a particular topic covered in a formal course, an introductory online course can help them get up to speed quickly.
- Offer deeper dives into specific subjects: Formal curricula may only cover certain topics broadly. Online courses can allow students to explore areas of particular interest in more detail (e.g., a specific renewable energy technology, a particular aspect of climate policy).
- Introduce new tools and skills: Students can use online courses to learn software (e.g., GIS, data analysis tools like R or Python), technical skills, or methodologies that may not be extensively covered in their formal program but are valuable in the job market.
- Offer diverse perspectives: Online courses taught by instructors from different institutions or countries can expose students to a wider range of viewpoints and approaches.
- Help prepare for advanced courses or research: Taking online courses on prerequisite topics can help students feel more confident and prepared for more challenging coursework or research projects.
- Bridge gaps in knowledge: If a student's formal program doesn't offer a specific course they are interested in (e.g., carbon accounting), an online course can fill that gap.
Building Portfolios for Career Transitions
For individuals looking to transition into a career related to greenhouse gases, building a strong portfolio that showcases relevant skills and knowledge is crucial, especially if their prior experience is in a different field. Online learning and independent projects can be instrumental in developing this portfolio.
Here’s how online and independent learning can contribute to portfolio building:
- Course Certificates: While not a substitute for a degree, certificates from reputable online courses can demonstrate a commitment to learning and foundational knowledge in specific areas (e.g., climate science, renewable energy, sustainability management). Listing these on a resume or LinkedIn profile can be beneficial. The OpenCourser Learner's Guide offers tips on how to effectively add online course certificates to your professional profiles.
- Project Outputs: Tangible outputs from project-based learning (as discussed earlier) can be powerful portfolio pieces. This could include reports from a carbon footprint analysis, presentations on climate data, a mock GHG inventory, or educational materials you've created.
- Written Work: Blog posts, articles, or research summaries on topics related to greenhouse gases or climate change can demonstrate your understanding and communication skills. These can be self-published or contributed to relevant platforms.
- Data Analysis Projects: If you've used online courses to learn data analysis skills, showcase projects where you've analyzed environmental data, visualized trends, or built simple models. Platforms like GitHub can be used to share code and project details.
- Volunteer Experience Documentation: If you've volunteered for environmental organizations, document your contributions and any projects you were involved in.
- Personal Website or Online Profile: Create a professional online presence where you can collate your portfolio items, resume, and a statement about your career goals in the GHG field.
Ethical and Global Challenges
The issue of greenhouse gases is intrinsically linked to complex ethical dilemmas and significant global challenges. Addressing climate change requires navigating these multifaceted problems, which often involve competing interests, historical responsibilities, and the need for unprecedented international cooperation.
Equity in Climate Mitigation Efforts
A central ethical challenge in addressing greenhouse gas emissions is ensuring equity in climate mitigation efforts. This pertains to fairness both between nations (international equity) and within nations (domestic equity).
International Equity: Historically, industrialized nations have been responsible for the vast majority of cumulative GHG emissions that have caused current climate change. Developing nations, while often contributing the least to historical emissions, are frequently the most vulnerable to the impacts of climate change (e.g., sea-level rise, extreme weather, food insecurity). This raises questions about differentiated responsibilities: should developed countries bear a greater burden in reducing emissions and providing financial and technological support to developing countries to help them transition to low-carbon economies and adapt to climate impacts? Concepts like "common but differentiated responsibilities and respective capabilities" (CBDR-RC), enshrined in the UNFCCC, attempt to address this.
Domestic Equity: Within countries, the impacts of climate change and the costs and benefits of mitigation policies can be unevenly distributed. Low-income communities, marginalized groups, and Indigenous populations often face greater exposure to climate risks and may have fewer resources to adapt. Furthermore, policies aimed at reducing GHG emissions, such as carbon taxes or the phase-out of fossil fuel industries, can disproportionately affect certain workers and communities if not designed with a "just transition" in mind. Ensuring that climate policies are fair and do not exacerbate existing inequalities is a critical ethical consideration. This involves inclusive decision-making processes and targeted support for vulnerable groups.
The concept of climate justice broadly encompasses these equity concerns, emphasizing that climate solutions must also address social, economic, and racial justice.
Political and Economic Barriers to Reduction
Despite the scientific consensus on the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, significant political and economic barriers hinder rapid and effective action.
Political Barriers:
- Short-term political cycles vs. long-term climate impacts: The long-term nature of climate change can be misaligned with shorter political and electoral cycles, making it difficult for policymakers to implement potentially costly or disruptive measures that have long-term benefits.
- Vested interests and lobbying: Powerful industries with significant investments in fossil fuels may resist policies aimed at transitioning to a low-carbon economy. Lobbying efforts can influence political decisions and slow down climate action.
- National interests vs. global cooperation: While climate change is a global problem requiring collective action, countries may prioritize their perceived national economic interests, leading to difficulties in reaching and implementing ambitious international agreements.
- Public opinion and political will: Lack of public awareness or a sense of urgency, sometimes fueled by misinformation, can weaken political will to implement strong climate policies.
Economic Barriers:
- Costs of transition: Shifting from a fossil fuel-based economy to a low-carbon one requires substantial investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable transportation, and new industrial processes. The upfront costs can be perceived as a barrier, even if the long-term economic benefits (including avoided climate damages) are significant.
- Path dependency and infrastructure lock-in: Existing infrastructure (e.g., power plants, transportation systems) is often heavily reliant on fossil fuels. Retiring these assets prematurely or retrofitting them can be economically challenging.
- Concerns about competitiveness: Industries in countries with strong climate policies may fear being at a competitive disadvantage compared to those in countries with laxer regulations (an issue "carbon border adjustments" aim to address).
- Distributional impacts: The economic costs and benefits of climate policies may not be evenly distributed across society, potentially leading to resistance from affected groups if not managed equitably.
Geoengineering Controversies
Geoengineering, also known as climate engineering, refers to large-scale, intentional interventions in Earth's climate system to counteract climate change. These technologies are broadly divided into two categories:
- Solar Radiation Management (SRM) or Solar Geoengineering: Aims to reflect a small percentage of incoming sunlight back into space to cool the planet. Proposed methods include stratospheric aerosol injection (releasing reflective particles into the upper atmosphere), marine cloud brightening (spraying sea salt to make clouds more reflective), and space-based reflectors.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) or Greenhouse Gas Removal (GGR): Aims to remove CO₂ from the atmosphere and store it. Methods include afforestation and reforestation, bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), direct air capture (DAC), enhanced weathering, and ocean fertilization.
Geoengineering technologies are highly controversial for several reasons:
- Effectiveness and Unintended Consequences: Many proposed techniques are still theoretical or in early stages of research. Their effectiveness at a climate-altering scale is uncertain, and they could have unforeseen and potentially harmful side effects on weather patterns, ecosystems, and global systems. For example, SRM does not address ocean acidification (caused by CO₂ absorption) and could have significant impacts on regional climates and precipitation.
- Governance and Ethical Concerns: Who would decide to deploy such technologies? How would they be governed internationally? There are concerns about unilateral action, potential weaponization, and the moral hazard that the prospect of a "techno-fix" could reduce incentives to cut emissions (the primary solution).
- Termination Effect (for SRM): If an SRM system were deployed and then suddenly stopped, global temperatures could rise very rapidly to the level they would have reached without SRM, potentially causing severe disruption.
- Cost and Feasibility: The costs and logistical challenges of deploying many geoengineering technologies at a meaningful scale are immense.
International Cooperation Challenges
Addressing climate change and managing greenhouse gas emissions inherently requires international cooperation because GHGs mix globally in the atmosphere, meaning emissions from one country affect all countries. However, achieving effective and equitable international cooperation faces numerous challenges:
- Differing National Circumstances and Priorities: Countries vary widely in their levels of economic development, historical responsibility for emissions, vulnerability to climate impacts, resource endowments, and political priorities. This makes it difficult to agree on fair and ambitious contributions to global climate efforts.
- Free-rider Problem: Since the benefits of climate mitigation (a stable climate) are a global public good, individual countries may be tempted to rely on others to take action while minimizing their own efforts and costs.
- Ensuring Compliance and Accountability: International agreements often rely on voluntary commitments and peer pressure for enforcement. Developing robust mechanisms for monitoring, reporting, and verifying emissions reductions and for holding countries accountable to their commitments is an ongoing challenge.
- Finance and Technology Transfer: Developing countries often require financial assistance and access to clean technologies from developed countries to pursue low-carbon development and adapt to climate impacts. Mobilizing sufficient and predictable climate finance and facilitating technology transfer remain key challenges.
- Short-term vs. Long-term Interests: As mentioned earlier, balancing immediate economic and political concerns with the long-term imperative of climate action is difficult for many governments.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Broader geopolitical conflicts and a lack of trust between nations can undermine cooperation on climate change.
Topics like Sustainability and Global Warming are central to understanding these global challenges.
Career Progression and Opportunities
The field related to greenhouse gases and climate change offers a dynamic and growing landscape for career development. From entry-level positions to leadership roles, opportunities exist across various sectors for individuals committed to addressing this critical global issue. Understanding the pathways for progression and the evolving job market can help professionals navigate their careers effectively.
For those starting out, gaining practical experience is key. As the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics notes, employment for environmental scientists and specialists is projected to grow. This indicates a healthy demand for skilled professionals. OpenCourser's Career Development resources can provide additional guidance for those planning their career paths.
Internships and Volunteer Work in NGOs
For individuals seeking to enter the field of greenhouse gas management or climate action, internships and volunteer work, particularly with Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs), can provide invaluable experience, skill development, and networking opportunities.
NGOs play a critical role in climate advocacy, research, policy development, community engagement, and implementing on-the-ground projects. Interning or volunteering with an NGO can offer exposure to:
- Policy research and analysis: Assisting with research on climate policies, tracking legislative developments, or contributing to policy briefs.
- Advocacy and campaigning: Supporting efforts to raise public awareness, mobilize public support for climate action, and influence policymakers.
- Project implementation: Participating in projects related to renewable energy deployment, energy efficiency, conservation, or climate adaptation in communities.
- Communications and outreach: Helping to develop educational materials, manage social media, or organize events.
- Data collection and analysis: Supporting research projects by gathering and analyzing environmental data.
Mid-Career Specialization Paths
As professionals gain experience in the field of greenhouse gases and climate change, opportunities for specialization emerge. Mid-career specialization allows individuals to develop deeper expertise in a particular niche, enhancing their value and impact.
Some common specialization paths include:
- Carbon Accounting and Reporting: Focusing on the technical aspects of measuring, verifying, and reporting GHG emissions for corporations or under regulatory schemes. This may involve expertise in specific protocols (e.g., GHG Protocol, ISO 14064) and assurance processes.
- Climate Risk and Resilience: Specializing in assessing the physical and transitional risks of climate change for businesses, communities, or infrastructure, and developing strategies to build resilience and adapt.
- Renewable Energy Development and Finance: Focusing on the technical, financial, and regulatory aspects of developing and deploying renewable energy projects (solar, wind, etc.).
- Sustainable Supply Chain Management: Working with companies to reduce GHG emissions and environmental impacts throughout their supply chains.
- Climate Policy and Regulation: Developing deep expertise in specific areas of climate policy, such as carbon pricing mechanisms, energy efficiency standards, or international climate negotiations.
- Corporate Sustainability Strategy: Advising or leading companies in developing and implementing comprehensive sustainability strategies that integrate GHG reduction with broader business goals.
- Climate Modeling and Data Science: Utilizing advanced computational and analytical skills to model climate systems, analyze climate data, and develop climate projections or impact assessments.
- Environmental Law with a Climate Focus: Specializing in legal issues related to climate change, environmental regulations, and climate litigation.
Leadership Roles in Sustainability
With significant experience and a proven track record, professionals can advance to leadership roles in sustainability. These positions involve shaping strategy, driving organizational change, and influencing stakeholders to achieve ambitious environmental goals, including significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
Examples of leadership roles include:
- Chief Sustainability Officer (CSO) or VP of Sustainability: In corporations, this executive is responsible for developing and overseeing the company's overall sustainability strategy, including setting GHG reduction targets, integrating sustainability into business operations, engaging with investors and other stakeholders on ESG issues, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- Director of Climate Change or Environmental Policy: In government agencies or large NGOs, this role involves leading the development and implementation of climate-related policies and programs, managing teams of analysts and specialists, and representing the organization in high-level forums.
- Partner or Practice Lead (Environmental Consulting): Senior positions in consulting firms, responsible for leading a practice area (e.g., climate change services, renewable energy consulting), managing client relationships, and driving business development.
- Head of ESG/Sustainable Investing: In financial institutions, leading the integration of ESG factors and climate considerations into investment analysis and decision-making processes.
- Research Director or Principal Investigator: Leading major research programs on climate change science, impacts, or solutions in academic institutions or research organizations.
Global Job Market Analysis
The job market for professionals with expertise in greenhouse gases and climate change is expanding globally, driven by increasing awareness, regulatory pressures, corporate sustainability commitments, and investments in the green economy. However, the specific opportunities and demand can vary by region and sector.
Growth Areas:
- Renewable Energy: The transition to renewable energy sources is a major driver of job growth worldwide, with demand for engineers, project managers, technicians, and policy specialists. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) regularly reports on employment trends in this sector.
- Environmental Consulting: As noted earlier, the environmental consulting market is projected for strong growth globally, as organizations seek expertise in GHG management, climate risk assessment, and sustainability reporting.
- Corporate Sustainability/ESG: An increasing number of companies are creating dedicated sustainability roles and departments to manage their environmental footprint and respond to investor and consumer expectations.
- Green Buildings and Energy Efficiency: Efforts to improve energy efficiency in buildings and develop sustainable infrastructure are creating demand for architects, engineers, and energy auditors.
- Climate Policy and Finance: Governments and international organizations continue to need professionals to develop and implement climate policies, manage climate finance flows, and support international negotiations.
Regional Variations: The European Union has been a leader in climate policy and has a well-developed market for carbon management and renewable energy professionals. North America also has a significant and growing market, particularly with increasing federal and state-level climate initiatives and corporate action. Asia-Pacific is a region with rapidly growing energy demand and increasing focus on sustainable development and climate mitigation, leading to expanding job opportunities, particularly in renewable energy and green technology. Developing countries often have a strong need for expertise in climate adaptation, sustainable land use, and accessing climate finance.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of environmental scientists and specialists in the U.S. is projected to grow 7 percent from 2023 to 2033, faster than the average for all occupations, with about 8,500 openings projected each year. Data from the U.S. Department of Labor also highlights rapid growth in occupations like wind turbine service technicians. While salaries can vary significantly based on role, experience, sector, and location, careers in the environmental field can be competitive.
Staying informed about global trends, policy developments, and technological advancements is crucial for navigating the global job market in this field. Networking internationally and considering opportunities in different regions can also broaden career prospects.
Frequently Asked Questions (Career Focus)
Embarking on or transitioning into a career focused on greenhouse gases can bring up many questions. Here are answers to some common queries that may help guide your journey.
What qualifications are needed for entry-level GHG roles?
For most entry-level roles in the greenhouse gas field, a bachelor's degree is typically the minimum educational requirement. Relevant degrees include Environmental Science, Environmental Engineering, Sustainability Studies, Chemistry, Biology, Earth Sciences, or Economics/Public Policy with an environmental focus. Strong analytical skills, proficiency in data handling (e.g., using Excel or other data tools), good communication abilities (both written and verbal), and a demonstrated passion for environmental issues are highly valued.
Internships, volunteer experience, or relevant coursework in climate science, energy policy, or carbon accounting can significantly strengthen an application. For some technical roles, specific software skills (like GIS) or familiarity with GHG inventory protocols might be beneficial. While a master's degree can be an advantage for some entry-level positions or provide a pathway to more specialized roles faster, it's not always a strict requirement to get started in the field.
How competitive are jobs in carbon management?
The field of carbon management, which includes roles in GHG accounting, emissions reduction strategy, carbon markets, and sustainability reporting, is growing, but it can also be competitive. The level of competition often depends on the specific role, location, and the candidate's qualifications and experience.
Entry-level positions may attract a larger pool of applicants, so having a strong academic record, relevant internships, and demonstrable skills can help candidates stand out. For more specialized or senior roles, competition can also be keen, as these positions often require specific expertise and a proven track record. The demand for professionals with carbon management skills is generally increasing as more companies and governments implement emission reduction targets and participate in carbon markets. Staying updated on industry trends, networking effectively, and continuously developing relevant skills can improve competitiveness in this job market.
Can remote work apply to this field?
Yes, remote work opportunities exist in the field of greenhouse gases, and the prevalence of such arrangements has increased, mirroring trends in many other professional sectors. Roles that are more analytical, research-oriented, policy-focused, or involve consulting can often be performed remotely, at least partially.
For example, data analysts, climate modelers, policy researchers, writers, and some types of consultants may be able to work effectively from a remote location. However, roles that require significant fieldwork (e.g., environmental monitoring, site assessments), hands-on laboratory work, or direct management of physical assets (e.g., renewable energy facilities) are less likely to be fully remote. Many organizations now offer hybrid models, combining remote work with some in-office presence. The availability of remote work will depend on the specific employer, the nature of the role, and the company's policies.
What industries hire GHG specialists?
Greenhouse gas specialists are hired across a wide range of industries as the importance of managing emissions and addressing climate change becomes more widely recognized. Key industries include:
- Environmental Consulting: A major employer, providing GHG expertise to diverse clients.
- Government: Federal, state, and local government agencies involved in environmental regulation, policy development, and climate programs.
- Energy Sector: Both traditional energy companies (managing their transition) and renewable energy companies (developing and deploying clean energy solutions).
- Manufacturing: Companies looking to reduce their operational emissions, improve energy efficiency, and develop sustainable products.
- Technology (Cleantech): Firms developing and commercializing clean technologies, including carbon capture, energy storage, and electric vehicles.
- Finance and Investment: Banks, investment firms, and insurance companies assessing climate risk, managing ESG investments, and financing green projects.
- Agriculture and Forestry: Organizations working on sustainable land management, carbon sequestration, and reducing emissions from agricultural practices.
- Transportation: Companies in aviation, shipping, and automotive sectors working on decarbonization strategies.
- Non-Profit Organizations (NGOs): Advocacy groups, research institutions, and foundations working on climate change issues.
- Academia: Universities and research institutions conducting climate science research and educating future professionals.
How do salaries compare to traditional sectors?
Salaries in the greenhouse gas and broader environmental field can vary widely depending on factors such as education, experience, specific role, industry, geographic location, and the size and type of the employer. In general, salaries can be competitive with those in some traditional sectors, particularly for specialized roles or positions requiring advanced degrees and significant experience.
For example, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for environmental scientists and specialists was $78,980 in May 2023. Some sources suggest median wages for environmental scientists around $63,570 in earlier years (e.g., 2012), with the top 10 percent earning significantly more. Roles in high-demand areas like renewable energy engineering, climate risk analysis for financial institutions, or senior corporate sustainability positions can command higher salaries. However, salaries in some non-profit or entry-level government positions might be lower than in comparable private sector roles in other industries. It's important to research salary benchmarks for specific roles and locations when considering career options. As the field grows and matures, compensation levels are likely to continue evolving.
Are GHG-related skills transferable to other fields?
Yes, many skills developed in roles focused on greenhouse gases are highly transferable to other fields. This is partly due to the interdisciplinary nature of climate change work. Transferable skills include:
- Data Analysis and Quantitative Skills: The ability to collect, analyze, interpret, and present data is valuable in numerous sectors, from finance and marketing to healthcare and technology.
- Project Management: Experience managing projects, timelines, budgets, and stakeholders is applicable in almost any industry.
- Regulatory Compliance and Policy Analysis: Understanding how to navigate complex regulatory environments and analyze policy implications is a skill sought after in many regulated industries and public sector roles.
- Communication Skills: The ability to communicate complex information clearly to diverse audiences, both verbally and in writing, is universally important.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Developing solutions to complex, multifaceted problems like climate change hones critical thinking skills that are valuable everywhere.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Collaboration: Working with diverse groups of people (e.g., government, industry, communities, scientists) to achieve common goals is a key transferable skill.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Skills in identifying, assessing, and managing risks (e.g., climate-related risks) are transferable to general risk management roles.
- Knowledge of Energy Systems or Sustainability Principles: This knowledge can be applied in various roles focused on operational efficiency, resource management, or corporate social responsibility in many industries.
Useful Links and Resources
To further your understanding of greenhouse gases and explore related topics, the following resources may be helpful. OpenCourser offers a wealth of information and tools to aid your learning journey.
- Explore a wide range of courses on Climate Science to deepen your scientific understanding.
- Discover courses in Environmental Sciences for a broader perspective on environmental issues.
- Learn about Sustainability practices and principles.
- For those interested in policy, explore courses in Public Policy.
- If you're looking for educational materials or need guidance on leveraging online learning, the OpenCourser Learner's Guide provides many helpful articles.
- Stay updated with the latest insights and tips on online learning through OpenCourser Notes, our official blog.
- If you find courses you're interested in, remember to use the "Save to List" feature to keep track of them and manage your learning path at OpenCourser Lists.
Additionally, for official information and data on greenhouse gases, consider these reputable external sources:
- The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides comprehensive information on greenhouse gas emissions, sources, and trends.
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) offers authoritative assessment reports on climate change science, impacts, and mitigation.
- NASA's Climate Change resource provides data, visualizations, and educational materials on Earth's changing climate.
The study of greenhouse gases is a journey into understanding one of the most critical challenges and opportunities of our time. Whether you are aiming to build a career, deepen your academic knowledge, or simply become a more informed global citizen, the pursuit of knowledge in this area is both vital and rewarding. With dedication and the right resources, you can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future.