Science Teacher
Science Teacher: Inspiring the Next Generation of Innovators
A Science Teacher plays a crucial role in education, guiding students through the fascinating realms of biology, chemistry, physics, earth science, and more. They are responsible for cultivating scientific literacy, fostering critical thinking skills, and igniting a passion for discovery in young minds. Their work involves designing engaging lessons, conducting experiments, managing classroom dynamics, and assessing student understanding of complex scientific concepts.
Working as a Science Teacher offers the unique opportunity to shape future generations by making science accessible and exciting. It involves the rewarding challenge of translating intricate scientific principles into understandable terms and fostering an environment where curiosity thrives. The role often extends beyond the classroom, involving mentorship, participation in science fairs, and collaboration with fellow educators to continuously improve the learning experience.
Science Teacher: Roles and Responsibilities
The daily life of a science teacher is dynamic and multifaceted, requiring a blend of subject matter expertise, pedagogical skill, and organizational ability. Understanding these responsibilities provides a clear picture of what the career entails.
Daily Tasks and Classroom Management
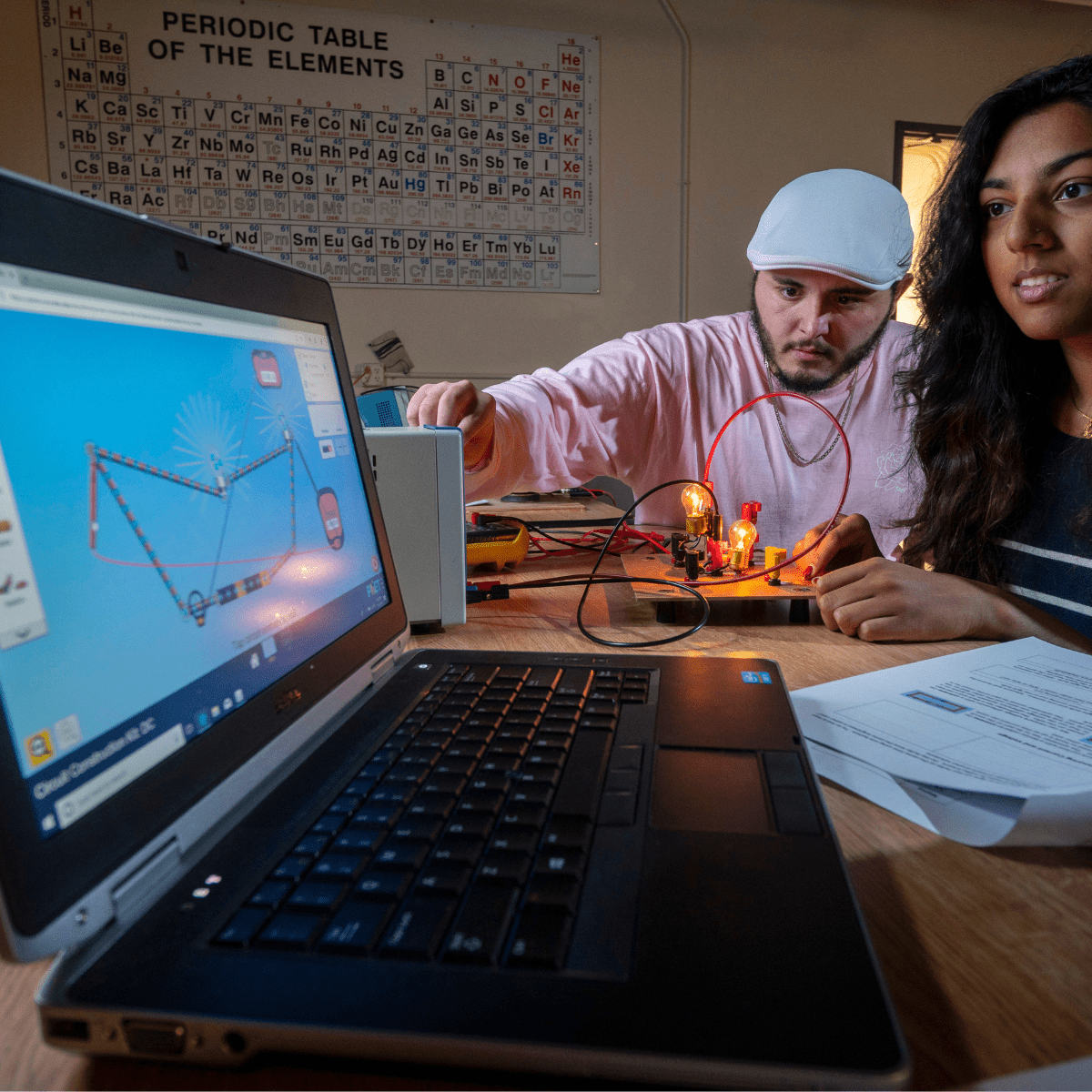
A significant portion of a science teacher's day involves direct instruction, leading lectures, discussions, and demonstrations. This requires careful lesson planning, tailoring content to meet curriculum standards and student needs. Preparing materials, setting up laboratory equipment, and ensuring a safe learning environment are essential daily tasks, especially given the hands-on nature of science.
Effective classroom management is paramount. Science teachers must establish clear expectations for behavior, particularly during lab activities where safety is critical. They spend time grading assignments, quizzes, and lab reports, providing constructive feedback to help students improve. Monitoring student progress and adapting teaching strategies accordingly are ongoing responsibilities.
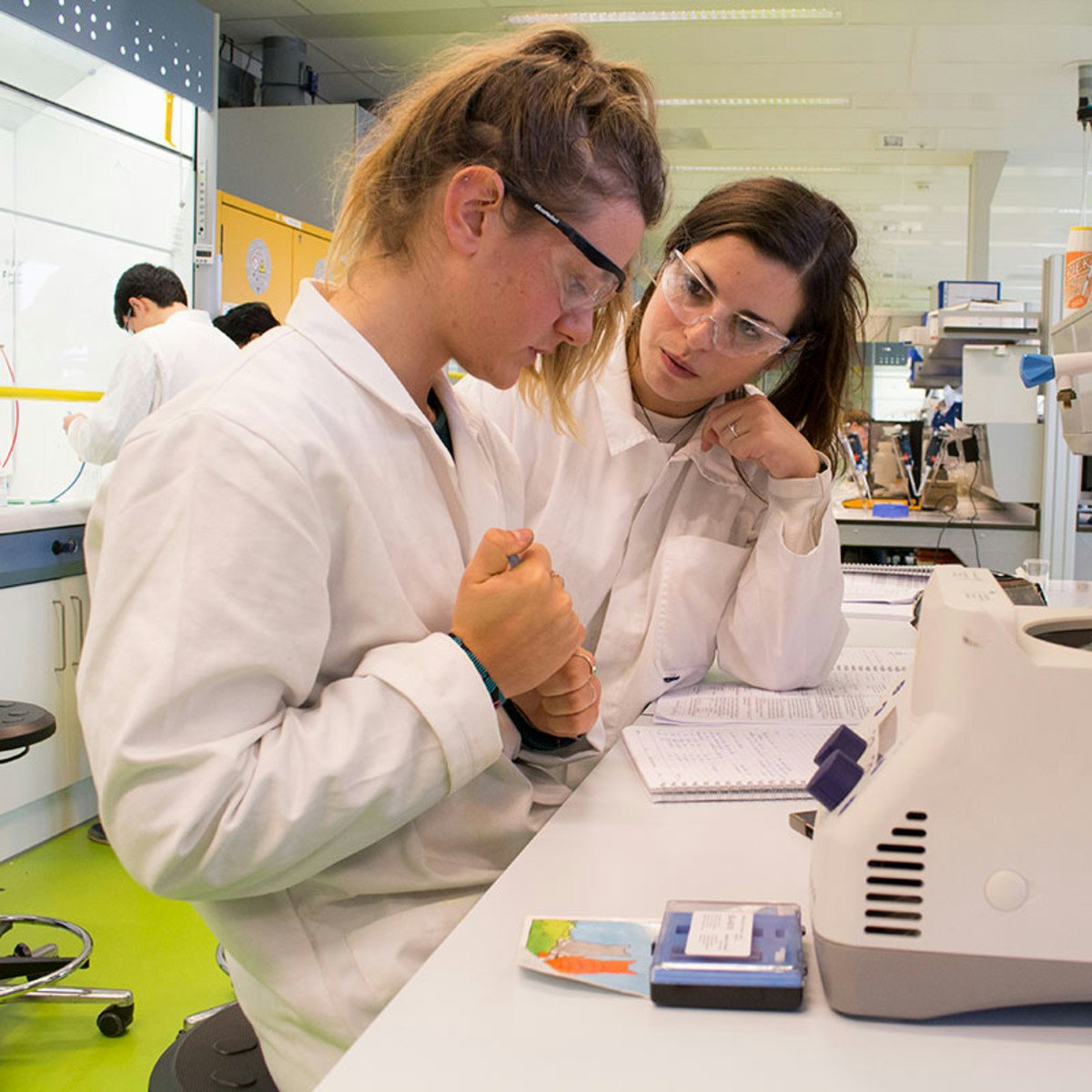
Supervising laboratory sessions demands vigilance and expertise. Teachers guide students through experiments, troubleshoot issues, reinforce safety protocols, and help students connect practical activities with theoretical concepts. This hands-on guidance is central to effective science education.
These courses offer insights into effective teaching strategies specifically tailored for science education, including managing diverse classroom environments.
Curriculum Development and Adaptation
Science teachers are often involved in developing or adapting curricula to align with state or national standards, school goals, and student populations. This may involve selecting textbooks, designing new learning units, or integrating new technologies and teaching methods.
They must stay current with scientific advancements and educational research to ensure their curriculum is relevant and effective. This includes finding ways to make science accessible and engaging for students with diverse learning styles and backgrounds.
Adapting lessons often means differentiating instruction to meet the needs of all learners, including those requiring additional support or advanced challenges. This creative aspect allows teachers to shape the learning journey in meaningful ways.
Mentorship and Extracurricular Activities
Beyond academics, science teachers often serve as mentors, offering guidance on academic paths, career options in STEM, or personal development. Building positive relationships with students is a key aspect of the role.
Many science teachers lead extracurricular activities, such as science clubs, robotics teams, or environmental groups. This involves organizing meetings, supervising projects, and sometimes coordinating participation in competitions or events.
These activities provide valuable opportunities for students to explore interests beyond the standard curriculum and develop teamwork and problem-solving skills. For teachers, it's a chance to connect with students on a different level and share their passion for science.
Collaboration and Professional Development
Effective teaching often involves collaboration. Science teachers work with colleagues within their department and across disciplines to share resources, develop interdisciplinary projects, and ensure a cohesive educational experience for students.
They also interact with school administrators, support staff, and parents or guardians to address student needs and progress. Communicating effectively with these stakeholders is crucial for student success.
Continuous learning is vital. Science teachers engage in ongoing professional development to stay abreast of new scientific discoveries, teaching technologies, and pedagogical strategies. This might involve attending workshops, conferences, or pursuing further education.
Formal Education Pathways
Pursuing a career as a science teacher typically requires a specific educational foundation, combining subject matter expertise with pedagogical training. The exact requirements can vary, but common pathways exist.
Undergraduate Degrees for Aspiring Science Teachers
A bachelor's degree is generally the minimum requirement. Many aspiring science teachers pursue a degree in a specific science field like Biology, Chemistry, Physics, or Earth Science. This provides the deep content knowledge necessary to teach the subject effectively.
Alternatively, some universities offer Bachelor of Science in Education (B.S.Ed.) degrees with a specialization in a science area. These programs integrate science coursework with pedagogy, child development, and classroom management training from the outset.
Regardless of the specific degree title, a strong foundation in the sciences is essential. Coursework typically includes laboratory components, ensuring future teachers have hands-on experience with scientific inquiry.
These foundational courses cover core concepts often required in undergraduate science programs.
For those exploring science subjects, these books offer broad overviews or delve into specific areas.
Teaching Certifications and Licensure
After obtaining a bachelor's degree, prospective teachers usually need to complete a state-approved teacher preparation program. These programs focus on teaching methods, educational psychology, curriculum development, and include a student teaching component (practicum).
Obtaining a teaching license or certification is mandatory for teaching in public schools in most regions. Requirements vary significantly by state or country but typically involve passing standardized tests covering subject matter knowledge and teaching skills, completing the teacher preparation program, and undergoing a background check.
Some states offer alternative certification routes for individuals who have a bachelor's degree in a science field but did not complete a traditional teacher preparation program. These often involve intensive pedagogical training and supervised teaching experience.
Graduate Studies in Science Education
While not always required for K-12 teaching, a master's degree (such as a Master of Education (M.Ed.) or Master of Arts in Teaching (MAT) with a science focus) can enhance qualifications, potentially lead to higher salaries, and open doors to leadership roles.
Graduate programs often delve deeper into advanced science topics, educational research, curriculum theory, and leadership in education. Some teachers pursue master's degrees while already working in the field.
For those interested in teaching at the post-secondary level (community college or university) or pursuing research in science education, a Ph.D. in Science Education or a related field is typically necessary. These programs involve rigorous research and contribution to the field's knowledge base.
Specializing within Science Education
Within science teaching, educators can often specialize. At the secondary level, teachers typically focus on a specific discipline like Biology, Chemistry, or Physics. Some may specialize further, teaching advanced placement (AP) or honors courses.
Emerging areas like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education encourage an integrated approach. Teachers might specialize in developing interdisciplinary STEM curricula or leading STEM-focused programs.
Other specializations could include environmental science education, focusing on ecological principles and sustainability, or adapting science instruction for students with special needs. These often require additional coursework or certifications.
Alternative and Online Learning Pathways
While traditional university programs are common, alternative routes into science teaching are available, particularly appealing to career changers or those seeking flexibility. Online learning plays an increasingly significant role in these pathways.
Accelerated and Non-Traditional Certification Routes
Many regions offer alternative teacher certification programs designed for individuals who already hold a bachelor's degree, especially in a STEM field. These programs often condense the pedagogical training and may allow candidates to start teaching sooner under supervision.
Post-baccalaureate certification programs are another option, focusing solely on the education coursework and student teaching required for licensure after a non-education bachelor's degree has been completed.
Organizations focused on placing professionals into high-need schools sometimes offer their own intensive training and certification pathways, combining pedagogical instruction with immediate classroom experience.
Leveraging Online Courses and Micro-credentials
Online courses offer tremendous flexibility for acquiring foundational science knowledge or specific pedagogical skills. Platforms like OpenCourser aggregate thousands of courses, allowing learners to browse science topics or explore education courses at their own pace.
Micro-credentials and specialized online certificates can demonstrate expertise in specific areas, such as educational technology, teaching specific science disciplines (like climate science), or inquiry-based learning. These can supplement formal qualifications and showcase commitment to professional growth.
For career changers, online courses can bridge knowledge gaps in science or pedagogy before committing to a formal certification program. They provide a low-risk way to explore the field and build foundational understanding. OpenCourser's features, like saving courses to a list and comparing syllabi, can help structure a self-directed learning path.
These courses cover specific skills or knowledge areas beneficial for science teachers, often available through online platforms.
Demonstrating Competency through Projects and Experience
While formal certification is usually required, practical experience and projects can significantly strengthen an application, especially for alternative routes. Volunteering in classrooms, tutoring students in science, or leading science-related youth groups demonstrates commitment and practical skills.
Developing a portfolio showcasing lesson plans, student work samples (anonymized), or videos of teaching (if possible and permitted) can provide tangible evidence of teaching abilities. This is particularly useful when traditional student teaching experience is limited.
For those transitioning from industry, highlighting relevant experiences—such as mentoring junior colleagues, training staff, or communicating complex technical information—can demonstrate transferable skills applicable to teaching.
Essential Skills and Competencies for Science Teachers
Excelling as a science teacher requires a unique blend of scientific knowledge, pedagogical expertise, and interpersonal skills. Mastering these competencies is key to creating an effective and engaging learning environment.
Scientific Literacy and Subject Matter Expertise
A deep understanding of the scientific concepts, principles, and methodologies relevant to the subject(s) being taught is fundamental. This includes not just factual knowledge but also an understanding of the nature of science—how scientific knowledge is developed, tested, and revised.
Teachers need the ability to explain complex ideas clearly and accurately, using appropriate analogies and models. They should also be able to connect scientific concepts to real-world applications and students' everyday lives.
Staying current with advancements in their field is crucial. Scientific literacy involves ongoing learning and the ability to critically evaluate scientific information from various sources.
These courses enhance scientific literacy and understanding of core scientific principles.
This book explores how science operates within society.
Pedagogical Skills and Classroom Management
Effective science teachers utilize a variety of instructional strategies to cater to diverse learners. This includes inquiry-based learning, project-based activities, direct instruction, and effective questioning techniques.
Strong classroom management skills are essential for creating a safe, respectful, and productive learning environment, especially during potentially hazardous lab activities. This involves setting clear expectations, managing student behavior, and organizing classroom routines efficiently.
Assessment skills are also vital. Teachers must be ableto design and implement various forms of assessment—formative and summative—to gauge student understanding, provide feedback, and inform instruction.
Integrating Technology in the Science Classroom
Proficiency in using educational technology enhances science teaching. This includes utilizing digital simulations like PhET simulations, virtual labs, data analysis software, online collaboration tools, and learning management systems.
Teachers should be able to integrate technology meaningfully to support learning objectives, facilitate inquiry, visualize complex phenomena, and provide access to real-time data or remote experiments.
Staying updated on relevant educational technologies and evaluating their pedagogical value is an ongoing aspect of the role. Digital literacy is crucial for both teachers and for modeling its importance to students.
These courses focus on using simulations and technology effectively in STEM education.
Communication and Cultural Competency
Clear communication skills are essential for explaining concepts, providing instructions, giving feedback, and engaging students in discussions. Active listening is equally important for understanding student questions and concerns.
Science teachers interact with a diverse group of students, parents, colleagues, and administrators. Strong interpersonal skills, empathy, and the ability to build positive relationships are crucial.
Cultural competency involves understanding and respecting the diverse backgrounds of students and creating an inclusive classroom environment where all students feel valued and empowered to learn science. This requires awareness of potential biases and adapting teaching practices accordingly.
Career Progression and Advancement Opportunities
A career in science teaching offers various avenues for growth and development, both within the classroom and beyond. Advancement often depends on experience, further education, and demonstrated leadership.
Early Career Roles and Building Experience
New science teachers typically begin in classroom teaching positions at the elementary, middle, or high school level. Initial years focus on honing pedagogical skills, mastering classroom management, and becoming proficient in curriculum delivery.
Some may start as teaching assistants or long-term substitutes, gaining valuable classroom experience before securing a full-time position. Mentorship from experienced colleagues is often crucial during this phase.
Building a strong foundation involves seeking feedback, participating in professional development, and gradually taking on more responsibilities, such as sponsoring a club or assisting with curriculum committees.
Mid-Career Growth: Leadership and Curriculum Roles
With experience, science teachers can pursue leadership opportunities. Becoming a department head or lead teacher involves mentoring newer teachers, coordinating curriculum within the science department, and managing departmental budgets or resources.
Opportunities often arise in curriculum development, either at the school or district level. Experienced teachers may design new courses, select instructional materials, or lead initiatives to integrate new standards or technologies.
Some teachers take on roles as instructional coaches or specialists, supporting colleagues in improving their teaching practices, integrating technology, or implementing specific pedagogical approaches like inquiry-based learning.
Senior Positions and Administrative Paths
Experienced educators may move into school administration roles, such as assistant principal or principal. These positions require leadership skills, knowledge of school operations, and often additional administrative credentials or degrees.
At the district level, roles like Science Coordinator or Director of STEM Education involve overseeing science programs across multiple schools, developing district-wide policies, and managing larger budgets and initiatives.
Some science educators transition into policy work, advising government agencies or educational organizations on science education standards, funding, or teacher training programs.
Pivoting to Related Fields
The skills developed as a science teacher are transferable to various other fields. Some transition into educational technology companies, developing science-related software, content, or professional development programs.
Science communication is another pathway, involving writing for science publications, developing museum exhibits, or working in public relations for scientific organizations. Strong communication and explanation skills are highly valued.
Others may move into corporate training, curriculum design for industry, or roles in non-profit organizations focused on science outreach or environmental education. A background in science education provides a unique perspective in these areas.
Addressing Challenges in Modern Science Education
Science educators today navigate a complex landscape marked by unique challenges. Understanding these issues is crucial for aspiring and current teachers to prepare for the realities of the profession and contribute to solutions.
Combating Skepticism and Misinformation
In an era of readily available information, distinguishing credible science from pseudoscience and misinformation is a significant challenge. Teachers play a vital role in equipping students with critical thinking skills to evaluate sources and understand the scientific process.
Addressing public skepticism towards established scientific concepts, such as climate change or evolution, requires careful pedagogical approaches. Teachers must foster open inquiry while upholding scientific integrity.
Developing science literacy includes teaching students how science works, acknowledging uncertainties, and differentiating between scientific consensus and fringe theories. This requires teachers to be well-informed and skilled communicators.
Navigating Funding and Resource Disparities
Access to adequate funding for laboratory equipment, technology, and updated materials varies significantly between schools and districts. This disparity can impact the quality and equity of science education.
Teachers in under-resourced schools often need creativity and resourcefulness to provide engaging hands-on experiences. Securing grants or finding low-cost alternatives for experiments are common strategies.
Advocating for equitable funding and resources for science education is an ongoing challenge within the profession and the broader community.
Adapting to Technological Advancements (like AI)
Rapid technological advancements, including the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), present both opportunities and challenges. Teachers need to learn how to effectively integrate new tools like AI tutors, simulations, or data analysis platforms into their instruction.
Ensuring equitable access to technology for all students remains a concern. Furthermore, educators must help students develop digital literacy and ethical awareness regarding technology use, including AI.
Professional development is crucial to help teachers stay current with emerging technologies and understand their potential impact on teaching and learning science.
Teacher Well-being: Burnout and Retention
Teaching, including science teaching, can be a demanding profession. High workloads, standardized testing pressures, and managing diverse student needs contribute to stress and potential burnout.
Teacher retention, particularly in STEM fields, is a concern in many regions. Supporting teacher well-being through mentorship, manageable workloads, professional autonomy, and adequate resources is critical for maintaining a strong science educator workforce.
Building supportive school cultures and professional learning communities can help mitigate burnout and foster resilience among science teachers.
Global Perspectives on Science Teaching
Science education is a global endeavor, with varying approaches, priorities, and challenges across different countries and cultures. Understanding these international perspectives can enrich teaching practices and highlight global trends.
Comparing Science Curricula Across Borders
Science curricula differ worldwide in their structure, content emphasis, and assessment methods. Some systems may prioritize deep conceptual understanding in specific disciplines, while others focus on integrated science or practical applications.
Comparing curricula can offer insights into different ways of organizing scientific knowledge and fostering scientific skills. International assessments like PISA (Programme for International Student Assessment) provide comparative data on student performance in science.
Understanding these differences is valuable for educators working in international schools or collaborating with colleagues globally.
International Demand and Opportunities
The demand for qualified science teachers varies globally. Some countries face significant shortages, particularly in specific disciplines or rural areas, creating opportunities for international educators.
Emerging economies often prioritize STEM education to foster innovation and economic growth, potentially increasing demand for skilled science teachers. However, navigating visa requirements and cultural adjustments are important considerations.
International schools cater to expatriate and local populations worldwide, often seeking teachers with experience in specific curricula (like IB or AP) and a willingness to work in diverse cultural contexts.
Cross-Cultural Teaching Approaches
Teaching methodologies can be influenced by cultural norms and educational philosophies. Approaches to classroom interaction, student participation, and the role of the teacher can differ significantly.
Effective cross-cultural teaching requires sensitivity, adaptability, and an understanding of students' diverse backgrounds and learning experiences. Building inclusive classrooms that respect cultural differences is paramount.
Learning about pedagogical approaches from other cultures can broaden a teacher's toolkit and offer new strategies for engaging students.
These courses, offered in various languages, touch upon science concepts taught globally.
Navigating International Certifications
Teacher certification requirements are country-specific and sometimes region-specific. Transferring teaching credentials from one country to another often involves evaluation processes and may require additional coursework or examinations.
Organizations exist that facilitate the placement of teachers in international schools, and they can often provide guidance on certification and qualification recognition.
Understanding the reciprocity agreements (or lack thereof) between different jurisdictions is crucial for teachers considering international opportunities.
The Future of Science Education
Science education is continually evolving, shaped by technological advancements, societal needs, and a deeper understanding of how students learn best. Anticipating future trends helps educators prepare students for a rapidly changing world.
Technology-Enhanced and Personalized Learning
Technology will likely play an even larger role, with adaptive learning platforms offering personalized pathways based on student needs and progress. Virtual and augmented reality could provide immersive experiences for exploring complex scientific phenomena.
Data analytics may help teachers better understand student learning patterns and tailor instruction more effectively. Tools for online collaboration and remote experimentation will continue to develop, supporting flexible learning environments.
The challenge lies in using technology effectively to enhance, not just replace, meaningful teacher-student interactions and hands-on inquiry.
Evolving Curricula: Climate Science and Ethics
Curricula are increasingly incorporating critical contemporary issues. Climate science literacy, including understanding the causes, impacts, and potential solutions to climate change, is becoming a core component of science education.
Ethical considerations related to scientific advancements, such as genetic engineering, AI, or data privacy, will likely receive greater emphasis. Preparing students to navigate these complex ethical dilemmas is crucial.
There's also a growing push for integrating computational thinking and data science skills across the science curriculum, reflecting the changing nature of scientific practice.
The Rise of Hybrid and Online Teaching Models
The experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of hybrid and fully online teaching models. While in-person learning remains vital, particularly for lab work, blended approaches are likely to persist.
Developing effective online pedagogical strategies for science, including virtual labs and engaging remote collaboration, will be an ongoing area of focus for educators and curriculum designers.
Ensuring equity of access and engagement in online and hybrid science learning environments remains a key challenge for the future.
Ethical Considerations in Science Pedagogy
Beyond teaching scientific ethics, ethical considerations apply to teaching practices themselves. This includes ensuring equitable access to high-quality science education for all students, regardless of background.
Addressing bias in curriculum materials and teaching practices is an ongoing process. Creating inclusive classrooms where diverse perspectives are welcomed and respected is fundamental to ethical science education.
Teachers must also navigate ethical issues related to student data privacy and the responsible use of educational technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the average salary range for science teachers?
Salaries for science teachers vary widely based on location (country, state, district), level (elementary, middle, high school, post-secondary), years of experience, and level of education (bachelor's vs. master's/doctorate). According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for high school teachers was $69,530 in May 2023. Salaries in private schools or other countries can differ significantly. It's best to research specific school districts or regions for accurate salary scales.
Can I transition from a lab research career to teaching?
Yes, transitioning from a research career to teaching is quite common. Your deep subject matter expertise is a significant asset. You will typically need to complete a teacher certification program, which focuses on pedagogy, classroom management, and student teaching. Alternative certification routes are often designed specifically for professionals making this transition.
How competitive are tenure-track positions in higher education?
Tenure-track positions teaching science at the university level are generally very competitive. They typically require a Ph.D. in the relevant science field or in Science Education, a strong research record (publications, grants), and teaching experience (often as a graduate teaching assistant or postdoctoral fellow). The number of applicants often far exceeds the number of available positions.
Do science teachers need industry work experience?
Industry work experience is generally not a requirement for K-12 science teaching, although it can be a valuable asset. Experience in a STEM field can provide real-world context for lessons, enhance credibility, and help in guiding students interested in STEM careers. For certain alternative certification pathways, relevant work experience might be considered favorably.
What are alternatives to classroom teaching with this background?
A background in science and education opens doors to many related fields. Alternatives include curriculum development, instructional design, educational technology, science communication (writing, journalism, museum work), science policy advising, educational consulting, professional development training, or working for non-profits focused on science outreach.
How does AI impact job security in this field?
While AI tools may automate certain tasks (like grading multiple-choice tests or providing basic explanations), they are unlikely to replace the core role of a science teacher in the foreseeable future. Effective teaching involves complex human interactions: fostering curiosity, managing classroom dynamics, providing mentorship, adapting to individual student needs, and facilitating hands-on inquiry—skills AI cannot replicate. AI is more likely to become a tool that teachers leverage, rather than a replacement.
Conclusion
Embarking on a career as a Science Teacher is a commitment to fostering scientific understanding and inspiring the next generation of thinkers, innovators, and citizens. It demands a strong foundation in science, a passion for teaching, and dedication to continuous learning. While the path involves challenges, from navigating educational requirements to adapting to evolving classroom dynamics, the rewards of sparking curiosity and empowering students with scientific knowledge are profound. Whether you are just starting your journey or considering a career change, the world needs dedicated science educators who can make the wonders of science accessible and engaging for all learners.
Useful Resources
Below are some resources that may be helpful for current and aspiring science teachers:
- National Science Teaching Association (NSTA): A major professional organization for science educators in the US, offering resources, publications, and professional development opportunities.
- Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS): Provides K–12 science content standards to improve science education for all students (primarily US-focused but influential globally).
- PhET Interactive Simulations: Free, research-based interactive math and science simulations from the University of Colorado Boulder.
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics - Education Occupations: Provides information on job outlook, salaries, and requirements for various teaching roles in the US.
- National Center for Education Statistics (NCES): The primary federal entity for collecting and analyzing data related to education in the U.S. and other nations.
- OpenCourser - Browse Science Courses: Explore a wide range of online courses in various scientific disciplines.
- OpenCourser - Browse Education Courses: Find online courses related to teaching methods, educational psychology, and curriculum development.
- OpenCourser Learner's Guide: Access articles and resources on how to effectively use online courses for professional development and skill acquisition.
Becoming a science teacher is a challenging yet deeply rewarding path, offering the chance to make a lasting impact by sharing the power and wonder of scientific discovery.