Power Systems Engineer
wer Systems Engineer: Energizing Our World
Power Systems Engineering is a specialized field of electrical engineering focused on the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of electric power, as well as the electrical apparatus connected to such systems. These engineers are the architects and custodians of the electrical grid, ensuring that electricity flows reliably and efficiently from power plants to our homes, businesses, and industries. Their work is fundamental to modern society, underpinning nearly every aspect of daily life and technological advancement.
Working as a Power Systems Engineer can be incredibly engaging. Imagine designing a new wind farm integration that powers an entire city or developing smart grid technologies that prevent widespread blackouts. The field offers constant intellectual challenges, from solving complex network problems to pioneering sustainable energy solutions. Furthermore, the societal impact is immense, as power systems engineers directly contribute to a more reliable, sustainable, and technologically advanced future.
Introduction to Power Systems Engineering
This section will lay the groundwork for understanding what a career as a Power Systems Engineer entails. We explore the fundamental concepts, the historical journey of our electrical infrastructure, and the pivotal role these engineers play in shaping a sustainable energy future. Whether you are a student contemplating your career path or a professional considering a transition, this introduction aims to provide a clear and concise overview of this vital engineering discipline.
Defining the Discipline: What Do Power Systems Engineers Do?
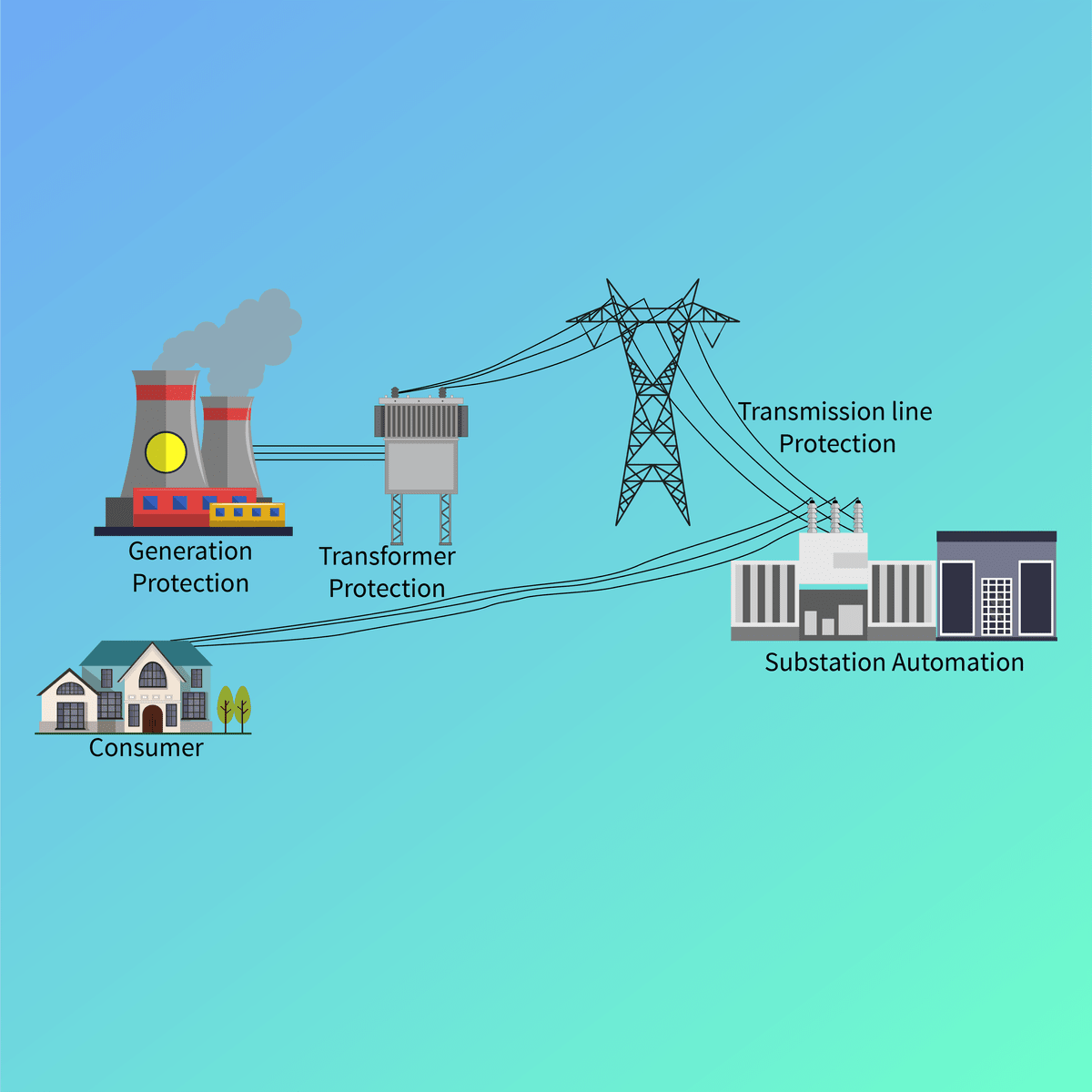
At its core, power systems engineering deals with the intricate network that delivers electricity. This involves the high-voltage transmission lines that carry power over long distances, the substations that step voltage up or down, and the distribution networks that bring electricity to end-users. Engineers in this field are responsible for the planning, design, operation, and maintenance of these complex systems. They work to ensure that the power grid is stable, reliable, and capable of meeting ever-growing demand. Their responsibilities also extend to protecting the system from faults and disturbances.
The scope of their work is broad, covering areas such as power generation from various sources (fossil fuels, nuclear, hydro, solar, wind), power system analysis to predict system behavior under different conditions, and the implementation of control systems to manage power flow and maintain system stability. They also engage with economic considerations, environmental impacts, and regulatory compliance, making it a multidisciplinary domain within electrical engineering. The field is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the global push towards cleaner energy sources.
For those new to the concepts of electrical grids, imagine a vast network of interconnected roads (transmission and distribution lines) that allow energy (cars) to travel from large production centers (power plants) to various destinations (homes and businesses). Power Systems Engineers are like the city planners, traffic controllers, and maintenance crews for this energy highway, ensuring everything runs smoothly, safely, and efficiently. They decide where new "roads" are needed, how to manage "traffic flow," and how to fix any "roadblocks" or "accidents" (faults or outages).
These foundational courses can help you understand the basics of electric power systems and circuits, which are crucial for anyone considering this career path. They offer a glimpse into the technical underpinnings of the work power systems engineers do.
From Pearl Street to Smart Grids: A Historical Perspective
The journey of electrical power systems began in the late 19th century. Thomas Edison's Pearl Street Station, launched in 1882 in New York City, marked one of the first central power plants, initially serving a small number of customers with direct current (DC). However, the "War of Currents" between Edison's DC systems and Nikola Tesla's alternating current (AC) systems, championed by George Westinghouse, soon followed. AC eventually triumphed for large-scale power transmission due to its ability to be easily transformed to high voltages, reducing transmission losses over long distances.
The 20th century saw a massive expansion of electrical grids, characterized by large, centralized power plants and extensive transmission and distribution networks. This era focused on improving reliability, increasing capacity, and interconnecting regional grids to form national and even international power networks. Technologies like synchronous generators, transformers, and circuit breakers became the backbone of these systems. The development of sophisticated control centers allowed for better management and monitoring of these sprawling infrastructures.
Today, we are in an era of significant transformation, moving towards "smart grids." Modern power systems are increasingly incorporating digital technologies, automation, and advanced communication systems. This evolution is driven by the need to integrate intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind, improve grid efficiency and resilience, and empower consumers with more control over their energy usage. The historical progression from simple, isolated systems to complex, intelligent networks highlights the continuous innovation inherent in power systems engineering.
These books provide deeper insights into the fundamental principles and historical development of power systems.
Powering the Future: Renewables and Intelligent Networks
The transition to renewable energy sources is one of the most significant drivers of change in modern power systems engineering. Integrating intermittent sources like solar and wind power presents unique challenges. Unlike traditional power plants that offer controllable output, the electricity generated from these renewables fluctuates with weather conditions. Power Systems Engineers are at the forefront of developing solutions to manage this variability, including energy storage systems, advanced forecasting techniques, and flexible grid operations.
Smart grid technology is pivotal in this transition. Smart grids utilize sensors, communication networks, and data analytics to monitor and manage electricity flow in real-time. This allows for better integration of distributed energy resources (DERs), such as rooftop solar panels and electric vehicles, enhances grid stability, and helps reduce energy losses. Engineers in this domain work on developing and implementing these intelligent systems, from smart meters in homes to sophisticated control algorithms for the entire grid.
The ultimate goal is to create a more sustainable, resilient, and efficient power system. This involves not only technological innovation but also addressing policy, regulatory, and economic factors. Power Systems Engineers play a crucial role in advising policymakers, developing new industry standards, and designing markets that support the evolving energy landscape. Their work is essential for achieving global climate goals and ensuring a secure energy future. If you're inspired by the potential of green energy, exploring sustainability courses could be a great starting point.
Online courses are excellent resources for understanding the shift towards renewable energy and the intricacies of modern electricity grids.
Key Responsibilities of a Power Systems Engineer
Understanding the day-to-day work and core responsibilities of a Power Systems Engineer provides a clearer picture of this career. This section details the critical tasks these professionals undertake, from the initial design of electrical grids to ensuring they operate safely and efficiently, especially with the increasing integration of new energy technologies.
Grid Architecture: Designing and Optimizing Electrical Networks
Power Systems Engineers are responsible for the intricate design of electrical grids. This involves planning the layout of transmission and distribution lines, determining the capacity and location of substations, and selecting appropriate equipment like transformers, circuit breakers, and protective relays. The goal is to create a system that can reliably and efficiently deliver power from generation sources to consumers. This design process requires careful consideration of factors such as load growth, geographical constraints, and economic viability.
Optimization is a continuous process in power systems. Engineers use sophisticated modeling and simulation tools to analyze existing grids and identify areas for improvement. This might involve reconfiguring networks to reduce power losses, upgrading equipment to handle increased demand, or implementing new technologies to enhance grid performance. The objective is always to maintain a balance between cost, reliability, and efficiency. They also consider the long-term evolution of the grid, anticipating future needs and technological advancements.
A key aspect of grid design is ensuring redundancy and resilience. Power systems must be able to withstand various contingencies, such as equipment failures or extreme weather events, without causing widespread outages. Engineers design systems with backup pathways and protection schemes that can isolate faults and quickly restore power. This often involves complex calculations and adherence to stringent industry standards. Learning more about engineering principles can provide a solid foundation for these concepts.
Courses focusing on power system analysis and design are invaluable for aspiring engineers to grasp these core responsibilities.
Ensuring Stability: Load Flow, Fault Analysis, and System Protection
A critical responsibility of Power Systems Engineers is to ensure the stability of the electrical grid. This involves conducting various types of analyses, including load flow studies, fault analysis, and stability assessments. Load flow studies determine how power flows through the network under normal operating conditions, helping to identify potential overloads or voltage issues. These studies are essential for planning grid expansions and ensuring efficient operation.
Fault analysis is equally important. Engineers simulate different types of faults (e.g., short circuits caused by lightning strikes or equipment failure) to understand their impact on the system. This analysis helps in designing effective protection systems that can quickly detect and isolate faults, minimizing disruption to consumers and preventing damage to equipment. The coordination of protective devices like relays and circuit breakers is a complex task that requires precise calculations and understanding of system dynamics.
System stability refers to the ability of the power system to remain in a state of equilibrium following a disturbance. Power Systems Engineers analyze transient stability (short-term response to large disturbances like a generator trip) and dynamic stability (response to smaller, continuous disturbances). Ensuring stability is crucial for preventing blackouts and maintaining power quality. This often involves the use of specialized software and advanced control techniques. Concepts from control systems engineering are heavily applied here.
The following resources delve into the techniques for analyzing and protecting power systems.
Integrating Green Energy: Incorporating Solar, Wind, and Other Renewables
One of the most dynamic areas of power systems engineering today is the integration of renewable energy sources. As the world shifts towards cleaner energy, Power Systems Engineers are tasked with incorporating large amounts of solar, wind, and other renewable generation into the existing grid. This presents unique challenges because these sources are often intermittent and geographically dispersed.
Engineers must design grid infrastructure that can accommodate the variability of renewable generation. This includes developing advanced forecasting tools to predict wind and solar output, implementing energy storage solutions (like batteries) to smooth out fluctuations, and designing more flexible grid control systems. They also work on interconnection standards to ensure that renewable energy facilities can safely and reliably connect to the grid.
Moreover, the rise of distributed energy resources (DERs), such as rooftop solar panels and small-scale wind turbines, requires a shift from a centralized to a more decentralized grid architecture. Power Systems Engineers are developing microgrids and other solutions that can manage these local energy resources effectively. This involves addressing technical challenges related to power flow, voltage control, and protection in networks with two-way power flows. The environmental sciences play a role in understanding the impact and potential of these sources.
These courses offer insights into how renewable energy is being integrated into power grids and the technologies involved.
Upholding Standards: Ensuring Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Safety is paramount in power systems engineering. Working with high voltages and complex electrical equipment inherently involves risks. Therefore, Power Systems Engineers must rigorously adhere to safety standards and protocols in all aspects of their work, from design and construction to operation and maintenance. This includes ensuring the safety of personnel working on the grid and the public. They develop and implement safety procedures, conduct risk assessments, and ensure that equipment is properly grounded and protected.
Regulatory compliance is another crucial aspect of the job. The power industry is heavily regulated by governmental and independent bodies that set standards for reliability, safety, and environmental impact. Power Systems Engineers must be knowledgeable about these regulations, such as those set by NERC (North American Electric Reliability Corporation) in North America or equivalent bodies elsewhere. They ensure that their designs and operations meet these requirements and prepare documentation for regulatory audits.
This involves staying updated with evolving standards and regulations, which can change in response to technological advancements, environmental concerns, or significant grid events. Engineers often participate in industry committees and working groups that develop these standards. Ensuring that all projects and operations comply with these often complex legal and technical frameworks is a significant responsibility that protects both the grid and the community it serves. Understanding legal frameworks can be supported by exploring resources in legal studies.
While specific safety and compliance courses vary by region and company, a strong foundation in electrical safety principles is essential.
Formal Education Pathways
Embarking on a career as a Power Systems Engineer typically begins with a strong educational foundation in engineering. This section outlines the common academic routes, from undergraduate studies to advanced research, and highlights the importance of accreditation in ensuring educational quality and professional recognition.
Building the Base: Undergraduate Degrees
A bachelor's degree in Electrical Engineering is the most common entry point into the field of power systems engineering. During their undergraduate studies, students build a strong foundation in mathematics, physics, and fundamental engineering principles. Core electrical engineering coursework typically includes circuit theory, electronics, electromagnetics, control systems, and an introduction to power systems. These subjects provide the essential knowledge base upon which specialized power engineering skills are built.
Many electrical engineering programs offer specialization tracks or elective courses in power systems during the later years of study. These courses delve deeper into topics like power generation, transmission and distribution, power system analysis, and protective relaying. Laboratory work and design projects are integral components, allowing students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical problems and gain hands-on experience with industry-relevant tools and techniques.
Some universities may also offer degrees in related fields, such as Energy Engineering or Electrical and Computer Engineering with a power focus, that can lead to a career in power systems. Regardless of the specific degree title, a curriculum rich in electrical power principles is key. For those exploring their options, OpenCourser offers a wide array of Electrical Engineering courses to supplement formal education or to get a taste of the subject matter.
These introductory courses provide a solid understanding of electric circuits and fundamental electrical engineering concepts, which are prerequisites for more specialized power systems studies.
This book offers a comprehensive introduction to electric circuits.
Advanced Learning: Graduate Specializations
For those seeking deeper expertise or wishing to pursue research or specialized roles, a graduate degree (Master's or Ph.D.) in Electrical Engineering with a focus on power systems is highly beneficial. Master's programs typically offer advanced coursework in areas like power system dynamics and stability, renewable energy integration, smart grid technologies, power electronics, and high-voltage engineering. These programs often include a research project or thesis, allowing students to specialize in a particular area of interest.
A Master of Science (M.S.) or Master of Engineering (M.Eng.) can open doors to more advanced technical roles, research and development positions, and leadership opportunities. Many employers value the specialized knowledge and analytical skills gained through graduate study, particularly in a rapidly evolving field like power systems. Some professionals pursue a master's degree part-time while working in the industry to enhance their qualifications and career prospects.
These programs often involve extensive use of simulation software and advanced analytical techniques, preparing graduates for complex problem-solving in the industry. The curriculum is usually designed to reflect current industry challenges and research frontiers, ensuring that graduates are equipped with up-to-date knowledge. Browsing energy-related courses can also complement specialized graduate studies.
Advanced courses in power electronics and control are fundamental for graduate-level specialization in power systems.
Pushing Boundaries: Doctoral Research Areas
A Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in power systems engineering is geared towards individuals interested in careers in academia, cutting-edge research and development, or high-level consulting. Doctoral research involves making original contributions to the field by investigating complex problems and developing innovative solutions. Current research areas are often driven by the challenges of modernizing the grid and transitioning to sustainable energy.
Prominent doctoral research areas include grid resilience against cyber-attacks and extreme weather, advanced control strategies for smart grids, integration of large-scale renewable energy and energy storage, High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission technologies, power system economics and electricity markets, and the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning to power system operation and planning. These research efforts aim to create more efficient, reliable, secure, and environmentally friendly power systems.
Ph.D. candidates work closely with faculty advisors, publish their findings in scholarly journals, and present at academic conferences. This rigorous training develops deep technical expertise, critical thinking, and research skills. Graduates with a Ph.D. are well-positioned to lead innovation in the power industry or contribute to the academic community by educating the next generation of engineers. Many find roles in national laboratories, research institutions, or specialized R&D departments within large corporations.
Exploring advanced topics and research methodologies can be supported by specialized texts.
The Stamp of Quality: Accreditation (e.g., ABET)
Accreditation is a critical factor to consider when choosing an engineering program. In the United States, ABET (Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology) is the primary organization that accredits college and university programs in applied and natural science, computing, engineering, and engineering technology. Graduating from an ABET-accredited program is often a prerequisite for professional licensure as an engineer (P.E.) and is generally preferred by employers.
ABET accreditation signifies that a program has met certain quality standards in terms of curriculum, faculty, facilities, and student support. It ensures that graduates have attained the knowledge, skills, and professional competencies expected in the engineering profession. When researching undergraduate or graduate programs, it is advisable to check their accreditation status. Many other countries have similar accrediting bodies that ensure the quality of engineering education.
While not always a strict requirement for all entry-level positions, particularly in certain industries or roles, an accredited degree significantly enhances job prospects and credibility. It provides a recognized benchmark of educational quality, which is valuable for career progression, especially if one plans to work in roles requiring professional certification or in sectors with stringent qualification criteria. You can often find accreditation information on the university's engineering department website or directly through ABET's public search tools.
Career Progression for Power Systems Engineers
A career in power systems engineering offers diverse pathways for growth and development. From initial entry-level positions to senior leadership roles, professionals can shape their careers based on their interests and expertise. This section explores typical career trajectories, specialization options, and potential transitions to related fields.
Starting the Journey: Entry-Level Roles
Graduates typically begin their careers in entry-level positions such as Junior Power Systems Engineer, Grid Analyst, Distribution Engineer, or Substation Engineer. In these roles, new engineers apply their academic knowledge to real-world projects under the guidance of experienced professionals. Initial responsibilities often involve assisting with design calculations, conducting power system studies using simulation software, preparing technical drawings, and supporting field operations or maintenance activities.
These early years are crucial for developing practical skills, understanding industry practices, and gaining exposure to different facets of power systems. Entry-level engineers might work on tasks like load forecasting, equipment specification, protective relay setting calculations, or assisting with the commissioning of new grid infrastructure. They learn to use industry-standard software tools and become familiar with relevant codes and safety regulations. Building a strong technical foundation and effective communication skills is key during this period.
Many companies offer graduate development programs or structured training for new hires, which can accelerate learning and provide a broad overview of the organization's operations. This phase is not just about technical development but also about understanding the business aspects of the power industry and building a professional network. Ambitious individuals can find many learning resources on OpenCourser to further hone their skills.
Foundational knowledge in substation engineering and general power distribution is valuable for those starting out.
Advancing Expertise: Specialization versus Management
As Power Systems Engineers gain experience, they typically face a choice between deepening their technical specialization or moving into management roles. Those who opt for a technical track may become subject matter experts in areas like power system protection, grid stability, renewable energy integration, power electronics, or smart grid technologies. They might take on roles such as Senior Protection Engineer, Lead Stability Analyst, or Principal Renewable Integration Specialist.
Technical specialists are highly valued for their in-depth knowledge and problem-solving abilities. They often lead complex projects, mentor junior engineers, and contribute to the development of new technologies and industry standards. This path often involves continuous learning to stay abreast of the latest advancements in their chosen area of expertise. Some may pursue advanced certifications or contribute to research and publications.
Alternatively, engineers with strong leadership and interpersonal skills may transition into management positions. This could involve roles like Engineering Manager, Project Manager, or Operations Supervisor. In these capacities, they oversee teams of engineers, manage project budgets and schedules, liaise with clients or stakeholders, and contribute to strategic planning. While technical knowledge remains important, management roles emphasize skills in communication, decision-making, and resource allocation. Some individuals may pursue an MBA or other management qualifications to support this transition. Exploring management courses can be beneficial for this path.
Reaching New Heights: Senior and Lead Engineer Roles
Senior and Lead Power Systems Engineers hold significant responsibility for the design, operation, and strategic direction of power systems. These roles require extensive experience, deep technical expertise, and often, a Professional Engineer (P.E.) license. They lead complex engineering projects, make critical technical decisions, and provide expert guidance to teams and management. Their work has a direct impact on grid reliability, efficiency, and safety.
Responsibilities at this level can include overseeing the planning and design of major grid expansions or upgrades, developing innovative solutions to complex technical challenges, and ensuring compliance with all relevant standards and regulations. Lead engineers often serve as technical authorities within their organizations, reviewing and approving designs, and mentoring less experienced engineers. They may also represent their company in industry forums or contribute to the development of national or international standards.
Strong analytical, problem-solving, and project management skills are essential for success in these senior roles. The ability to communicate complex technical information clearly to diverse audiences, including non-technical stakeholders, is also crucial. Many senior engineers have a proven track record of successfully delivering large-scale projects and a deep understanding of the economic and regulatory landscape of the power industry.
Advanced books on power system operation and control are essential for those in senior roles.
Branching Out: Transitions to Adjacent Fields
The skills and knowledge gained as a Power Systems Engineer can open doors to opportunities in various adjacent fields. One common transition is into energy policy and regulation. Engineers with a strong understanding of power systems are well-equipped to advise government agencies, regulatory bodies, or think tanks on policies related to energy infrastructure, market design, and the integration of new technologies. This path often requires strong analytical and communication skills, as well as an interest in public policy.
Another area is energy consulting, where engineers provide expert advice to utilities, industrial clients, or investors on power system projects, market strategies, or technology adoption. This can involve a wide range of activities, from feasibility studies for new power plants to developing strategies for grid modernization. Consulting roles often require a blend of technical expertise, business acumen, and client management skills.
Furthermore, with the rise of renewable energy and smart grid technologies, new career opportunities are emerging in areas like electric vehicle infrastructure development, energy storage solutions, and data analytics for the energy sector. Some engineers may also transition into academic roles, teaching and conducting research at universities. The versatility of a power systems engineering background provides a solid foundation for a dynamic and evolving career. Consider exploring roles like a
or other specialized positions.Technical Skills and Tools
Proficiency in a range of technical skills and specialized software tools is essential for Power Systems Engineers. This section highlights the key software platforms, modeling techniques, and industry standards that professionals in this field must master to effectively design, analyze, and manage modern electrical grids.
Software Proficiency: PSS/E, ETAP, MATLAB/Simulink
Power Systems Engineers rely heavily on specialized software for various analyses and simulations. PSS/E (Power System Simulator for Engineering) is a widely used tool for transmission system planning and operations, allowing engineers to conduct load flow, short circuit, and dynamic stability studies. Familiarity with PSS/E is often a requirement for roles involving high-voltage transmission networks.
ETAP (Electrical Transient Analyzer Program) is another comprehensive software suite used for the analysis, simulation, monitoring, control, and automation of electrical power systems. It is commonly used in industrial power systems, distribution networks, and generation facilities for studies such as arc flash analysis, protective device coordination, and harmonic analysis. Proficiency in ETAP is highly valued across many sectors.
MATLAB/Simulink is a versatile platform used for a wide range of engineering applications, including power systems modeling, control system design, and data analysis. Engineers use MATLAB for scripting and algorithm development, while Simulink provides a graphical environment for modeling and simulating dynamic systems, including power electronic converters and renewable energy systems. These tools are indispensable for research, development, and complex system analysis.
Many online courses offer training in these critical software packages, enabling engineers to develop practical skills.
Modeling Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
The increasing penetration of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs), such as rooftop solar PV, battery storage, and electric vehicles, presents new modeling challenges for Power Systems Engineers. Unlike traditional centralized generators, DERs are numerous, often inverter-based, and located closer to the load on distribution networks. Accurately modeling their behavior and impact on the grid is crucial for system planning and operation.
Engineers use specialized tools and techniques to model the aggregate behavior of DERs and their interaction with the distribution system. This includes developing models for power electronic converters that interface DERs with the grid, as well as understanding their control characteristics and response to grid disturbances. These models are used to assess impacts on voltage profiles, power quality, protection system coordination, and overall grid stability.
The dynamic and often unpredictable nature of some DERs (like solar PV, which depends on weather) requires probabilistic and stochastic modeling approaches. Engineers must also consider the role of DER management systems and aggregators in coordinating the operation of multiple DERs. As DER adoption continues to grow, the ability to effectively model these resources will become an increasingly important skill for power systems professionals.
Courses focusing on renewable energy integration and smart grids often cover aspects of DER modeling.
Grid Automation: SCADA Systems and Modern Control
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are fundamental to the operation of modern power grids. These systems allow operators to monitor and control grid equipment remotely from a central control room. Power Systems Engineers are involved in the design, implementation, and maintenance of SCADA systems, ensuring they provide accurate real-time data and reliable control capabilities. SCADA data is essential for situational awareness, fault detection, and efficient grid management.
Grid automation extends beyond SCADA to include a range of technologies that enable more intelligent and responsive grid operations. This includes distribution automation (DA) systems, which use sensors and automated switches to detect and isolate faults, reroute power, and optimize voltage levels on distribution networks. Substation automation (SA) involves using intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) and communication networks to automate control and protection functions within substations.
Modern control strategies, often leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning, are being developed to manage the increasing complexity of the grid, especially with the integration of renewables and DERs. These include wide-area monitoring, protection, and control (WAMPAC) systems that use synchronized phasor measurements (PMUs) to provide a comprehensive view of grid dynamics. Engineers working in grid automation and control are at the cutting edge of power system technology.
Understanding automation and control theory is key for engineers working with SCADA and modern grid technologies.
Adherence to Standards: IEEE, IEC, NERC
Compliance with industry standards is non-negotiable in power systems engineering. These standards ensure the safety, reliability, and interoperability of electrical equipment and systems. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) develops a wide range of standards covering various aspects of power engineering, from equipment design and testing to grid operation and protection. Power Systems Engineers frequently refer to IEEE standards in their work.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is another major international standards organization that publishes standards for electrical, electronic, and related technologies. IEC standards are widely adopted globally and are crucial for ensuring compatibility and safety in international projects and equipment manufacturing. Familiarity with relevant IEC standards is important, especially for engineers working in a global context or with internationally sourced equipment.
In North America, the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) develops and enforces mandatory reliability standards for the bulk power system. These standards cover areas such as system operating limits, critical infrastructure protection (including cybersecurity), and emergency preparedness. Power Systems Engineers working for utilities and other entities subject to NERC oversight must ensure their operations and planning activities comply with these rigorous requirements. Adherence to these and other relevant national or regional standards is a fundamental aspect of professional practice.
Industry Applications and Employers
Power Systems Engineers find employment across a diverse range of industries and organizations. Their expertise is critical wherever electrical power is generated, transmitted, distributed, or heavily utilized. This section explores the primary sectors that employ these engineers and highlights emerging areas with growing demand.
Core Employers: Utilities, Consultancies, and OEMs
Electric utilities are traditional and major employers of Power Systems Engineers. These companies are responsible for generating, transmitting, and distributing electricity to residential, commercial, and industrial customers. Engineers at utilities work on planning grid expansions, operating and maintaining existing infrastructure, ensuring reliability, and integrating new technologies. Roles can range from system planning and design to operations, protection, and asset management.
Engineering consulting firms also hire a significant number of Power Systems Engineers. Consultants provide specialized expertise to utilities, industrial clients, developers, and government agencies on a project basis. Their work can involve feasibility studies, detailed design, technical due diligence, regulatory support, and specialized analyses like power quality assessments or grid interconnection studies. Consulting offers exposure to a wide variety of projects and clients.
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) that produce power system equipment—such as transformers, switchgear, protective relays, generators, and control systems—employ Power Systems Engineers in design, research and development, application engineering, and technical sales. These engineers work on developing new products, customizing solutions for specific applications, and providing technical support to customers. Working for an OEM provides deep insight into specific technologies.
Fundamental courses in power engineering are beneficial regardless of the specific sector.
Public Service: Government and Regulatory Roles
Government agencies and regulatory bodies at national, regional, and local levels employ Power Systems Engineers to oversee the energy sector, develop policies, and enforce regulations. For instance, organizations like the U.S. Department of Energy or national energy ministries work on long-term energy strategy, research funding, and critical infrastructure protection. Engineers in these roles might contribute to developing energy efficiency standards or assessing the impact of new energy technologies.
Regulatory commissions, such as state Public Utility Commissions (PUCs) in the U.S. or national energy regulators in other countries, are responsible for setting electricity rates, ensuring utility compliance with service standards, and overseeing market operations. Power Systems Engineers in these bodies provide technical expertise to inform regulatory decisions, review utility investment plans, and investigate grid incidents. These roles require a strong understanding of both technical and economic aspects of the power industry.
Engineers in government and regulatory roles play a critical part in shaping the future of the energy landscape, balancing the needs of consumers, utilities, and the environment. Their work ensures that the power system operates safely, reliably, and in the public interest. This path often appeals to those with an interest in public policy and a desire to contribute to societal well-being through their engineering expertise.
New Frontiers: Microgrids, EV Charging, and Beyond
The evolving energy landscape is creating exciting opportunities in emerging sectors. Microgrid development is one such area. Microgrids are localized power grids that can operate autonomously or connect to the larger utility grid. Power Systems Engineers are involved in designing, implementing, and operating microgrids for communities, industrial facilities, or critical infrastructure, often integrating renewable energy and storage. This field is growing as interest in resilience and distributed generation increases.
The rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) is driving demand for engineers to design and implement EV charging infrastructure. This involves planning the location and capacity of charging stations, ensuring their safe and efficient integration into the distribution grid, and developing smart charging solutions that can manage the impact of EV charging on local power networks. This sector combines power systems knowledge with an understanding of transportation electrification.
Other emerging areas include utility-scale energy storage, data analytics for smart grids, cybersecurity for power systems, and the development of hydrogen energy infrastructure. These fields often require a blend of traditional power engineering skills with expertise in newer technologies like data science, artificial intelligence, or advanced materials. For those interested in innovation, these sectors offer dynamic and impactful career paths. Learners can explore these new frontiers via resources found on OpenCourser's browse page, searching for specific topics like "microgrids" or "EV charging."
Courses related to renewable energy and smart grid technologies are particularly relevant for these emerging sectors.
Global Opportunities: Market Variations and International Work
The demand for Power Systems Engineers is global, though the specific needs and opportunities can vary significantly by region. Developed countries often focus on modernizing aging infrastructure, integrating renewable energy, enhancing grid resilience, and implementing smart grid technologies. There's a strong emphasis on efficiency, reliability, and environmental sustainability. Engineers in these regions may work on complex grid upgrades or innovative R&D projects.
In developing countries, the focus may be more on expanding access to electricity, building new generation and transmission infrastructure, and improving the reliability of existing systems. There are often significant opportunities for engineers to contribute to basic electrification efforts and the development of robust power systems from the ground up. International development banks and multinational corporations often fund and execute large-scale power projects in these regions.
Working internationally can offer unique experiences and challenges, including adapting to different technical standards, regulatory environments, and cultural contexts. Some Power Systems Engineers pursue international assignments with multinational corporations, consulting firms, or non-governmental organizations. A willingness to learn and adapt, along with strong technical skills, can open doors to a truly global career. Language skills and cross-cultural communication abilities are also valuable assets for international work. You can explore language courses to prepare for such opportunities.
Challenges in Modern Power Systems Engineering
The field of power systems engineering is dynamic and faces numerous contemporary challenges. These hurdles drive innovation and require engineers to continuously adapt and develop new solutions. This section explores some of the most pressing issues confronting the industry today, from integrating fluctuating renewables to safeguarding against cyber threats.
The Renewable Puzzle: Managing Intermittency
One of the foremost challenges is integrating large volumes of intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the grid. Unlike conventional power plants, the output from these sources is variable and depends on weather conditions, making it harder to predict and balance supply with demand. This intermittency can affect grid stability, requiring new operational strategies and technologies.
Power Systems Engineers are working on several fronts to address this. Advanced forecasting methods are being developed to better predict renewable generation. Energy storage systems, particularly batteries, are being deployed to store excess renewable energy when it's abundant and release it when generation is low. Furthermore, demand-side management programs encourage consumers to shift their electricity use to times when renewable energy is plentiful. Grid operators also need more flexible conventional generation that can quickly ramp up or down to compensate for renewable fluctuations.
The sheer scale of the transition also poses infrastructural challenges. New transmission lines may be needed to connect remote renewable energy zones to load centers. Distribution grids must be upgraded to handle bidirectional power flows from rooftop solar and other distributed resources. Effectively managing these complexities requires sophisticated control systems and innovative market designs. Finding relevant courses on OpenCourser Deals might help in acquiring skills to tackle these issues affordably.
Understanding how to manage the variable nature of renewables is a key skill for modern power systems engineers.
Digital Fortification: Cybersecurity in Smart Grids
As power grids become "smarter" through increased digitalization and connectivity, they also become more vulnerable to cyber threats. A successful cyberattack on the power grid could have devastating consequences, leading to widespread blackouts, equipment damage, or theft of sensitive data. Ensuring the cybersecurity of critical energy infrastructure is a major challenge for Power Systems Engineers and cybersecurity professionals.
Engineers must design and implement robust cybersecurity measures at all levels of the power system, from control centers and substations to smart meters and distributed energy resources. This includes deploying firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption technologies. Developing secure communication protocols and ensuring the integrity of software and firmware updates are also critical. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing help identify and address potential weaknesses.
The challenge is compounded by the fact that power systems often consist of a mix of legacy equipment and modern digital technologies, creating a complex attack surface. Furthermore, the interconnected nature of the grid means that a vulnerability in one part of the system could potentially impact other parts. A multi-layered, defense-in-depth approach to cybersecurity, combined with continuous monitoring and rapid incident response capabilities, is essential. Professionals looking to specialize can explore cybersecurity courses.
Revitalizing the Backbone: Modernizing Aging Infrastructure
Much of the existing power grid infrastructure in developed countries was built decades ago and is approaching the end of its operational life. Aging equipment, such as transformers, circuit breakers, and transmission lines, can be less efficient, more prone to failure, and more costly to maintain. Modernizing this aging infrastructure is a significant undertaking that requires substantial investment and careful planning.
Power Systems Engineers are involved in assessing the condition of existing assets, prioritizing replacement and refurbishment projects, and integrating new, more efficient technologies. This modernization effort is not just about replacing old equipment with new; it's also an opportunity to incorporate smart grid features, enhance resilience to extreme weather, and improve the grid's capacity to accommodate renewable energy and electric vehicles.
The scale of this challenge is enormous, involving thousands of miles of lines and countless pieces of equipment. Engineers must balance the need for modernization with affordability for consumers and minimize disruptions during upgrade projects. Strategic asset management, predictive maintenance techniques based on sensor data and analytics, and innovative financing models are all part of addressing this critical issue. This often involves detailed power system planning.
Navigating the Maze: Regulatory and Policy Uncertainties
The power industry operates within a complex web of regulations and policies that can significantly impact investment decisions, technology adoption, and market structures. Regulatory and policy uncertainties can create challenges for Power Systems Engineers and the companies they work for. Changes in government administrations, shifts in energy policy priorities, or delays in regulatory approvals can affect project timelines and economic viability.
For example, policies related to carbon pricing, renewable energy mandates, or incentives for energy storage can drive or hinder the adoption of certain technologies. The processes for siting and permitting new transmission lines or power plants can be lengthy and subject to legal challenges. Evolving market rules for wholesale electricity can also impact the business case for new generation or grid modernization projects.
Power Systems Engineers often need to stay informed about these regulatory and policy developments and understand their implications for their work. They may be involved in providing technical input to policymakers, participating in regulatory proceedings, or developing strategies to navigate these uncertainties. A stable and predictable policy environment is generally conducive to long-term investment and innovation in the power sector.
Ethical and Safety Considerations
Power Systems Engineers bear significant ethical and safety responsibilities due to the critical nature of their work. Their decisions directly impact public safety, environmental well-being, and economic stability. This section delves into the key ethical dilemmas and safety imperatives that define the profession.
Balancing Act: Grid Reliability vs. Affordability
A primary ethical challenge for Power Systems Engineers is balancing the need for a highly reliable power supply with the imperative of keeping electricity affordable for all consumers. Investing in measures to enhance grid reliability, such as undergrounding lines, adding redundancy, or deploying advanced technologies, often comes with significant costs that can translate to higher electricity rates. Engineers must make informed decisions about the appropriate level of reliability, considering both technical feasibility and socio-economic impacts.
This balancing act involves careful risk assessment and cost-benefit analysis. For instance, what is an acceptable frequency and duration of power outages, and how much should society invest to reduce these further? Different communities may have different priorities and willingness to pay for enhanced reliability. Engineers have a responsibility to provide clear, objective information to policymakers and the public about these trade-offs.
Furthermore, decisions about grid investments can have distributional consequences. For example, infrastructure upgrades in one area might be funded by ratepayers across a wider region. Ensuring that these decisions are made equitably and transparently is an important ethical consideration. The push for universal access to reliable and affordable electricity remains a global challenge where engineering ethics play a crucial role.
Powering Justice: Environmental and Social Equity in Energy Transitions
The transition to cleaner energy sources, while environmentally beneficial overall, can also raise issues of environmental and social justice. Power Systems Engineers have a role in ensuring that this transition is equitable and does not disproportionately burden vulnerable communities. For example, the siting of new energy infrastructure, whether it's a large solar farm or a transmission line, can have local environmental and social impacts.
Engineers must consider these impacts in their planning and design processes, engaging with affected communities and seeking to minimize negative consequences. This includes concerns about land use, visual impact, noise, and potential effects on local ecosystems. Environmental justice also involves ensuring that the benefits of clean energy, such as cleaner air and lower energy costs, are shared equitably and that disadvantaged communities are not left behind in the energy transition.
Moreover, the sourcing of materials for renewable energy technologies (like rare earth minerals for wind turbines and batteries) can have environmental and social implications in the regions where these materials are extracted. While engineers may not directly control these supply chains, an awareness of these broader issues is part of a responsible engineering practice. Striving for sustainable and ethically sourced solutions is an emerging dimension of their work.
Prioritizing Safety: Workplace Protocols (e.g., Arc Flash Protection)
Workplace safety is a paramount concern in power systems engineering, given the inherent dangers of working with high-voltage electricity. Engineers are responsible for designing systems and developing procedures that protect themselves, technicians, and the public from electrical hazards. This includes implementing robust safety protocols, providing adequate training, and ensuring that all work is conducted in compliance with safety regulations.
One critical safety concern is arc flash, a dangerous condition caused by an electrical fault that results in a high-temperature explosion of plasma. Power Systems Engineers conduct arc flash hazard analyses to determine the incident energy levels at various points in an electrical system and specify appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for workers. They also design systems to minimize arc flash risks, such as using current-limiting devices or remote racking circuit breakers.
Beyond arc flash, engineers address a range of other safety issues, including electrical shock, falls from height (when working on transmission towers or poles), and hazards associated with rotating machinery or confined spaces. A strong safety culture, continuous training, and adherence to established procedures like lockout/tagout are essential for preventing accidents and ensuring a safe working environment. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics provides general occupational safety information, though specific power system safety is highly specialized.
Smart Data, Secure Lives: Privacy in Metering and Grid Data
The proliferation of smart meters and other grid sensors generates vast amounts of data about consumers' electricity usage patterns. While this data is valuable for improving grid efficiency, optimizing operations, and enabling new services, it also raises significant privacy concerns. Detailed energy consumption data can reveal information about occupants' lifestyles, when they are home or away, and even the types of appliances they use.
Power Systems Engineers, particularly those involved in designing smart grid systems and data management platforms, have an ethical responsibility to ensure that consumer data is collected, stored, and used in a way that protects privacy. This involves implementing strong data security measures, anonymizing data where possible, and adhering to data privacy regulations. Clear policies regarding data access, usage, and sharing are also crucial.
Transparency with consumers about what data is being collected and how it is being used is important for building trust. Engineers should design systems with privacy-enhancing technologies and provide consumers with control over their data where feasible. Balancing the benefits of data-driven grid optimization with the fundamental right to privacy is a key ethical challenge in the era of smart grids.
Future Trends Impacting Power Systems Engineers
The field of power systems engineering is on the cusp of transformative changes, driven by technological advancements and global imperatives. Understanding these future trends is crucial for engineers to adapt, innovate, and shape the energy systems of tomorrow. This section explores key developments that will significantly impact the profession.
Intelligent Grids: AI/ML in Predictive Maintenance and Operations
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize power system operations and maintenance. Engineers are increasingly using AI/ML algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data from sensors across the grid to predict equipment failures, optimize power flow, and improve energy forecasting. Predictive maintenance, for example, uses ML to identify early signs of equipment degradation, allowing for proactive repairs and reducing unexpected outages.
In grid operations, AI can help manage the complexity introduced by distributed energy resources and fluctuating renewables. Machine learning models can optimize the dispatch of generation and storage, control voltage levels, and even assist in rapid fault detection and restoration. These technologies can enhance grid reliability, efficiency, and resilience, leading to more autonomous and self-healing power systems. For those interested, exploring Artificial Intelligence courses can provide valuable skills.
However, the adoption of AI/ML also presents challenges, including data quality and availability, model interpretability, and cybersecurity concerns related to AI systems. Power Systems Engineers will need to develop new skills in data science and AI to effectively leverage these technologies, alongside their core electrical engineering expertise. The integration of AI promises a more intelligent and adaptive energy future.
The Hydrogen Horizon: Integration Challenges and Opportunities
The emerging "hydrogen economy" presents both significant opportunities and complex challenges for Power Systems Engineers. Green hydrogen, produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy, is seen as a potential clean fuel for hard-to-decarbonize sectors like heavy industry and transportation, and as a medium for long-term energy storage. Integrating large-scale hydrogen production into the power system will require careful planning and new infrastructure.
Power Systems Engineers will be involved in designing the electrical systems for electrolysis plants, ensuring they can operate flexibly with variable renewable energy supplies. They will also need to consider the impact of large electrolyzer loads on grid stability and power quality. Furthermore, if hydrogen is used to generate electricity (e.g., in fuel cells or hydrogen turbines), engineers will work on integrating these new generation sources into the grid.
The infrastructure for transporting and storing hydrogen also intersects with the power sector, particularly if existing natural gas pipelines are repurposed or if hydrogen is used to produce synthetic fuels. This trend could significantly reshape energy systems, requiring engineers to develop expertise in new areas at the interface of electricity and chemical energy carriers. Exploring chemical engineering principles might become relevant for some specializations.
Racing the Clock: Global Decarbonization Timelines
Ambitious global decarbonization timelines, driven by the urgent need to address climate change, are putting immense pressure on the power sector to transform rapidly. Many countries and regions have set targets for achieving net-zero emissions, often with significant milestones for the power sector by 2030 or 2040. Meeting these aggressive timelines requires an unprecedented pace of innovation, investment, and deployment of clean energy technologies.
Power Systems Engineers are central to this race against time. They must rapidly design and implement solutions for integrating massive amounts of renewable energy, electrifying transportation and heating, and modernizing the grid to support a decarbonized energy system. This involves overcoming technical hurdles, navigating regulatory processes, and managing large-scale infrastructure projects under tight deadlines. According to a report by the McKinsey & Company, the pace of decarbonization varies by sector but requires substantial acceleration.
The scale and speed of this transition demand new approaches to project management, workforce development, and supply chain management. Engineers will need to be adaptable, innovative, and collaborative to meet these challenges. The societal imperative to decarbonize provides a strong sense of purpose for many professionals in the field, who see their work as directly contributing to a more sustainable future.
Passing the Torch: Workforce Aging and Succession Planning
Like many engineering disciplines, the power systems engineering workforce is facing challenges related to an aging demographic. A significant number of experienced engineers are approaching retirement age, potentially leading to a loss of valuable knowledge and expertise. Effective workforce development and succession planning are crucial to ensure that the industry has the skilled professionals needed to manage and evolve the power grid.
Attracting new talent to the field is a priority. This involves promoting power systems engineering as an exciting and impactful career choice for students and young professionals. Universities and industry organizations are working to update curricula, offer scholarships, and provide mentorship opportunities to encourage a new generation of engineers. There's a particular need to attract individuals with skills in areas like data science, cybersecurity, and power electronics.
Knowledge transfer from experienced engineers to their younger colleagues is also vital. Companies are implementing mentorship programs, creating knowledge repositories, and using other strategies to capture and share institutional memory. Continuous learning and upskilling are essential for all engineers in this rapidly changing field. The OpenCourser Learner's Guide offers resources that can help professionals at all career stages plan their learning paths and stay current.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common queries that individuals exploring a career as a Power Systems Engineer often have. From salary expectations to entry requirements and future prospects, these answers aim to provide practical insights to help you make informed decisions.
What are typical salary ranges for Power Systems Engineers?
Salary ranges for Power Systems Engineers can vary significantly based on factors such as experience level, geographic location, industry sector (e.g., utility, consulting, manufacturing), company size, and educational qualifications. Entry-level positions typically offer competitive salaries, which can increase substantially with experience, specialization, and assumption of greater responsibilities. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, electrical engineers, a category that includes many power systems engineers, earned a median annual wage of $104,610 in May 2023. Engineers in management roles or those with highly specialized expertise often command higher salaries. It's advisable to research salary data specific to your region and desired industry segment.
Is it feasible to enter this field without an Electrical Engineering degree?
While a Bachelor's degree in Electrical Engineering is the most direct and common pathway, it is sometimes possible to enter the field with a degree in a closely related engineering discipline, such as Energy Engineering, Mechanical Engineering (with a strong focus on power or control systems), or Physics. In such cases, individuals would typically need to supplement their education with specific coursework or training in power systems fundamentals, circuit theory, and power electronics. Some employers might also value practical experience or certifications in relevant areas. However, for many roles, particularly those requiring Professional Engineer (P.E.) licensure, an accredited electrical engineering degree is often a firm requirement. If you are considering a pivot, exploring foundational electrical engineering courses on OpenCourser can be a good first step to gauge your interest and build necessary knowledge.
Which industries show the highest demand growth for Power Systems Engineers?
The demand for Power Systems Engineers is generally stable and growing, driven by several factors. Industries focused on renewable energy integration, such as solar and wind power development, are experiencing high growth. Similarly, the expansion of smart grid technologies, including grid automation, data analytics, and cybersecurity for power systems, is creating new opportunities. The electric vehicle (EV) sector, particularly in the development of charging infrastructure and grid integration solutions, also shows strong demand. Furthermore, the ongoing need to modernize aging grid infrastructure and improve resilience ensures continued demand in traditional utility and consulting sectors. The global push for decarbonization underpins much of this growth.
What are essential certifications for career advancement (e.g., PE, PMP)?
For Power Systems Engineers in the United States, the Professional Engineer (P.E.) license is a highly valuable certification, especially for those in roles involving public safety, design approval, or consulting. It signifies a high level of competence and ethical commitment. Requirements for P.E. licensure typically include graduating from an ABET-accredited engineering program, passing the Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) and Principles and Practice of Engineering (PE) exams, and gaining several years of relevant work experience. For those involved in managing projects, the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification can be beneficial, demonstrating expertise in project management principles and practices. Other specialized certifications related to cybersecurity (e.g., CISSP) or specific vendor technologies might be relevant depending on the career path.
How is AI expected to impact the job market for Power Systems Engineers?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is expected to transform many aspects of power systems engineering, but it's more likely to augment rather than replace Power Systems Engineers. AI tools can automate certain tasks, enhance analytical capabilities, and improve decision-making, allowing engineers to focus on more complex problem-solving, design, and strategic planning. For example, AI can assist with predictive maintenance, load forecasting, and optimizing grid operations. This means that engineers who can leverage AI tools and understand data science principles will be increasingly valuable. The job market will likely evolve to demand engineers with a combination of core power systems knowledge and AI/ML skills. Continuous learning will be key to adapting to these changes. The World Economic Forum's Future of Jobs Report highlights the growing importance of AI and big data skills across many industries.
Are remote work possibilities common in grid operations or design roles?
Remote work possibilities for Power Systems Engineers have increased, particularly for design, analysis, and consulting roles that primarily involve computer-based work using simulation software and communication tools. Many tasks, such as power system modeling, conducting studies, and report writing, can often be performed remotely. However, roles directly involved in grid operations (e.g., control center operators), field engineering, equipment testing, and construction supervision typically require a significant on-site presence. Even for design roles, some on-site visits for project meetings, site assessments, or commissioning may be necessary. The prevalence of remote work can also vary by company culture, project requirements, and the nature of the specific job functions.
Embarking on a career as a Power Systems Engineer is a commitment to a field that is both intellectually stimulating and profoundly impactful. It requires a strong educational foundation, a dedication to lifelong learning, and a passion for solving some of the world's most critical energy challenges. As our society increasingly relies on reliable, sustainable, and intelligent electrical power, the role of the Power Systems Engineer will only grow in importance. We hope this overview has provided valuable insights to help you determine if this energizing career path is right for you.