Experimental Design
Understanding Experimental Design
Experimental design is the systematic process of planning, conducting, analyzing, and interpreting experiments to ensure that the results are objective and valid. At its core, it's about structuring an investigation to answer a specific question or test a hypothesis with the highest possible degree of confidence. This involves carefully considering all factors that could influence the outcome and devising a method to isolate the effect of the factor being studied. For anyone new to the concept, think of it as creating a fair test – if you want to know if a new fertilizer helps plants grow taller, experimental design helps you set up a comparison where the only significant difference between plant groups is the fertilizer they receive.
Working with experimental design can be intellectually stimulating. It allows individuals to become detectives in their respective fields, systematically uncovering cause-and-effect relationships. Imagine the thrill of designing an experiment that conclusively proves a new drug's efficacy, or one that optimizes a manufacturing process to save millions, or even an A/B test that significantly boosts a website's user engagement. The principles of experimental design are also highly transferable, opening doors to diverse industries, from healthcare and technology to agriculture and social policy. This versatility and the direct impact one can have on decision-making and innovation are often what draw people to this field.
Introduction to Experimental Design
Defining the Blueprint: Core Objectives
Experimental design provides a formal framework for researchers and practitioners to investigate relationships between variables. Its primary objective is to establish causality – determining if a change in one variable (the independent variable) directly causes a change in another variable (the dependent variable). To achieve this, a well-structured experiment aims to maximize the signal (the true effect of the independent variable) while minimizing the noise (the influence of extraneous factors or random error). This structured approach ensures that conclusions drawn from the experiment are both reliable and valid, meaning the results are consistent and accurately reflect the phenomenon being studied.
Beyond just identifying cause and effect, experimental design seeks to quantify the magnitude of that effect. It's not enough to know that a new teaching method improves test scores; a good design will also help determine how much it improves them. Furthermore, it allows for the comparison of multiple treatments or conditions simultaneously, making the research process more efficient. For instance, a company could test several different website layouts at once to see which one leads to the most sales, rather than testing them one by one.
Ultimately, the core of experimental design is about making informed decisions based on data. Whether in a scientific laboratory, a business setting, or a policy-making environment, well-designed experiments provide the robust evidence needed to support or refute claims, optimize processes, and drive progress. It is a foundational skill for anyone looking to make evidence-based contributions in their field.
A Journey Through Time: Historical Roots and Guiding Principles
The concepts of experimental design are not new; they have evolved over centuries. Early forms can be traced back to agricultural experiments aimed at improving crop yields. However, the formalization of experimental design principles largely began in the early 20th century, significantly influenced by the work of Sir Ronald A. Fisher. His research in agriculture at the Rothamsted Experimental Station in England led to the development of foundational concepts like randomization, replication, and blocking, which remain central to experimental design today.
Fisher's work emphasized the importance of statistical analysis in interpreting experimental results, leading to the development of techniques like Analysis of Variance (ANOVA). Randomization, the practice of assigning treatments to experimental units purely by chance, helps to ensure that any observed differences between groups are due to the treatments themselves and not some underlying bias. Replication, repeating the experiment multiple times or on multiple units, increases the reliability of the results and allows for the estimation of experimental error. Blocking involves grouping experimental units into similar blocks to reduce the impact of known sources of variability, making it easier to detect treatment effects.
These principles have since been refined and expanded upon, leading to a diverse array of experimental designs tailored to different research questions and constraints. The historical journey of experimental design reflects a continuous effort to improve the rigor and efficiency of scientific inquiry and data-driven problem-solving across various disciplines.
These foundational ideas are explored in many introductory texts and courses. For those interested in the historical context and core ideas, seminal works often provide deep insights.
We think these books provide a strong introduction to the foundational principles of planning and executing experiments.
Impacting Discovery: The Role of Experimental Design in Research and Decision-Making
Experimental design is the backbone of rigorous scientific research across countless fields. In medicine, randomized controlled trials (RCTs), a sophisticated form of experimental design, are the gold standard for testing the efficacy of new drugs and treatments. Without carefully designed experiments, it would be impossible to distinguish between a genuine therapeutic effect and a placebo effect or natural recovery. Similarly, in psychology, experiments are crucial for understanding human behavior, cognition, and emotion by systematically manipulating variables in controlled settings.
The influence of experimental design extends far beyond academic research into the heart of industry and data-driven decision-making. Technology companies heavily rely on A/B testing, a type of experiment, to optimize websites, apps, and user experiences. By presenting different versions of a product to different user groups and measuring outcomes like click-through rates or conversion rates, companies can make data-backed choices that improve performance and profitability. In manufacturing, experimental design, often under the umbrella of Design of Experiments (DoE), is used to improve product quality, reduce defects, and optimize production processes by systematically testing different factor settings.
Even in areas like public policy and education, experimental design plays a vital role in evaluating the effectiveness of interventions. For example, a government might use an experiment to assess the impact of a new job training program on employment rates, or a school district might test different teaching methods to see which leads to better student outcomes. The ability to draw sound conclusions about cause and effect makes experimental design an indispensable tool for innovation, improvement, and informed action in a world increasingly reliant on data. Its principles help ensure that decisions are based on evidence rather than intuition or anecdotal experience.
Key Concepts and Terminology in Experimental Design
To fully grasp experimental design, one must become familiar with its specialized vocabulary and core concepts. These terms form the language through which experiments are planned, executed, and communicated. Understanding them is crucial for anyone wishing to delve deeper into designing or interpreting research.
The Building Blocks: Understanding Variables
At the heart of any experiment are variables – characteristics or conditions that can change or take on different values. The primary types are independent, dependent, and confounding variables. An independent variable is the factor that the researcher manipulates or changes to observe its effect. Think of it as the "cause" in a cause-and-effect relationship. For instance, in an experiment testing a new drug, the dosage of the drug would be an independent variable.
A dependent variable is what the researcher measures to see if the independent variable had an effect. It's the "effect" in a cause-and-effect relationship. In the drug example, the dependent variable might be the reduction in symptoms or the speed of recovery. The goal is to see if changes in the independent variable lead to predictable changes in the dependent variable.
Confounding variables (also known as lurking variables) are extraneous factors that can influence the dependent variable and potentially distort the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. If not controlled, they can lead to incorrect conclusions. For example, if one group receiving a new teaching method also has a more experienced teacher than the control group, the teacher's experience becomes a confounding variable, making it difficult to isolate the true effect of the teaching method. A key aim of good experimental design is to identify and control for potential confounding variables.
To explain this with a simple analogy, imagine you're testing which brand of popcorn pops the most kernels (dependent variable). You try Brand A and Brand B (independent variable - type of popcorn). If you pop Brand A in a brand-new microwave and Brand B in an old, weak microwave, the microwave's power is a confounding variable. You wouldn't know if Brand A was truly better or if the new microwave just popped it more efficiently. Good experimental design would ensure both brands are popped under identical conditions.
Framing the Inquiry: Hypothesis Formulation and Testing
A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about the relationship between variables. It serves as the starting point for an experiment. Typically, researchers formulate a null hypothesis (H0), which states there is no effect or no difference between groups, and an alternative hypothesis (H1 or Ha), which states there is an effect or a difference. For example, if testing a new fertilizer, the null hypothesis might be "The new fertilizer has no effect on plant height," while the alternative hypothesis would be "The new fertilizer increases plant height."
The process of hypothesis testing involves collecting data through the experiment and then using statistical methods to determine the likelihood that the observed results occurred by chance if the null hypothesis were true. If this likelihood (known as the p-value) is very small (typically below a pre-determined significance level, often 0.05), the researcher rejects the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. This suggests that the observed effect is statistically significant and not likely due to random chance alone.
It's important to remember that failing to reject the null hypothesis doesn't necessarily prove it's true; it simply means the experiment did not provide sufficient evidence to support the alternative hypothesis. Hypothesis testing is a cornerstone of the scientific method, providing a structured way to make inferences from experimental data.
Developing skills in hypothesis formulation and testing is crucial for experimental design.
Ensuring Accuracy: Validity and Reliability
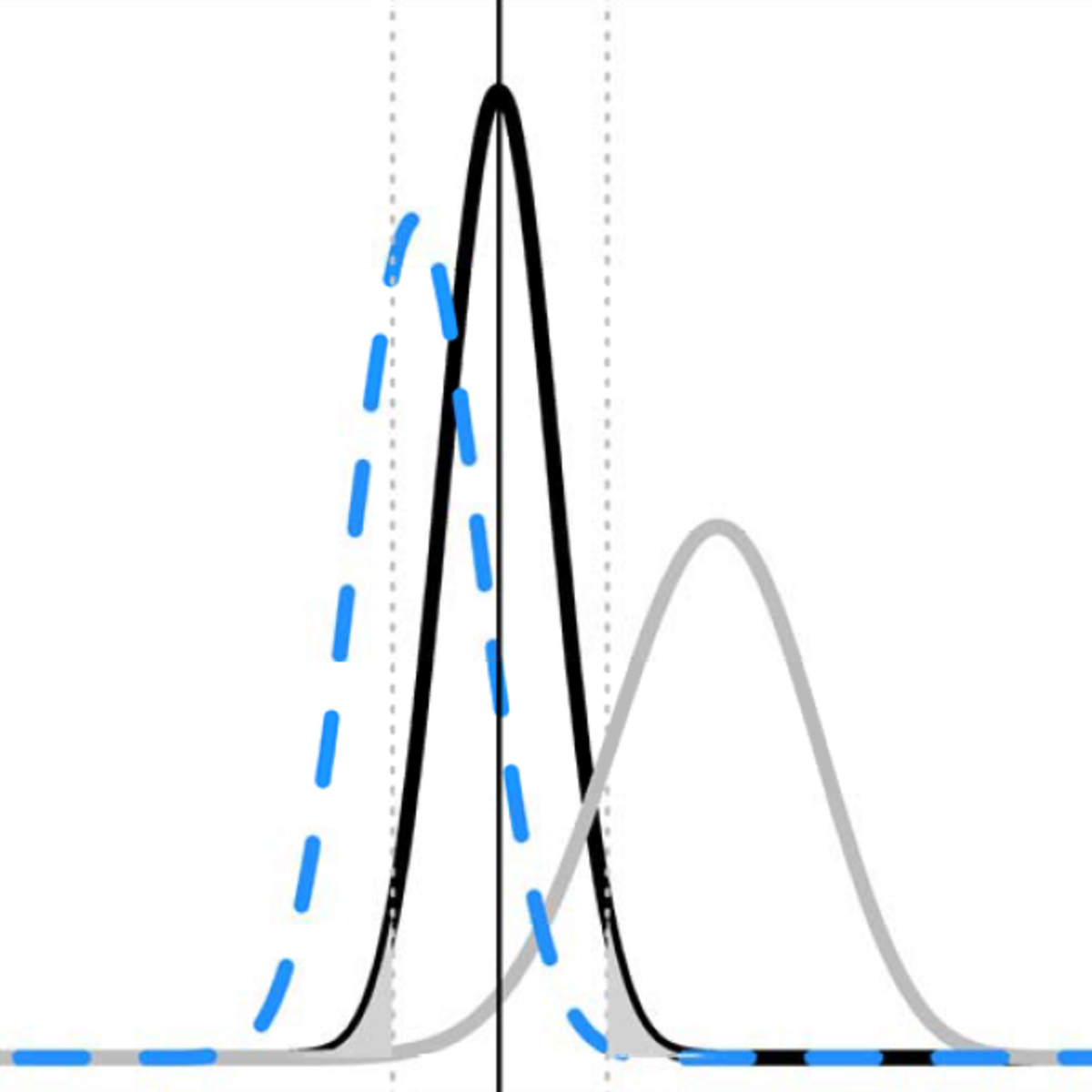
Validity and reliability are two critical measures of an experiment's quality. Validity refers to the extent to which an experiment accurately measures what it intends to measure. There are two main types: internal and external. Internal validity is the degree of confidence that the causal relationship being tested is trustworthy and not influenced by other factors or variables. High internal validity means that changes in the dependent variable are indeed caused by the manipulation of the independent variable, with minimal influence from confounding variables. Random assignment and control groups are key to achieving high internal validity.
External validity refers to the extent to which the results of an experiment can be generalized to other populations, settings, or times. An experiment might have high internal validity (showing a clear cause-effect in the lab) but low external validity if its findings don't apply to real-world situations or different groups of people. For instance, a drug trial conducted only on young, healthy males might have limited external validity for older populations or females.
Reliability, on the other hand, refers to the consistency and stability of the experimental results. If an experiment is repeated under the same conditions, it should yield similar results. Unreliable results can stem from inconsistent measurement tools, unclear procedures, or excessive random error. Ensuring that measurement instruments are precise and that experimental protocols are followed consistently helps to enhance reliability. Both validity and reliability are essential for the credibility and utility of experimental findings.
The Cornerstones of Comparison: Control Groups and Randomization
A control group is a fundamental component of many experimental designs. This group does not receive the experimental treatment (or receives a standard treatment or a placebo) and serves as a baseline against which the treatment group is compared. By comparing the outcomes of the treatment group to the control group, researchers can isolate the effect of the independent variable. Without a control group, it's difficult to determine if observed changes are due to the treatment or other factors like natural progression, the placebo effect, or regression to the mean.
Randomization is the process of assigning participants or experimental units to different treatment groups (including the control group) by chance. This is a critical technique for minimizing bias and ensuring that groups are comparable at the start of the experiment. Random assignment helps to distribute potential confounding variables evenly across the groups, so that any systematic differences observed at the end of the experiment are more likely attributable to the treatment itself rather than pre-existing differences between the groups. It is a cornerstone of establishing cause-and-effect relationships with high internal validity.
For example, if researchers are testing a new educational software, randomly assigning students to either use the new software or continue with the standard curriculum helps ensure that, on average, both groups have a similar mix of prior academic abilities, motivation levels, and other characteristics that could affect learning outcomes. This makes any observed difference in test scores more attributable to the software itself.
These courses can help build a solid foundation in the statistical methods frequently employed in experimental design.
You may also wish to explore this broader topic related to data interpretation.
Types of Experimental Designs
Experimental designs come in various forms, each suited to different research questions, resources, and ethical constraints. Choosing the appropriate design is a critical step that influences the validity and interpretability of the results. Advanced practitioners and researchers often need to weigh the strengths and weaknesses of each type in the context of their specific study.
The Gold Standard: Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) are often considered the most rigorous type of experimental design, particularly in fields like medicine and public health. In an RCT, participants are randomly assigned to either an experimental group (receiving the intervention being tested, such as a new drug) or a control group (receiving a placebo, standard treatment, or no treatment). The "randomized" aspect is crucial as it helps to ensure that the groups are comparable at the outset, minimizing selection bias and the influence of confounding variables.
The "controlled" aspect refers to the presence of a comparison group. By comparing outcomes between the experimental and control groups, researchers can more confidently attribute any observed differences to the intervention itself. RCTs can also be "blinded" (single-blind where participants don't know their group, or double-blind where neither participants nor researchers interacting with them know) to reduce bias in reporting or assessment of outcomes.
While powerful, RCTs can be expensive, time-consuming, and sometimes ethically challenging or impractical to implement. For example, it would be unethical to randomly assign people to smoke cigarettes to study the long-term health effects. However, when feasible and ethically sound, RCTs provide strong evidence for cause-and-effect relationships. AI tools are also beginning to assist in designing more effective and efficient RCTs by analyzing past trial data to suggest optimal protocols.
When Randomization Isn't Possible: Quasi-Experimental Designs
Quasi-experimental designs are employed when true randomization of participants to treatment groups is not feasible or ethical. This often occurs in real-world settings like schools, communities, or workplaces where researchers may have to work with pre-existing groups. For instance, a researcher might want to compare a new teaching method implemented in one school with the traditional method used in another comparable school. While the schools might be similar in many ways, the students were not randomly assigned to the schools or the teaching methods.
Because of the lack of random assignment, quasi-experimental designs are more susceptible to threats to internal validity, particularly selection bias. Researchers using these designs must be meticulous in identifying and attempting to control for potential confounding variables through statistical methods or by carefully matching groups on key characteristics. Common quasi-experimental designs include non-equivalent groups designs, interrupted time-series designs (where measurements are taken multiple times before and after an intervention), and regression discontinuity designs.
Despite their limitations in establishing causality as strongly as RCTs, quasi-experimental designs are valuable for evaluating interventions in natural settings where RCTs are impractical. They often offer a good balance between internal and external validity, providing useful insights for policy and practice. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses is critical for interpreting their findings appropriately.
This course offers insights into evaluation methods, including experimental and quasi-experimental approaches, particularly in digital health.
Exploring Multiple Factors: Factorial Designs and Crossover Studies
Factorial designs are powerful tools for investigating the effects of two or more independent variables (factors) simultaneously, as well as the interactions between them. Instead of studying one factor at a time, researchers can efficiently examine how multiple factors, each at different levels, influence an outcome. For example, in agriculture, a factorial experiment might test different types of fertilizer (Factor A, with levels like 'Nitrogen-rich' and 'Phosphorus-rich') and different watering schedules (Factor B, with levels like 'Daily' and 'Every other day') on crop yield. This design not only reveals the main effect of each factor (e.g., does fertilizer type matter? does watering schedule matter?) but also if there's an interaction effect (e.g., does the best fertilizer type depend on the watering schedule?).
Crossover studies, also known as repeated measures designs, involve exposing the same participants to a sequence of different treatments over time. Each participant acts as their own control, which can be very efficient for reducing variability between subjects. For example, in a study testing two different pain relievers, participants might receive Drug A for a period, have a "washout" period to eliminate its effects, and then receive Drug B. The order of treatments is typically randomized to control for order effects. Crossover designs are particularly useful when individual differences between participants are large, but they are not suitable for treatments with permanent effects or when carryover effects from one treatment to the next cannot be eliminated.
Both factorial and crossover designs offer sophisticated ways to answer more complex research questions than simple two-group comparisons, allowing for a deeper understanding of how different variables operate and interact.
Innovations in Experimentation: Adaptive and Bayesian Experimental Designs
Adaptive experimental designs are a modern approach where information gathered during the course of an experiment is used to modify the trial's design as it progresses. This flexibility can lead to more efficient, ethical, and informative studies. For instance, in a clinical trial, if an early analysis shows one treatment is clearly superior, an adaptive design might allow for more new participants to be allocated to that more effective treatment, or for the trial to be stopped early for efficacy or futility. This contrasts with traditional fixed designs where all aspects are pre-specified and remain unchanged throughout the study.
Bayesian experimental design leverages Bayesian statistics, incorporating prior knowledge (from previous studies or expert opinion) with new experimental data to update beliefs about hypotheses. This approach allows for a more nuanced interpretation of results, particularly with smaller sample sizes or when dealing with uncertainty. Bayesian methods can be used to optimize the design by selecting experimental conditions that are expected to be most informative, given the current state of knowledge. They are increasingly used in areas like drug development and A/B testing where iterative learning and optimization are key.
Both adaptive and Bayesian approaches represent a shift towards more dynamic and data-responsive experimental strategies. While they can be more complex to design and analyze than traditional methods, their potential to accelerate discovery and improve resource allocation makes them increasingly important in various research domains. The rise of computational power and sophisticated software has made these advanced designs more accessible.
These courses touch upon modern approaches and specific frameworks in experimental design.
For those seeking a comprehensive understanding of the statistical underpinnings and practical applications of various experimental designs, these books are highly recommended.
Formal Education Pathways in Experimental Design
Embarking on a career that involves experimental design often begins with a structured educational journey. While self-study can be valuable, formal education provides a comprehensive understanding of the theoretical underpinnings, statistical methods, and practical applications necessary for proficiency in this field. For those considering this path, it's helpful to understand the typical academic progression.
Laying the Groundwork: Undergraduate Studies
A strong foundation in experimental design typically starts at the undergraduate level. Students often encounter these principles in courses within statistics, psychology, biology, economics, engineering, or other research-intensive disciplines. Introductory statistics courses will usually cover basic concepts like hypothesis testing, probability, and data analysis, which are prerequisites for understanding experimental design. More specialized undergraduate courses might be titled "Research Methods," "Experimental Psychology," "Biostatistics," or "Design of Experiments."
These courses aim to equip students with the ability to understand, critique, and perhaps even design simple experiments. They will learn about different types of variables, control groups, randomization, and basic experimental structures. Emphasis is often placed on understanding the logic behind experimental control and the importance of avoiding bias. Practical components, such as designing a small study or analyzing existing datasets, are common.
For students who discover a passion for experimental design at this stage, excelling in these foundational courses and seeking out research opportunities with faculty members can be highly beneficial. Building a solid understanding of statistical software like R or SPSS can also be an asset. While an undergraduate degree might lead to entry-level research assistant or data analyst roles, further specialization often requires graduate study.
Many universities offer undergraduate-level courses that introduce the core principles of experimental design and statistical analysis, which are essential for this field.
Deepening Expertise: Graduate Programs
For those seeking to specialize in experimental design or pursue careers as independent researchers or expert consultants, graduate study is often necessary. Master's or doctoral programs in fields like statistics, biostatistics, data science, quantitative psychology, epidemiology, or specific scientific disciplines (e.g., pharmacology, engineering) will offer more advanced coursework and in-depth training in experimental design and analysis. Many statistician roles, for example, require a master's degree in statistics, biostatistics, or data science.
At the graduate level, students delve into more complex designs, such as factorial designs, repeated measures designs, quasi-experimental designs, and mixed-effects models. There's a greater emphasis on the mathematical theory underlying these methods, as well as the practical considerations of implementing them in real-world research. Courses might cover topics like power analysis (determining appropriate sample sizes), advanced statistical modeling, causal inference, and the ethical conduct of research.
A significant component of graduate education, particularly at the PhD level, is conducting original research, which invariably involves designing, executing, and analyzing experiments. This hands-on experience is invaluable for developing true expertise. Graduates with advanced degrees in areas emphasizing experimental design are well-prepared for roles as research scientists, statisticians, data scientists, and academic faculty.
This course, while advanced, gives a flavor of the statistical modeling often involved in graduate-level work.
The Pinnacle of Research Training: PhD-Level Requirements
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) represents the highest level of academic training in research, and experimental design is often a critical component of doctoral work across many disciplines. For those aspiring to lead cutting-edge research projects, direct research labs, or hold senior academic positions, a PhD is typically essential. Doctoral programs demand a profound understanding of research methodology, including the sophisticated application of experimental design principles.
PhD candidates are expected not only to master existing experimental designs but also, in some cases, to contribute to methodological advancements or apply designs in novel ways. Their dissertation research invariably involves formulating complex research questions, designing rigorous experiments to address them, collecting and analyzing data (often using advanced statistical techniques), and interpreting the findings in the context of existing literature. This process hones critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills to a very high degree.
Beyond coursework and dissertation, PhD programs emphasize the ability to communicate research findings effectively through publications in peer-reviewed journals and presentations at scientific conferences. The rigorous training prepares individuals to become independent investigators capable of pushing the frontiers of knowledge in their chosen field, often relying heavily on their expertise in experimental design to do so.
Augmenting Skills: Certifications and Workshops
Beyond formal degree programs, certifications and workshops can offer valuable opportunities to gain specialized knowledge or update skills in experimental design. These are often shorter, more focused learning experiences that can be beneficial for working professionals looking to enhance their expertise or for individuals transitioning into research-oriented roles. Some professional organizations offer certifications in areas like statistics or quality engineering, which may include components related to experimental design.
Workshops, often offered by universities, research institutions, or private training providers, can cover specific types of experimental designs (e.g., factorial designs, clinical trial methodology), software for experimental design and analysis (e.g., advanced R packages, JMP, SAS), or emerging topics like adaptive designs or Bayesian methods. These can be an excellent way to learn new techniques or refresh existing knowledge without the commitment of a full degree program.
While certifications and workshops may not replace a formal degree for certain high-level research positions, they can be a practical way to acquire specific competencies, demonstrate a commitment to ongoing professional development, and make one's skillset more competitive in the job market. They are particularly useful for applying experimental design principles in industry settings where practical application is key.
Self-Directed and Online Learning for Experimental Design
In today's interconnected world, formal education is not the only path to acquiring knowledge in experimental design. Self-directed learning, particularly through online courses and resources, offers a flexible and accessible way for individuals to build foundational skills or supplement existing expertise. This route can be especially appealing for career pivots, lifelong learners, or professionals looking to apply experimental principles in their current roles.
Platforms like OpenCourser make it easier than ever to find and compare a vast array of online learning materials. With a comprehensive catalog of courses and books, learners can tailor their educational journey to their specific needs and interests. Features such as detailed course summaries, syllabi (when available), and user reviews help in selecting the most suitable resources. You can even save courses to a list to curate your own learning path.
Building Your Foundation: Core Competencies for Self-Study
To effectively learn experimental design through self-study, focusing on core competencies is key. A fundamental understanding of basic statistics is non-negotiable. This includes concepts like descriptive statistics (mean, median, variance), probability distributions, hypothesis testing, p-values, and confidence intervals. Without this statistical literacy, the principles of experimental design will be difficult to grasp and apply correctly.
Beyond statistics, learners should aim to understand the core principles of experimental design itself: variables (independent, dependent, confounding), control groups, randomization, replication, and blocking. Grasping the "why" behind these principles—how they contribute to reducing bias and increasing the validity of results—is more important than rote memorization. Developing an analytical mindset, with attention to detail and a systematic approach to problem-solving, is also crucial.
Finally, familiarity with ethical considerations in research is important, even for those not in formal academic settings. Understanding issues like informed consent and data privacy is vital if any experiments involve human participants or their data. Many online resources and introductory texts cover these fundamental areas, providing a solid starting point for self-directed learners.
These online courses provide a strong introduction to experimental design and related data science principles, suitable for self-study.
Learning by Doing: Project-Based Strategies
One of the most effective ways to learn experimental design, especially through self-study, is via project-based learning. Theoretical knowledge is essential, but applying that knowledge to real or simulated problems solidifies understanding and builds practical skills. This could involve designing and (if feasible) conducting small experiments related to one's interests or professional field.
For example, someone interested in web design could conduct A/B tests on different versions of a personal website to see which layout leads to more time spent on page. A home gardener could design an experiment to test different fertilizers on a set of plants. Even analyzing publicly available datasets with an experimental mindset, trying to understand how the study might have been designed and what conclusions can be drawn, can be a valuable learning experience. The key is to actively engage with the material by planning, executing (even if hypothetically), and analyzing.
Many online courses incorporate projects or case studies. Learners can also seek out challenges on platforms like Kaggle or contribute to open-source projects that involve data analysis. The process of grappling with the complexities of real data, dealing with missing values, and interpreting results in context is where deep learning often occurs. Documenting these projects can also form the basis of a portfolio.
Essential Tools: Integrating Open-Source Software
Proficiency in statistical software is a critical skill for anyone serious about experimental design. Fortunately, powerful open-source tools like R and Python (with libraries such as SciPy, Statsmodels, and scikit-learn) are freely available and widely used in both academia and industry. Learning to use these tools for data manipulation, visualization, statistical analysis, and power calculations is an integral part of modern experimental design practice.
R is particularly strong for statistical analysis and has a vast ecosystem of packages specifically designed for various types of experimental designs and analyses. Python, with its versatility, is excellent for data handling, machine learning applications, and integrating experimental analysis into larger software workflows. Many online courses and tutorials are dedicated to teaching these tools in the context of data analysis and statistics.
Integrating these tools into project-based learning is highly recommended. For instance, after designing an experiment on paper, a learner could use R or Python to simulate data according to that design, perform power analysis to determine an adequate sample size, and then practice analyzing the (simulated or real) data to test hypotheses. This hands-on practice with software is invaluable for developing practical skills.
For those looking to apply their skills, exploring courses in Data Science can provide broader context and additional analytical techniques.
Showcasing Your Skills: Portfolio Development for Career Transitions
For individuals aiming to transition into roles that utilize experimental design skills, especially those relying on self-study or online learning, a well-curated portfolio is essential. A portfolio provides tangible evidence of one's abilities and understanding, going beyond a list of completed courses. It should showcase projects where experimental design principles were applied, data was analyzed, and meaningful conclusions were drawn.
Projects in a portfolio could include detailed write-ups of self-designed experiments (even if small-scale or simulated), analyses of public datasets where you critically evaluate the original study design and offer improvements, or contributions to open-source data analysis projects. Each project should clearly articulate the problem, the methods used (including the experimental design and statistical techniques), the results, and the interpretation. Code (e.g., R or Python scripts) should be clean, well-commented, and ideally hosted on a platform like GitHub.
A strong portfolio demonstrates not only technical skills but also critical thinking, problem-solving ability, and communication skills. It can be a powerful tool during job applications and interviews, helping to bridge the gap if one lacks traditional academic credentials in the specific area. Highlighting how you used resources like OpenCourser's Learner's Guide to structure your learning or found relevant courses can also demonstrate initiative and resourcefulness.
Career Progression and Opportunities in Experimental Design
A strong grasp of experimental design opens doors to a variety of career paths across numerous sectors. The ability to design studies, analyze data rigorously, and draw valid conclusions is highly valued. As organizations increasingly rely on data to make decisions, individuals with these skills are in demand. The career trajectory can vary, but generally involves increasing responsibility and complexity of work.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects strong growth for statisticians, a field closely related to experimental design. Overall employment for mathematicians and statisticians is projected to grow 11 percent from 2023 to 2033, much faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is driven by the widespread use of statistical analysis in business, healthcare, and policy decisions. Similarly, medical scientists, who heavily rely on experimental design for clinical trials and research, are also projected to see employment growth of 11 percent from 2023 to 2033.
Starting Your Journey: Entry-Level Roles
Entry-level positions for those with a foundational understanding of experimental design often include roles like Research Assistant, Data Analyst, Junior Statistician, or Quality Control Analyst. In these roles, individuals typically work under the guidance of more senior researchers or scientists. Responsibilities might involve assisting with the implementation of experiments, collecting and cleaning data, performing basic statistical analyses, and preparing reports.
For example, a research assistant in a university lab or a pharmaceutical company might help set up experimental conditions, monitor subjects, record observations, and manage datasets. A data analyst in a tech company might be involved in the execution of A/B tests, tracking metrics, and summarizing results for product teams. A quality control analyst in manufacturing might use experimental design principles to test product variations or identify sources of defects.
A bachelor's degree in a relevant field (e.g., statistics, biology, psychology, economics, engineering) with coursework in research methods and statistics is often the minimum requirement. Strong analytical skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in statistical software are also important. These entry-level roles provide invaluable hands-on experience and a platform for further skill development and career advancement.
Here are some careers that often serve as entry points or are closely related to experimental design expertise.
Advancing Your Career: Mid-Level and Senior Paths
With experience and often further education (such as a Master's or PhD), professionals can advance to mid-career and senior roles. These may include titles like Lead Researcher, Senior Data Scientist, Experimental Design Consultant, Statistician, or Principal Investigator. At this level, individuals take on more responsibility for designing complex experiments, leading research teams, interpreting sophisticated data, and communicating findings to stakeholders or the scientific community.
An Experimental Design Consultant might work with various clients across different industries to help them design efficient and effective experiments to solve specific problems or optimize processes. A Lead Researcher in a biotech firm would be responsible for the overall design and execution of preclinical or clinical trials. A Senior Data Scientist in a technology company might design and analyze large-scale online experiments that drive key business decisions. Many senior roles require not only deep technical expertise but also strong project management, leadership, and communication skills.
Continuous learning is crucial at this stage, as methodologies and tools evolve. Specializing in a particular type of experimental design or a specific application area can also enhance career prospects. Networking through professional organizations and conferences becomes increasingly important for staying abreast of new developments and opportunities.
These careers often require significant experience and/or advanced degrees where experimental design is a core competency.
New Frontiers: Emerging Industries and Applications
The principles of experimental design are continuously finding applications in new and emerging industries. The rise of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence has created fertile ground for sophisticated experimentation. For instance, in AI development, experiments are crucial for testing the performance of different machine learning models and algorithms. Companies are designing experiments to optimize AI systems for tasks ranging from image recognition to natural language processing.
Sustainability and climate science are other areas where experimental design is becoming increasingly important. Researchers might design experiments to test the effectiveness of different conservation strategies, evaluate new renewable energy technologies, or understand the impact of climate change on ecosystems. In the field of user experience (UX) design, rigorous A/B testing and other experimental methods are core to creating intuitive and effective digital products. Even in fields like finance (e.g., testing trading algorithms) and urban planning (e.g., evaluating the impact of new infrastructure), experimental approaches are gaining traction.
The ability to adapt experimental design principles to these novel contexts requires creativity and a deep understanding of the underlying logic of experimentation. Professionals who can bridge the gap between traditional experimental methods and the unique challenges of these emerging fields will be highly sought after. This continuous expansion of applications ensures that experimental design remains a dynamic and relevant skillset.
The Global Landscape: Job Market Trends
The job market for individuals with skills in experimental design and related statistical analysis is generally strong globally, driven by the increasing reliance on data-driven decision-making across various sectors. As mentioned, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects a robust growth of 11% for mathematicians and statisticians between 2023 and 2033, significantly faster than the average for all occupations. This translates to about 2,500 openings per year in the U.S. alone. The demand is fueled by the growing volume of data generated by businesses and research activities. Healthcare, technology, government, and finance are major employers of statisticians.
In the realm of medical science, which heavily utilizes experimental design, the BLS also projects an 11% growth in employment from 2023 to 2033, with about 8,900 openings projected annually. This demand is partly due to ongoing research into diseases and the development of new treatments. The World Economic Forum's "Future of Jobs Report 2025" highlights that analytical thinking remains a highly sought-after core skill, and skills related to AI and big data are among the fastest-growing. These trends indirectly support the demand for experimental design expertise, as designing studies to generate and interpret this data is crucial.
While specific market conditions can vary by region and specialization, the overall trend indicates a healthy and growing demand for professionals who can design, conduct, and interpret experiments. For those considering a career pivot, this positive outlook can be encouraging. However, it's also a field that demands continuous learning to keep up with methodological advancements and new application areas. For up-to-date information, consulting resources like the Occupational Outlook Handbook by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics is advisable.
Ethical Considerations in Experimental Design
While the technical aspects of experimental design focus on validity and reliability, the ethical dimension is equally, if not more, critical, especially when research involves human or animal subjects. Adherence to ethical principles ensures the protection of participants, maintains public trust in science, and upholds the integrity of the research process. Ignoring these considerations can lead to harm, invalidate research, and have severe professional and legal consequences.
Respecting Participants: Informed Consent Protocols
Informed consent is a cornerstone of ethical research involving human participants. It means that potential participants must be fully informed about the purpose of the study, the procedures involved, any potential risks and benefits, their right to withdraw at any time without penalty, and how their data will be kept confidential. This information must be presented in a clear, understandable language, allowing individuals to make a voluntary and autonomous decision about whether or not to participate.
Obtaining informed consent is not just a one-time event but an ongoing process. Researchers have a responsibility to ensure participants continue to understand what their participation entails, especially in long-term studies or if new information about risks or benefits emerges. Special considerations apply to vulnerable populations, such as children, prisoners, or individuals with cognitive impairments, where additional safeguards may be needed to protect their rights and welfare.
Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) in the United States, and similar ethics committees in other countries, play a crucial role in overseeing research involving human subjects. They review research proposals to ensure that informed consent procedures are adequate and that the rights and welfare of participants are protected. Researchers must typically obtain IRB approval before commencing any study involving human participants.
Striving for Objectivity: Bias Mitigation Strategies
Bias in experimental design or execution can systematically distort results, leading to incorrect conclusions. Ethical research practice demands a commitment to objectivity and the active implementation of strategies to minimize bias. Selection bias can occur if participants are not randomly assigned to groups, leading to systematic differences between groups before the experiment even begins. Randomization is a key strategy to mitigate this.
Experimenter bias can occur if the researcher's expectations or preferences unintentionally influence how the experiment is conducted or how results are interpreted. Blinding (or masking), where either the participants (single-blind) or both participants and researchers interacting with them (double-blind) are unaware of group assignments, is a common technique to reduce this type of bias, as well as participant bias (e.g., placebo effect).
Publication bias, where studies with statistically significant or "positive" results are more likely to be published than those with null or "negative" results, is another concern. This can skew the overall scientific literature. Initiatives like pre-registration of studies (committing to a research plan before data collection) aim to mitigate this by making all research attempts more transparent, regardless of their outcomes. Vigilance in identifying and addressing potential sources of bias is an ethical obligation for researchers.
Addressing the Challenges: Reproducibility and Transparency in Research
The "reproducibility crisis" refers to concerns in recent years that many scientific findings, across various disciplines, are difficult or impossible to replicate when other researchers attempt to repeat the original studies. This has significant ethical implications, as irreproducible research wastes resources, can erode public trust, and may lead to misguided policies or treatments if based on faulty findings. Several factors contribute to this issue, including publication bias, methodological flaws, insufficient reporting of methods, and sometimes, questionable research practices.
Promoting transparency is a key strategy to address this challenge. This includes detailed reporting of experimental methods, making data and analysis code openly available (where ethically appropriate), and pre-registering studies. Open science practices encourage researchers to share all phases of the research process, fostering greater scrutiny and collaboration. When methods and data are transparent, other researchers can more easily assess the validity of the findings and attempt replication.
Ensuring that experiments are designed with sufficient statistical power to detect meaningful effects is also crucial for reproducibility. Underpowered studies are more likely to produce statistically non-significant results even if a true effect exists, or conversely, any significant findings they do report may be less reliable. Ethical experimental design, therefore, includes careful attention to methodological rigor and transparency to support the robustness and trustworthiness of scientific knowledge.
Navigating the Rules: Regulatory Compliance
Researchers conducting experiments, particularly in fields like healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and any study involving human or animal subjects or sensitive data, must navigate a complex landscape of regulatory compliance. These regulations are in place to protect participants, ensure data integrity, and maintain ethical standards. For example, in the United States, research involving human subjects funded by federal agencies must comply with the Common Rule, which outlines ethical principles and requirements for IRBs. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has specific regulations for clinical trials of drugs and medical devices.
In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has significant implications for how personal data collected during research is handled, emphasizing data minimization, consent, and data security. Similar data protection and research ethics regulations exist in many other countries. Researchers working with animals must adhere to guidelines regarding humane treatment, minimization of pain and distress, and the justification for using animals in research.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in serious consequences, including legal penalties, loss of funding, and damage to professional reputation. Therefore, a crucial aspect of experimental design is understanding and adhering to all applicable local, national, and international laws and guidelines. This often involves close consultation with ethics committees and institutional compliance offices throughout the research process.
Learning about ethical frameworks and compliance is essential for responsible research. These guidelines from the National Institutes of Health provide a strong overview of ethical principles in clinical research: Guiding Principles for Ethical Research.
Current Trends and Future Directions in Experimental Design
The field of experimental design is not static; it continually evolves with technological advancements, methodological innovations, and changing scientific priorities. Staying aware of current trends and future directions is important for anyone involved in designing or interpreting experiments, as these developments can offer new tools, improve efficiency, and open up novel areas of inquiry.
The Rise of Intelligent Experimentation: AI-Driven Optimization
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into the experimental design process, promising to make research smarter, faster, and more efficient. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets from previous experiments to identify optimal parameters, suggest novel hypotheses, and even automate aspects of the experimental setup and data collection. For instance, AI can help determine the optimal sample size needed to achieve statistically significant results, balancing robustness with practical constraints like cost and time.
AI-powered tools can assist in designing complex experiments, such as factorial designs with many variables, by identifying the most influential factors to test. In fields like materials science or drug discovery, AI can guide high-throughput screening experiments, rapidly testing thousands of candidates. Bayesian optimization, an AI technique, is used to sequentially choose experimental conditions that are most likely to lead to desired outcomes, making the search for optimal solutions more efficient.
While AI offers immense potential, ethical considerations and human oversight remain crucial. AI-generated designs must be transparent and interpretable. The goal is to augment human expertise, not replace it, by leveraging AI's capacity to process complex information and identify patterns that might elude human researchers. As AI technology continues to mature, its role in optimizing and even automating experimental design is expected to expand significantly.
Enhancing Transparency and Rigor: Pre-registration and Open Science
The open science movement is a significant trend aimed at making all aspects of the research process more transparent, accessible, and reproducible. Key practices include open access publishing (making research articles freely available), sharing data and code, and pre-registration of studies. Pre-registration involves publicly documenting the research plan—including hypotheses, methods, and planned analyses—before data collection begins. This practice helps to mitigate issues like publication bias (where only "positive" results get published) and HARKing (Hypothesizing After Results are Known), thereby increasing the credibility of research findings.
Open science principles encourage collaboration and allow for greater scrutiny of research, which can help identify errors and improve overall quality. Funding agencies and journals are increasingly encouraging or requiring open science practices. For experimental design, this means more detailed reporting of methodological choices, making experimental protocols readily available, and sharing the data generated (where ethically permissible) so that others can verify the results or conduct secondary analyses.
The shift towards open science and pre-registration is a response to concerns about the reproducibility of research and aims to foster a more robust and trustworthy scientific ecosystem. Resources like the Open Science Framework (OSF) provide platforms and tools to support these practices.
The following course provides insights that are relevant to understanding the broader context of scientific communication and evaluation, which ties into open science principles.
Expanding Horizons: Cross-Disciplinary Applications
While experimental design has strong roots in fields like agriculture, medicine, and psychology, its principles are being increasingly applied across a diverse range of disciplines. This cross-disciplinary adoption highlights the versatility and fundamental importance of rigorous experimentation. For example, in user experience (UX) design and human-computer interaction, A/B testing and other experimental methods are standard practice for optimizing digital interfaces and user engagement.
In climate science and environmental studies, researchers design experiments to understand the impacts of climate change on ecosystems, test mitigation strategies (like new carbon capture technologies), or evaluate the effectiveness of conservation programs. Social scientists are using field experiments more extensively to evaluate the impact of public policies, educational interventions, and behavioral "nudges." Even in the arts and humanities, experimental approaches are sometimes used to explore questions about perception, creativity, or the impact of different artistic techniques.
This expansion into new domains often requires adapting traditional experimental design techniques to fit unique contexts and challenges. It also fosters innovation as insights from one field can inspire new approaches in another. The ability to apply experimental thinking to novel problems is a valuable skill in an increasingly interdisciplinary world.
Navigating Support: The Funding Landscape
The funding landscape for research, including studies that rely heavily on experimental design, is dynamic and competitive. Government agencies (like the National Institutes of Health or the National Science Foundation in the US), private foundations, and industry partners are major sources of research funding. Trends in funding often reflect societal priorities, scientific breakthroughs, and economic conditions.
Currently, there is significant interest and funding available for research related to areas like artificial intelligence, personalized medicine, renewable energy, and climate change solutions—all areas where experimental design plays a crucial role. Funders are increasingly emphasizing the importance of rigorous methodology, reproducibility, and the potential for broader societal impact. Many funding bodies now encourage or mandate open science practices, such as data sharing and pre-registration, as a condition of grants.
Understanding the priorities of different funding organizations, crafting compelling research proposals that clearly articulate the experimental design and its justification, and demonstrating a strong track record are essential for securing research funding. For individuals and institutions, navigating this landscape successfully requires strategic planning, collaboration, and persistence. The emphasis on robust experimental design within grant applications underscores its importance in the scientific enterprise.
Applications of Experimental Design Across Industries
The principles of experimental design are not confined to academic laboratories; they are powerful tools utilized across a multitude of industries to solve practical problems, drive innovation, and make informed decisions. The ability to systematically test ideas and measure outcomes is valuable whether one is developing a new drug, optimizing a website, improving crop yields, or evaluating a social program.
Advancing Health: Pharmaceutical Clinical Trials
Perhaps one of the most well-known and critical applications of experimental design is in pharmaceutical clinical trials. Before a new drug or medical treatment can be approved for public use, it must undergo rigorous testing to demonstrate both safety and efficacy. Clinical trials are typically conducted in phases, with later phases (Phase II and III) often employing randomized controlled trial (RCT) designs.
In these trials, participants are randomly assigned to receive either the investigational drug or a control (placebo or standard treatment). Researchers then carefully monitor outcomes, such as symptom improvement, side effects, and biomarkers. The meticulous design, including aspects like blinding, sample size determination, and statistical analysis plans, is crucial for producing reliable evidence about the drug's effects. Regulatory bodies like the FDA rely heavily on the quality of these experimental designs when making approval decisions. Expertise in biostatistics and clinical trial design is highly sought after in the pharmaceutical industry and contract research organizations (CROs).
For those interested in this intersection of biology and statistics, exploring courses in Biology or specifically Biostatistics can be beneficial.
These courses delve into biological applications and experimental methods relevant to the life sciences.
Optimizing Digital Experiences: Tech A/B Testing Frameworks
The technology industry, particularly in software development and online services, extensively uses experimental design in the form of A/B testing (also known as split testing). A/B testing is a method of comparing two versions of a webpage, app feature, email, or advertisement to determine which one performs better in achieving a specific goal, such as higher click-through rates, conversion rates, or user engagement.
In a typical A/B test, users are randomly assigned to see either Version A (the control, often the existing version) or Version B (the variation with a specific change). Data is collected on user behavior, and statistical analysis is used to determine if the difference in performance between the two versions is statistically significant. This allows companies to make data-driven decisions about product changes, marketing campaigns, and user interface designs. Large tech companies run thousands of A/B tests constantly to optimize their platforms.
Experimental design principles ensure these tests are conducted rigorously, avoiding common pitfalls that could lead to misleading results. Skills in designing and analyzing A/B tests are valuable for roles like data scientist, product manager, UX researcher, and marketing analyst in the tech sector.
This course covers analytics in a marketing context, where A/B testing is often applied.
Cultivating Better Yields: Agricultural Field Experiments
Agriculture is one of the historical birthplaces of formal experimental design, thanks to pioneers like Sir Ronald A. Fisher. Today, agricultural scientists continue to use sophisticated experimental designs to improve crop yields, develop disease-resistant plant varieties, optimize fertilizer and pesticide use, and enhance sustainable farming practices. These experiments are often conducted in fields, greenhouses, or laboratories.
Common designs in agriculture include randomized complete block designs (RCBD), split-plot designs, and factorial experiments. For example, a researcher might use an RCBD to compare the yields of several different crop varieties while accounting for known variations in soil fertility across a field. A factorial experiment could test the combined effects of different irrigation levels and fertilizer types. Statistical analysis, particularly ANOVA, is heavily used to interpret the results of these experiments.
The goal is to identify farming practices and inputs that lead to better outcomes in a reliable and cost-effective manner. The findings from agricultural experiments contribute to food security, environmental sustainability, and the economic viability of farming operations. Experimental design is a core skill for agricultural researchers, agronomists, and plant breeders.
These books are seminal texts in the field and cover many designs applicable to various scientific and industrial settings, including those historically rooted in agricultural experiments.
Informing Society: Policy Evaluation Methodologies
Experimental and quasi-experimental designs play a crucial role in public policy evaluation. Governments and non-profit organizations often implement programs and interventions aimed at addressing social problems, such as poverty, unemployment, public health issues, or educational disparities. Rigorous evaluation is needed to determine whether these policies are effective, how they can be improved, and whether they represent a good use of public funds.
When feasible, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are used to assess policy impact. For instance, to evaluate a new job training program, eligible individuals might be randomly assigned to either participate in the program or be part of a control group that does not. Researchers then compare outcomes like employment rates and earnings between the two groups. When RCTs are not possible, quasi-experimental designs, such as regression discontinuity or difference-in-differences, are employed to estimate causal effects.
The findings from these evaluations provide evidence to policymakers, helping them make informed decisions about which programs to expand, modify, or discontinue. Expertise in experimental and quasi-experimental design is valuable for policy analysts, program evaluators, economists, and researchers working in government agencies, think tanks, and academic institutions focused on public policy. The broader field of Social Sciences often employs these methods.
Frequently Asked Questions about Experimental Design
Navigating the world of experimental design can prompt many questions, especially for those new to the field or considering it as a career path. Here are some common inquiries with concise answers to help provide clarity.
Q: What qualifications are typically needed for entry-level roles involving experimental design?
A: For most entry-level roles, such as research assistant or junior data analyst, a bachelor's degree in a relevant field like statistics, psychology, biology, economics, engineering, or a related quantitative discipline is usually expected. Coursework in statistics and research methods is highly beneficial. Practical experience with data analysis software (e.g., R, Python, SPSS) and strong analytical skills are also attractive to employers.
Q: Which industries most commonly hire specialists in experimental design?
A: Specialists in experimental design are sought after in a wide range of industries. Key sectors include pharmaceuticals and healthcare (for clinical trials and medical research), technology (for A/B testing and product development), market research, manufacturing (for quality control and process optimization), agriculture (for crop improvement), and government and non-profit organizations (for policy evaluation).
Q: How does strong experimental design impact product development or service profitability?
A: Strong experimental design allows businesses to make data-driven decisions rather than relying on guesswork. In product development, it helps identify which features resonate most with users, leading to better products and increased customer satisfaction. In marketing, it can optimize campaigns for higher conversion rates. By systematically testing different approaches (e.g., website layouts, pricing strategies, service protocols), companies can identify what works best to improve efficiency, enhance user experience, and ultimately increase profitability.
Q: Can skills in experimental design facilitate a transition to remote work?
A: Yes, many roles that heavily utilize experimental design, particularly those focused on data analysis, statistical modeling, and research planning, can be well-suited for remote work. The ability to design experiments, analyze data using software, and communicate findings through reports and presentations can often be done effectively from any location. The tech industry, in particular, offers many remote opportunities for data scientists and analysts involved in A/B testing and online experimentation.
Q: What are some common career advancement barriers in fields relying on experimental design?
A: Common barriers can include a lack of advanced education (as many senior research roles require a Master's or PhD), insufficient practical experience with complex designs or large datasets, and challenges in keeping up with rapidly evolving methodologies and software tools. Developing strong communication and leadership skills also becomes increasingly important for moving into roles that involve managing teams or influencing organizational strategy. Sometimes, specialization in a niche area can be both an advantage and a barrier if demand shifts.
Q: How can someone transition from an academic research role using experimental design to an industry position?
A: Transitioning from academia to industry often involves reframing academic experience in terms relevant to business objectives. Highlight practical problem-solving skills, proficiency with industry-standard software (like Python and R), and experience with managing projects and deadlines. Emphasize how your experimental design skills can translate into tangible outcomes like product improvement, cost savings, or risk reduction. Networking with industry professionals, tailoring your resume to industry language (focusing on impact and results rather than just publications), and potentially building a portfolio of industry-relevant projects can be very helpful. Understanding the faster pace and different incentive structures of industry is also key.
To further explore related subjects, you might find the broader topic of Research Methods illuminating.
Concluding Thoughts
Experimental design is a rigorous and rewarding field that stands at the intersection of curiosity, critical thinking, and data-driven discovery. It is a discipline that empowers individuals to ask meaningful questions and seek reliable answers, whether in the pursuit of scientific knowledge, technological innovation, or societal improvement. The journey to mastering experimental design involves a commitment to learning its foundational principles, statistical underpinnings, and diverse methodologies. While the path can be challenging, requiring precision, patience, and an analytical mindset, the ability to design and interpret experiments is an invaluable skill in an increasingly complex world.
For those considering this path, remember that the demand for individuals who can navigate data and derive actionable insights is strong and growing. Whether you choose a formal academic route or leverage the wealth of online resources available through platforms like OpenCourser, opportunities abound to develop expertise. The skills gained are not only intellectually stimulating but also highly transferable across a multitude of exciting career domains. Embrace the challenge, and you may find yourself contributing to the next wave of breakthroughs and innovations.
If you're keen to start your learning journey, you can explore a wide variety of courses and materials by using the browse feature on OpenCourser or searching for specific topics like statistics or data science.