Spreadsheet Software
Navigating the World of Spreadsheet Software
Spreadsheet software is a cornerstone of modern data management, enabling users to organize, analyze, and store data in a tabular format. At its core, this software allows for the manipulation of data within a grid of cells, arranged in rows and columns, typically within multiple "worksheets." Its applications are vast, spanning across business, scientific research, and personal organization. The fundamental appeal of spreadsheet software lies in its robust capabilities for calculation, its intuitive methods for data visualization, and its straightforward approach to simple data management. Whether for balancing a budget, tracking project progress, or analyzing experimental results, spreadsheets provide a versatile and accessible platform.
Working with spreadsheet software can be surprisingly engaging. The process of transforming raw data into insightful charts and graphs offers a unique sense of discovery. Furthermore, the ability to automate complex calculations with formulas and functions can be a powerful motivator, turning tedious tasks into efficient processes. For those new to the field or considering a career that heavily utilizes this tool, the journey of mastering spreadsheet software can be both intellectually stimulating and professionally rewarding, opening doors to a wide array of analytical and organizational roles.
A Brief History and Evolution of Spreadsheet Software
Understanding the trajectory of spreadsheet software provides valuable context for its current capabilities and future potential. This historical perspective is particularly insightful for academic researchers, curious learners, and anyone interested in the broader technological landscape that shaped these ubiquitous tools.
From Paper Ledgers to Electronic Pioneers
The concept of organizing data in rows and columns predates computers by centuries, with paper ledgers serving as the primary tool for financial record-keeping and analysis. The transition to electronic spreadsheets marked a significant leap in efficiency and capability. The launch of VisiCalc in 1979 for the Apple II is widely considered a pivotal moment, as it transformed the personal computer from a hobbyist's gadget into a serious business tool. VisiCalc allowed users to create digital balance sheets where changing one number would automatically update all related calculations – a revolutionary concept at the time.
This innovation paved the way for other influential spreadsheet programs. The ability to perform "what-if" scenarios almost instantaneously changed how businesses approached financial planning and analysis. No longer were analysts bogged down by manual recalculations; they could now explore different possibilities and make more informed decisions with unprecedented speed.
The Rise of Industry Standards and Cloud Computing
Following VisiCalc, Lotus 1-2-3 emerged in the early 1980s, quickly becoming the dominant spreadsheet software for IBM-compatible personal computers. It offered improved performance, more features, and a more user-friendly interface. However, the landscape shifted again with the rise of graphical user interfaces and the introduction of Microsoft Excel. Excel's integration with the Windows operating system and its continuous addition of powerful features eventually led it to become the industry standard for desktop spreadsheet applications.
More recently, the advent of cloud computing has ushered in a new era for spreadsheet software. Google Sheets, a key component of Google Workspace, exemplifies this shift. Cloud-based spreadsheets offer real-time collaboration, accessibility from any device with an internet connection, and automatic saving, fundamentally changing how teams work together on data-driven projects. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards more integrated and collaborative digital tools.
Integration and the Future
Today, spreadsheet software is no longer a standalone application. Modern spreadsheet programs are increasingly integrated with other data analysis tools, databases, and even programming languages like Python and R. This allows for more complex data manipulation, sophisticated statistical analysis, and the automation of workflows that were previously unimaginable. The journey from simple electronic ledgers to these powerful, interconnected analytical platforms highlights a continuous drive towards making data more accessible, manageable, and insightful.
Understanding Core Spreadsheet Software Concepts
To effectively harness the power of spreadsheet software, a solid understanding of its fundamental concepts is essential. These building blocks are crucial for anyone who intends to use spreadsheets for practical purposes, whether you are a student, an industry practitioner, or a financial analyst. Mastering these basics will enable you to organize data efficiently, perform accurate calculations, and derive meaningful insights.
Data Types and Cell Formatting
At the heart of any spreadsheet are cells, and each cell can contain different types of data. The most common data types include text (labels, names, descriptions), numbers (quantities, monetary values), dates (for tracking timelines and scheduling), and booleans (TRUE/FALSE values for logical operations). Understanding how spreadsheet software interprets these different data types is crucial for accurate calculations and data manipulation.
Cell formatting plays a vital role in how data is displayed and understood. This includes changing font styles, colors, and sizes, as well as applying specific formats for numbers (e.g., currency, percentages, scientific notation) and dates (e.g., MM/DD/YYYY, DD-Mon-YY). Proper formatting not only enhances readability but also helps in presenting data in a professional and clear manner. For instance, formatting numerical data as currency instantly communicates its financial nature, while consistent date formatting ensures clarity in time-sensitive information.
For those starting their journey with data, understanding these foundational elements is a key first step. Online courses can provide a structured approach to learning these basics.
These courses can help build a foundation for understanding data within spreadsheets:
Formulas and Functions
The true power of spreadsheet software lies in its ability to perform calculations using formulas and functions. A formula is an expression that calculates the value of a cell. For example, =A1+B1 is a formula that adds the values in cells A1 and B1. Formulas can range from simple arithmetic operations to complex calculations involving multiple cells and conditions.
Functions are predefined formulas that perform specific calculations. Spreadsheet programs offer a vast library of functions, categorized typically as mathematical (e.g., SUM, AVERAGE, ROUND), logical (e.g., IF, AND, OR), lookup (e.g., VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, INDEX/MATCH), and text (e.g., CONCATENATE, LEFT, RIGHT, TRIM). Learning to use these functions effectively can significantly automate tasks and improve analytical capabilities. For example, the IF function allows you to perform conditional logic, returning one value if a condition is true and another if it's false, which is invaluable for decision-making processes.
Mastering formulas and functions is a critical skill for anyone serious about using spreadsheets for analysis or reporting. Many resources are available to help learners grasp these concepts, from beginner to advanced levels.
To gain proficiency in using formulas and functions, consider exploring comprehensive guides and practical exercises found in dedicated books.
Cell Referencing
When creating formulas, you will often need to refer to other cells. Understanding cell referencing is crucial for writing formulas that can be easily copied and adapted. There are three main types of cell references: relative, absolute, and mixed.
A relative reference (e.g., A1) changes when a formula is copied to another cell. If you copy a formula with a relative reference down a column, the row number in the reference will adjust accordingly. This is useful for applying the same calculation to multiple rows or columns of data. An absolute reference (e.g., $A$1) remains constant no matter where the formula is copied. This is essential when you always want to refer to a specific cell, such as a fixed interest rate or a tax percentage. A mixed reference (e.g., $A1 or A$1) has either the column or the row fixed. For example, $A1 keeps the column fixed but allows the row to change when copied, while A$1 keeps the row fixed and allows the column to change.
Grasping the nuances of cell referencing allows for the creation of flexible and robust spreadsheet models. It prevents errors when replicating formulas and makes your spreadsheets more dynamic and easier to maintain.
Basic Data Manipulation
Beyond calculations, spreadsheet software provides powerful tools for basic data manipulation. Sorting allows you to arrange data in ascending or descending order based on the values in one or more columns. This is helpful for quickly finding the highest or lowest values, or for organizing data alphabetically or chronologically.
Filtering enables you to display only the rows that meet specific criteria, hiding the rest. This is incredibly useful for focusing on subsets of your data. For example, you could filter a sales report to show only transactions from a particular region or above a certain value. Conditional formatting allows you to automatically apply formatting (like colors, icons, or data bars) to cells based on their values or predefined rules. This visual cue helps to quickly identify trends, outliers, or important data points without needing to manually examine each cell.
These fundamental data manipulation techniques are essential for exploring and understanding your data, forming the basis for more advanced analysis.
For learners aiming to build a comprehensive understanding of Excel, from basic operations to more complex data handling, structured courses can be very beneficial.
Key Features and Essential Functions
Beyond the fundamental concepts, spreadsheet software offers a suite of powerful features and functions that can dramatically enhance productivity and analytical capabilities. These tools are invaluable for industry practitioners, financial analysts, and students aiming for a high level of proficiency. Understanding and utilizing these features can transform a simple data repository into a dynamic analytical tool.
Data Visualization: Charts and Graphs
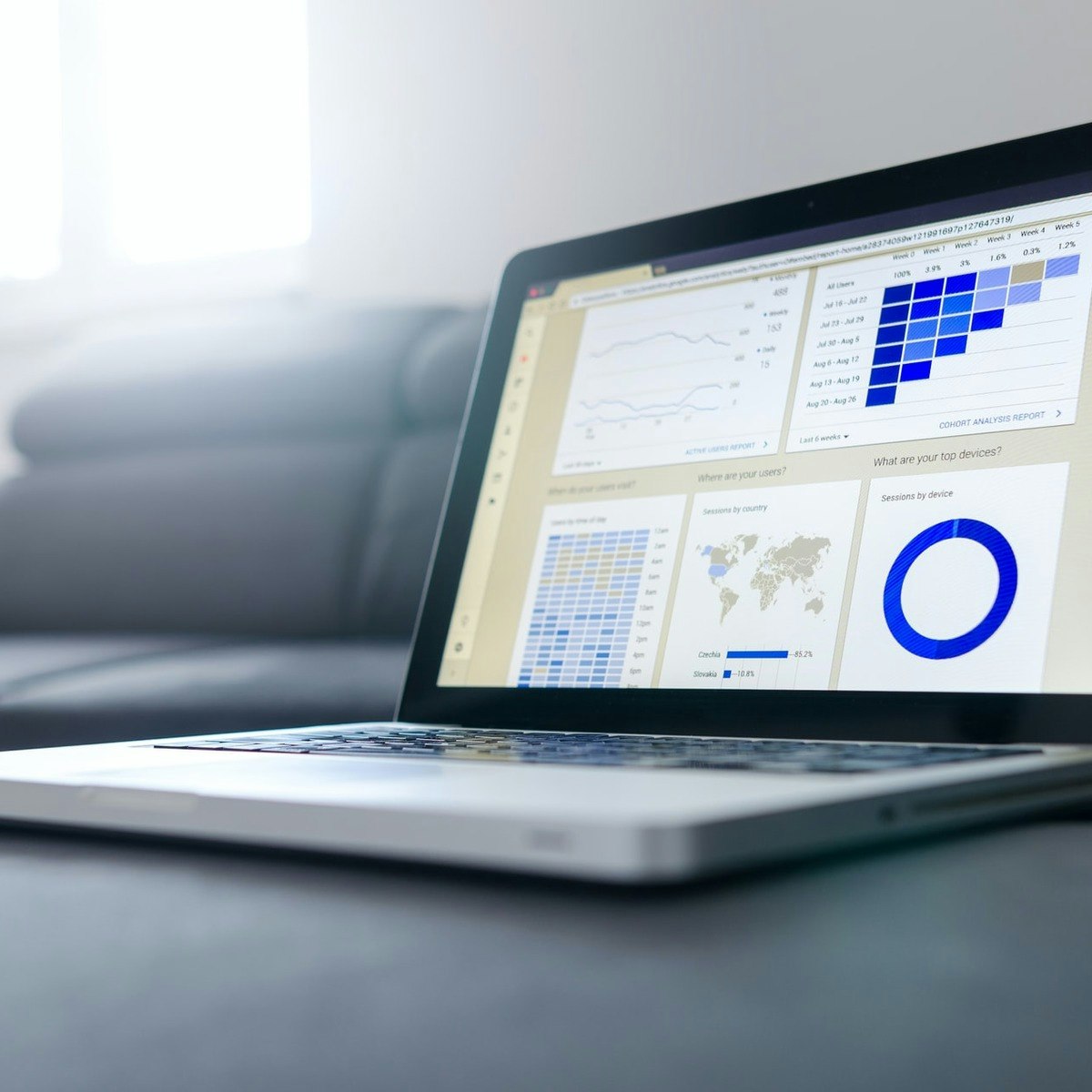
One of the most compelling features of spreadsheet software is its ability to transform raw data into meaningful visual representations like charts and graphs. These visualizations make it easier to identify trends, patterns, and outliers that might be difficult to discern from tables of numbers alone. Common chart types include bar charts for comparing categories, line charts for showing trends over time, pie charts for illustrating proportions, and scatter plots for examining relationships between variables.
Modern spreadsheet programs offer a wide array of customization options for charts, allowing users to tailor titles, labels, colors, and other elements to effectively communicate their message. The ability to create clear and impactful visualizations is a critical skill in many professional roles, as it aids in presenting complex information in an accessible and persuasive manner. For example, a sales manager might use a line chart to track monthly sales performance, while a scientist might use a scatter plot to analyze the correlation between two experimental variables.
Online courses focusing on data visualization can provide practical skills in creating effective charts and graphs.
For those looking to deepen their understanding of how to present data effectively, certain books offer invaluable guidance.
Pivot Tables for Data Summarization and Analysis
Pivot tables are an incredibly powerful feature for summarizing, analyzing, exploring, and presenting large amounts of data. With just a few clicks, you can reorganize and aggregate data to reveal insights without writing complex formulas. Pivot tables allow you to group data by different categories, calculate sums, averages, counts, or other statistics, and then "pivot" the table to view the data from different perspectives.
For instance, a marketing analyst could use a pivot table to summarize sales data by product, region, and quarter, quickly identifying top-performing products or regions. Financial analysts frequently use pivot tables to analyze financial statements and create summary reports. The interactivity of pivot tables makes them an excellent tool for exploratory data analysis, enabling users to drill down into details or slice and dice the data in various ways to answer specific questions.
Mastering pivot tables is often considered a hallmark of an intermediate to advanced spreadsheet user. Many books provide in-depth knowledge on leveraging these tools.
Data Validation and Protection
Maintaining data integrity and security is crucial, especially when working with sensitive or critical information. Spreadsheet software offers features for data validation and protection to help ensure accuracy and control access. Data validation allows you to define rules for what kind of data can be entered into a cell. For example, you can restrict input to whole numbers, dates within a specific range, or items from a predefined list. This helps prevent errors at the point of data entry.
Protection features enable you to control who can view or modify parts of your spreadsheet. You can protect entire worksheets or workbooks with passwords, or you can allow users to edit only specific ranges while keeping other cells locked. This is particularly useful in collaborative environments or when distributing spreadsheets with sensitive formulas or data that should not be altered accidentally.
These features are essential for ensuring the reliability and security of your spreadsheet data, contributing to more trustworthy analysis and reporting.
Advanced Features: Macros, Power Query, and Analysis ToolPaks
For users looking to push the boundaries of what spreadsheets can do, there are several advanced features available. Macros, often written in Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), allow you to automate repetitive tasks by recording a sequence of actions or writing custom code. This can save significant time and reduce the potential for manual errors in routine processes.
Tools like Power Query (available in Excel, and with similar functionalities in other software) provide powerful capabilities for importing, transforming, and combining data from various sources. This is invaluable for cleaning and shaping "dirty" data before analysis. Analysis ToolPaks, often available as add-ins, provide access to more advanced statistical analysis functions, such as regression analysis, ANOVA, and Fourier analysis, catering to users with more specialized analytical needs.
While these advanced features may require a steeper learning curve, mastering them can unlock significant efficiencies and analytical power. For professionals in data-heavy roles, these skills can be a major differentiator.
Books dedicated to advanced Excel programming and data analysis can be excellent resources for mastering these powerful features.
Common Applications Across Industries
The versatility of spreadsheet software makes it an indispensable tool across a multitude of industries and roles. From small businesses to large corporations, and from scientific labs to classrooms, spreadsheets provide a common platform for organizing information, performing calculations, and gaining insights. Understanding these diverse applications can help students exploring career paths, industry practitioners seeking to broaden their skill sets, and even recruiters looking for specific competencies.
Finance and Accounting
Perhaps the most well-known application of spreadsheet software is in finance and accounting. Professionals in these fields rely heavily on spreadsheets for tasks such as budgeting, forecasting, financial modeling, and creating financial statements. Spreadsheets allow for complex calculations of metrics like net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), and various financial ratios. They are used to track expenses, manage accounts payable and receivable, and perform variance analysis by comparing actual results to budgeted figures. Financial models built in spreadsheets are crucial for investment analysis, business valuation, and strategic planning.
The ability to perform "what-if" analysis by changing input variables and observing the impact on outcomes is particularly valuable in financial decision-making. The structured nature of spreadsheets also lends itself well to creating auditable records and reports, which are essential for compliance and financial transparency.
Specialized books can guide learners through the intricacies of financial modeling and analysis using spreadsheets.
Sales and Marketing
In sales and marketing, spreadsheet software is widely used for a variety of analytical and organizational tasks. Sales teams often use spreadsheets to track leads, monitor sales pipelines, calculate commissions, and analyze sales performance by region, product, or salesperson. Dashboards created in spreadsheets can provide a quick overview of key sales metrics, helping managers to identify trends and make timely decisions.
Marketing professionals utilize spreadsheets for planning and tracking marketing campaigns, managing budgets, analyzing campaign performance (e.g., click-through rates, conversion rates), and conducting market research. Spreadsheets can help in organizing customer data for segmentation, analyzing survey results, and managing content calendars. The ability to sort, filter, and visualize data makes spreadsheets a practical tool for deriving actionable insights from marketing activities.
Project Management
Spreadsheet software also finds significant application in project management. Project managers can use spreadsheets to create project plans, outline tasks, set timelines, and allocate resources. Gantt charts, which visually represent project schedules, can be created or emulated within spreadsheets to track progress and dependencies. Spreadsheets are also used for budgeting project costs, tracking expenses against the budget, and managing lists of risks and issues.
While specialized project management software exists, many professionals and smaller organizations find spreadsheets to be a flexible and accessible tool for managing various aspects of their projects. The ability to customize the layout and calculations to fit specific project needs is a key advantage.
Science, Engineering, Education, and Personal Finance
Beyond the core business functions, spreadsheets are ubiquitous in scientific research and engineering for collecting experimental data, performing calculations, statistical analysis, and creating charts to visualize results. In education, spreadsheets are used by teachers for grading and by students for various assignments involving data analysis. Educators also use spreadsheet software as a teaching tool to explain mathematical and statistical concepts.
On a personal level, many individuals use spreadsheet software for managing personal finances, creating household budgets, tracking investments, or even organizing collections or planning events. The fundamental principles of data organization and calculation are just as applicable to personal tasks as they are to complex business operations.
Different roles within these fields utilize spreadsheets in distinct ways, reflecting the software's adaptability. An engineer might use it for complex simulations, while a teacher uses it to track student progress, and an individual uses it to plan a monthly budget. This wide-ranging utility underscores why spreadsheet proficiency is such a valuable and transferable skill.
For learners interested in the broader applications of data analysis in business contexts, relevant courses are available.
Learning Path: Formal Education Routes
The journey to spreadsheet proficiency often begins within the formal education system. From secondary school through university and even into postgraduate research, spreadsheet skills are increasingly integrated into curricula across various disciplines. Understanding how these skills are typically developed can be beneficial for high school and university students, as well as academic researchers who rely on data organization and analysis.
Introduction in Secondary Education
For many students, the first encounter with spreadsheet software occurs in secondary education, often as part of computer literacy or information technology classes. At this stage, the focus is typically on basic functionalities: navigating the interface, entering and formatting data, creating simple formulas (like SUM and AVERAGE), and generating basic charts. The goal is to provide students with a foundational understanding of how spreadsheets work and their potential uses for organizing information.
These early introductions lay the groundwork for more advanced applications in later studies. Even a basic grasp of spreadsheet concepts can be helpful for students in other subjects, such as science (for recording experimental data) or mathematics (for exploring numerical relationships). The aim is to cultivate digital literacy and equip students with tools that have broad applicability.
Integration in University Coursework
At the university level, spreadsheet skills become more directly relevant to specific fields of study. Business and economics programs, for example, heavily integrate spreadsheet software into courses on accounting, finance, statistics, and operations management. Students learn to build financial models, perform statistical analyses, manage datasets, and create more sophisticated visualizations. Engineering and science disciplines also frequently require students to use spreadsheets for data analysis, modeling, and presenting research findings.
The integration of spreadsheets into coursework is often project-based, requiring students to apply their skills to solve real-world or simulated problems. This hands-on approach helps solidify understanding and demonstrates the practical utility of the software. Many university courses assume a baseline level of spreadsheet competency, and some may offer workshops or supplementary materials for students needing to catch up.
Specialized courses might focus on advanced spreadsheet techniques, such as complex financial modeling, data mining with spreadsheet tools, or using VBA for automation. These courses cater to students who wish to develop a deeper level of expertise, often in preparation for careers that are heavily reliant on sophisticated spreadsheet analysis.
A comprehensive introduction to Microsoft Excel can be a valuable starting point for university students across various disciplines.
Role in Postgraduate Research
In postgraduate research, spreadsheet software continues to be a valuable tool, particularly for data organization, preliminary analysis, and visualization. Researchers across many fields use spreadsheets to manage datasets collected from experiments, surveys, or other sources. While more specialized statistical software (like R or SPSS) is often used for complex analyses, spreadsheets provide an accessible way to clean data, perform initial calculations, and generate charts for presentations or publications.
For PhD students and academic researchers, proficiency in using spreadsheets efficiently can save considerable time in the research process. The ability to quickly manipulate and explore data can also lead to new insights or help in formulating hypotheses for further investigation. Furthermore, the collaborative features of cloud-based spreadsheets can facilitate teamwork among researchers working on joint projects.
The development of spreadsheet skills through formal education provides a strong foundation for both academic pursuits and future career opportunities where data literacy is increasingly essential.
Learning Path: Online Resources and Self-Study
Beyond formal education, a wealth of online resources and self-study opportunities exists for individuals looking to learn or enhance their spreadsheet software skills. This pathway is particularly appealing to curious learners, those considering a career pivot, students seeking supplementary learning, and industry practitioners aiming to upskill. The flexibility and accessibility of online learning make it a powerful option for mastering spreadsheet software at any proficiency level.
Availability and Effectiveness of Online Learning Materials
The internet is replete with resources for learning spreadsheet software, ranging from official documentation and help files provided by software developers to countless free tutorials, blog posts, and video courses. Platforms like YouTube host numerous channels dedicated to teaching spreadsheet skills, covering everything from the absolute basics to highly advanced techniques. Many educational websites and MOOC (Massive Open Online Course) providers also offer structured courses, often taught by industry experts or university faculty.
The effectiveness of these online resources can be quite high, especially when learners are self-motivated and disciplined. Video tutorials allow learners to see concepts demonstrated in real-time and follow along at their own pace. Interactive exercises and quizzes, often included in structured online courses, help reinforce learning and assess understanding. For many, the ability to learn on their own schedule and revisit materials as needed is a significant advantage over traditional classroom settings.
OpenCourser is an excellent platform for discovering a wide array of online courses tailored to different learning needs. You can easily browse through software tools courses to find options that suit your current skill level and learning goals. Many courses offer certificates upon completion, which can be a valuable addition to your professional profile.
Structured Online Learning Pathways
For those who prefer a more guided approach, many online platforms offer structured learning pathways designed to take learners from beginner to advanced proficiency. These pathways often consist of a series of courses that build upon each other, covering a comprehensive range of topics from basic navigation and data entry to complex formulas, pivot tables, data visualization, and even automation with macros or scripting.
Some programs may focus on specific applications of spreadsheet software, such as financial analysis, data analytics, or business intelligence. These specialized tracks can be particularly beneficial for individuals targeting specific career roles. The advantage of a structured pathway is that it provides a clear roadmap for learning, ensuring that foundational concepts are mastered before moving on to more complex topics. Often, these pathways include projects or case studies that allow learners to apply their skills in a practical context.
Consider exploring courses that offer a comprehensive curriculum if you're aiming to progress from a beginner to a professional level in spreadsheet software.
Importance of Hands-on Practice and Personal Projects
Regardless of the learning resources used, hands-on practice is paramount for developing true proficiency in spreadsheet software. Simply watching tutorials or reading documentation is not enough; learners must actively apply what they are learning. Working through exercises, replicating examples, and, most importantly, undertaking personal projects are crucial steps in the learning process.
Personal projects allow learners to tackle problems that are meaningful to them, which can increase motivation and lead to a deeper understanding. This could involve creating a personal budget, analyzing data related to a hobby, or developing a tool to solve a problem at work. The challenges encountered during these projects, and the process of overcoming them, are invaluable learning experiences. Building a portfolio of such projects can also be a great way to showcase skills to potential employers.
Community Forums and Online Help
The journey of self-study is rarely a solitary one. Numerous online communities, forums (like Reddit's r/excel or Stack Overflow), and help websites are dedicated to spreadsheet software. These platforms provide a space where learners can ask questions, seek help with specific problems, share their knowledge, and learn from the experiences of others. When you encounter a particularly tricky formula or an unexpected error, these communities can be an invaluable resource for troubleshooting and finding solutions.
Engaging with these communities not only helps in overcoming learning hurdles but also provides exposure to different ways of using spreadsheet software and keeps learners updated on new features and best practices. This collaborative aspect of online learning can significantly enhance the self-study experience and help learners stay motivated and on track.
Ultimately, self-study, supported by the vast array of online resources, offers a flexible and effective path to mastering spreadsheet software. It empowers individuals to take control of their learning journey, supplement formal education, or acquire new skills to facilitate career transitions and continuous professional development.
Career Opportunities Utilizing Spreadsheet Skills
Proficiency in spreadsheet software is not just a useful skill; it's a fundamental requirement in a vast number of job roles across nearly every industry. From entry-level positions to senior analytical roles, the ability to effectively manage, analyze, and present data using spreadsheets can significantly enhance career prospects. For students exploring potential career paths, individuals considering a career change, and recruiters seeking qualified candidates, understanding the landscape of opportunities linked to spreadsheet skills is crucial.
Entry-Level Roles Requiring Spreadsheet Proficiency
Many entry-level positions across various sectors list spreadsheet skills as a core requirement. Roles such as data entry clerk, administrative assistant, office coordinator, and junior analyst often involve tasks like inputting data into spreadsheets, organizing information, creating simple reports, and performing basic calculations. In these roles, accuracy, attention to detail, and a good understanding of fundamental spreadsheet operations (data entry, formatting, basic formulas) are key.
While these roles might be considered "entry-level," they provide valuable experience in working with real-world data and business processes. They can serve as a stepping stone to more advanced positions as individuals gain more experience and develop their analytical capabilities. For those starting their careers, demonstrating solid spreadsheet skills can make their applications more competitive.
Roles Requiring Intermediate to Advanced Skills
As career paths progress, the demand for more sophisticated spreadsheet skills increases. Roles such as financial analyst, market research analyst, business analyst, and data analyst require intermediate to advanced proficiency. These positions involve more complex data analysis, financial modeling, forecasting, creating detailed reports with charts and pivot tables, and sometimes automating tasks using macros or VBA.
For example, a financial analyst might build intricate models to assess investment opportunities or predict company performance. A data analyst might use spreadsheets to clean, transform, and analyze large datasets to uncover business insights. In these roles, the ability to not only use the software's features but also to think critically about the data and communicate findings effectively is paramount. The job outlook for roles like financial analysts and data analysts is projected to grow faster than the average for all occupations, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. For financial analysts, employment is projected to grow 9 percent from 2023 to 2033. Similarly, data analyst-related jobs are expected to see significant increases, with operations research analysts projected to grow by 23% and computer systems analysts by 10% between 2022 and 2032.
Several resources can provide further insights into the job market for these analytical roles. For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Occupational Outlook Handbook offers detailed information on financial analysts. Additionally, reports from firms like Robert Half often highlight in-demand finance and accounting roles, underscoring the continued need for spreadsheet-savvy professionals.
For those aspiring to these analytical roles, books focusing on data analysis and business modeling are highly recommended.
Foundation Skill in Specialized Fields
Even in highly specialized fields, spreadsheet skills often serve as a foundational competency. Scientists, engineers, healthcare professionals, educators, and many others regularly use spreadsheets for data collection, organization, analysis, and reporting. While they may also use more specialized software for certain tasks, the versatility and accessibility of spreadsheets make them an indispensable tool in their daily workflows.
For example, an engineer might use spreadsheets for preliminary design calculations or for tracking project component data. A medical researcher might use them to manage clinical trial data (while adhering to strict data privacy regulations). This widespread applicability means that strong spreadsheet skills can enhance career prospects even in fields not traditionally associated with office software. Proficiency in spreadsheets is a transferable skill that adds value across diverse professional domains.
Career Progression and Freelance Opportunities
Mastery of spreadsheet software can significantly contribute to career advancement. As professionals become more adept at leveraging spreadsheets for complex analysis, reporting, and automation, they become more valuable to their organizations. This can lead to promotions, increased responsibilities, and opportunities to move into roles with a greater strategic focus. The ability to derive actionable insights from data and present them clearly is a hallmark of effective leadership in many areas.
Furthermore, strong spreadsheet skills can open up freelance and project-based work opportunities. Many businesses, especially small to medium-sized enterprises, require assistance with tasks like financial modeling, data analysis, creating custom spreadsheet solutions, or providing spreadsheet training. Professionals with proven expertise can offer their services on a consulting basis, providing flexibility and diverse work experiences.
The demand for spreadsheet skills remains robust in the job market, making it a valuable asset for anyone looking to build or advance their career. Exploring job boards and professional networking sites often reveals the extent to which these skills are sought after across various industries and roles.
The Future Landscape of Spreadsheet Software and Automation
The world of spreadsheet software is not static; it's continually evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing user needs. For industry practitioners, financial analysts, researchers, and forward-looking learners, understanding these trends is crucial for staying relevant and harnessing new capabilities. The future points towards more collaborative, intelligent, and integrated spreadsheet environments.
Cloud Collaboration and Real-Time Co-authoring
The shift towards cloud-based spreadsheet solutions, exemplified by platforms like Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel Online, has already revolutionized how teams work with data. Real-time co-authoring, where multiple users can simultaneously edit the same spreadsheet and see each other's changes instantly, has become a standard feature. This facilitates seamless collaboration, eliminates the version control headaches of the past (e.g., "Sales_Report_Final_v2_Johns_Edits.xlsx"), and speeds up workflows significantly.
Future developments will likely see even tighter integration of communication and project management tools within the spreadsheet environment. Imagine discussing specific data points in a built-in chat, assigning tasks related to data verification directly within the sheet, or tracking the history of changes with greater granularity and context. The emphasis will continue to be on making collaborative data work as efficient and intuitive as possible.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning Features
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being integrated into spreadsheet platforms, promising to transform them from passive data containers into intelligent analytical assistants. Current AI-driven features already include automated data analysis, where the software can identify trends, suggest chart types, and even generate narrative summaries of data. Some tools offer natural language processing (NLP), allowing users to ask questions about their data in plain English (e.g., "What were the total sales for Q3 in the North region?") and receive answers directly within the spreadsheet.
Looking ahead, AI could enable more sophisticated predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and automated data cleaning suggestions. Imagine a spreadsheet that not only helps you build a forecast but also explains the confidence level of that forecast and highlights the key drivers. AI could also assist in formula generation, error checking, and even automating the creation of complex models based on user objectives. This "intelligent assistance" aims to make advanced analytical power accessible to a broader range of users, not just data scientists.
Several sources discuss this integration. For instance, articles on platforms like TechRadar and specialized AI blogs often explore how AI is reshaping spreadsheet functionalities.
Impact of Automation (Scripting, RPA)
Automation has long been a part of spreadsheet software through features like macros (e.g., VBA in Excel). However, the synergy between spreadsheets and broader automation technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is expanding. RPA can automate tasks that involve interacting with spreadsheets as part of a larger business process, such as extracting data from emails to populate a sheet, or generating reports from spreadsheet data and distributing them.
The ability to write custom scripts (using languages like Python, which is increasingly integrated with spreadsheet software, or Google Apps Script for Google Sheets) provides users with powerful tools to automate complex workflows, perform custom data manipulations, and connect spreadsheets to other applications and services via APIs. This trend means that tasks traditionally done manually in spreadsheets, especially repetitive data processing and reporting, will become increasingly automated, freeing up human users to focus on higher-value analysis and decision-making.
Books focusing on automation within specific spreadsheet environments are valuable for learning these skills.
Relationship with Specialized Data Analysis Tools
While spreadsheets are becoming more powerful, they exist within a larger ecosystem of data analysis tools. Business Intelligence (BI) platforms (like Tableau or Power BI), databases (SQL and NoSQL), and programming languages (Python, R) offer capabilities that go beyond what even the most advanced spreadsheets can typically handle, especially for very large datasets (big data) or highly complex statistical modeling.
The future will likely see even stronger interoperability between spreadsheets and these specialized tools. Spreadsheets will continue to be a primary tool for initial data exploration, quick analysis, and presenting summarized results, often serving as an interface or a data source for more powerful BI platforms or custom analytical scripts. The ability to easily move data between spreadsheets and these other tools will be crucial. This means that while core spreadsheet skills remain vital, an awareness of and potential proficiency in these complementary tools will become increasingly important for data professionals.
The enduring relevance of core spreadsheet skills is high, but the landscape is dynamic. Adaptability and a willingness to learn how to integrate spreadsheets with new technologies will be key for professionals who want to leverage the full power of their data.
Frequently Asked Questions (Career Focused)
Navigating career choices and skill development can bring up many questions. Here are some common queries related to the role of spreadsheet skills in the professional world, particularly for students, career pivoters, and individuals exploring job opportunities.
What level of spreadsheet skill is typically required for entry-level office jobs?
For most entry-level office jobs (e.g., administrative assistant, data entry, customer service representative), a basic to intermediate level of spreadsheet proficiency is usually expected. This typically includes understanding the software interface, accurate data entry, cell formatting, creating and using simple formulas (e.g., SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT), basic sorting and filtering, and perhaps creating simple charts. Employers will look for candidates who can efficiently organize data and perform straightforward calculations without errors. While advanced features might not be a daily requirement, a willingness to learn and adapt is always valued.
Can advanced spreadsheet skills alone secure a high-paying job?
While advanced spreadsheet skills (e.g., complex financial modeling, VBA programming, advanced pivot table analysis, Power Query) are highly valuable and can certainly contribute to securing higher-paying roles, they are often most powerful when combined with other competencies. For example, an advanced spreadsheet modeler in finance also needs strong analytical skills, an understanding of financial principles, and the ability to communicate complex findings. A data analyst needs statistical knowledge and critical thinking in addition to their spreadsheet prowess. Therefore, while advanced spreadsheet skills are a significant asset and can differentiate a candidate, they are typically part of a broader skill set required for high-paying positions. These skills can certainly open doors to roles with excellent earning potential, especially in fields like finance, data analysis, and business intelligence.
How do spreadsheet skills compare in importance to learning programming languages like Python for data analysis roles?
For many data analysis roles, both spreadsheet skills and programming languages like Python (or R) are important, though their emphasis can vary depending on the specific job and company. Spreadsheets excel at quick data exploration, ad-hoc analysis, creating visualizations for smaller datasets, and tasks where a graphical interface is more intuitive. They are also widely understood by non-technical stakeholders, making them good for sharing results. Python, on the other hand, is more powerful for handling very large datasets, performing complex statistical analyses, automating sophisticated data processing pipelines, and integrating machine learning models.
Many data analysts use both: spreadsheets for initial exploration or final presentation, and Python for the heavy lifting in between. Increasingly, spreadsheet software is integrating with Python, blurring the lines. For entry-level data analysis, strong spreadsheet skills are often a prerequisite, while Python knowledge might be a highly desired or required skill for more advanced roles. Learning both provides the most versatile toolkit.
What are common tasks for a financial analyst using spreadsheet software?
Financial analysts rely heavily on spreadsheet software for a wide array of tasks. Common tasks include:
- Building financial models for forecasting revenue, expenses, and profits.
- Performing valuation analysis (e.g., discounted cash flow - DCF).
- Analyzing financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement).
- Creating budgets and comparing actual performance against budgets (variance analysis).
- Tracking investment portfolios and calculating returns.
- Developing charts and graphs to present financial data and trends to management or clients.
- Performing sensitivity analysis and scenario planning.
They use features like advanced formulas, pivot tables, data tables, scenario manager, and often VBA for custom automation.
How can I demonstrate my spreadsheet proficiency to potential employers?
Demonstrating spreadsheet proficiency goes beyond simply listing "Microsoft Excel" on your resume. Here are several effective ways:
- Be specific in your resume's skills section: Instead of "Excel proficiency," list specific skills like "Pivot Tables," "VLOOKUP," "Financial Modeling," "Data Visualization," "VBA Macros," etc.
- Quantify achievements in your work experience: Describe how you used spreadsheet skills to achieve specific outcomes. For example, "Developed an Excel model that automated a reporting process, saving 10 hours per week" or "Analyzed sales data using pivot tables to identify key trends, contributing to a 15% increase in regional sales."
- Create a project portfolio: For more technical roles, consider creating a portfolio of your best spreadsheet projects (e.g., a complex model, a dashboard, an automated tool). This can be shared via platforms like GitHub or a personal website.
- Prepare for practical tests or case studies: Many employers use Excel tests or case studies during the interview process to assess practical skills. Practice common tasks and be ready to explain your approach.
- Mention relevant certifications or courses: If you've completed specific Excel certifications (like Microsoft Office Specialist - MOS) or advanced online courses, include them on your resume.
- Discuss real-world examples during interviews: Be prepared to talk about specific situations where you used your spreadsheet skills to solve a problem or add value.
The key is to provide tangible evidence of your abilities and how they can benefit the employer.
Are spreadsheet skills transferable across different industries and roles?
Yes, absolutely. Spreadsheet skills are among the most transferable skills in today's job market. The ability to organize data, perform calculations, analyze information, and create visualizations is valuable in virtually every industry, from finance and healthcare to marketing, education, and non-profits. Whether you're moving from an administrative role to an analytical one, or from one industry to another, your spreadsheet proficiency will almost certainly be a relevant and sought-after asset. This is because the fundamental principles of data management and analysis remain consistent, even if the specific data and contexts change.
What's the best way to stay updated with new spreadsheet features and techniques?
Spreadsheet software is constantly evolving, with new features and functions being added regularly. To stay updated:
- Follow official blogs and release notes: Software developers like Microsoft and Google typically announce updates and new features on their official blogs or support websites.
- Join online communities and forums: Platforms like Reddit (e.g., r/excel, r/googlesheets), specialized Excel/Sheets forums, and LinkedIn groups are great places to learn about new tricks, best practices, and see how others are using new features.
- Subscribe to newsletters and YouTube channels: Many experts and training providers offer newsletters or create video content showcasing new features and advanced techniques.
- Engage in continuous learning: Periodically take short online courses or workshops that cover new functionalities or advanced topics. Platforms like OpenCourser can help you find relevant and up-to-date learning materials.
- Experiment: Don't be afraid to explore new features within the software itself. Often, the best way to learn is by doing.
Continuous learning and active engagement with the user community are key to keeping your spreadsheet skills sharp and current.
Mastering spreadsheet software is a journey that offers immense rewards, both in terms of personal productivity and professional advancement. The skills you develop are highly sought after and broadly applicable, providing a solid foundation for a wide range of career paths. Whether you are just starting or looking to deepen your expertise, the continuous evolution of these tools ensures that there is always something new to learn and apply.