Social Media Management
vigating the World of Social Media Management
Social Media Management is the strategic orchestration of a brand's or individual's online presence across various social media platforms. It encompasses a wide array of activities, from crafting and publishing engaging content to analyzing performance and fostering community interaction. At its core, social media management aims to build and maintain a positive public image, drive engagement, and achieve specific organizational or personal goals. This dynamic field requires a blend of creativity, analytical prowess, and a deep understanding of online communication trends.
Working in social media management can be an engaging and exciting career path. It offers the opportunity to be at forefront of digital communication, shaping how organizations connect with their audiences. Professionals in this field often find satisfaction in crafting compelling narratives, building vibrant online communities, and seeing the direct impact of their work on brand perception and business objectives. The constant evolution of social media platforms and trends also means that it's a career of continuous learning and adaptation, appealing to those who thrive in dynamic environments.
Introduction to Social Media Management
Social Media Management is a multifaceted discipline focused on curating and maintaining an organization's or individual's presence on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, X (formerly Twitter), LinkedIn, TikTok, and YouTube. It involves developing strategies, creating and scheduling content, engaging with followers, analyzing data, and managing online communities. The ultimate aim is to enhance visibility, build brand loyalty, and drive desired actions, such as website visits or purchases.
Definition and scope of social media management
Social media management is the process of creating, scheduling, analyzing, and engaging with content posted on social media platforms. This isn't just about posting updates; it's about managing a comprehensive social media strategy. This includes everything from developing content that resonates with the target audience to monitoring conversations and responding to feedback. The scope is broad, covering content creation, community management, advertising, analytics, and more. It requires a strategic blend of data-driven insights, engaging content, and authentic audience interactions.
The field is constantly evolving with new platforms emerging and user behaviors shifting. Social media managers must stay agile and adapt their strategies accordingly. This means not only understanding current platforms but also anticipating future trends and how they might impact their approach.
Ultimately, effective social media management translates likes and shares into tangible value, such as increased sales, lead generation, or improved customer loyalty. It's about proving the return on investment (ROI) of social media efforts and demonstrating how they contribute to overall business growth.
Role in modern business and communication
In today's digital world, social media management plays a critical role in how businesses communicate and operate. It's no longer an optional extra but a fundamental component of a successful marketing and communication strategy. A strong social media presence can significantly amplify brand awareness, support customer care, and extend reach to new audiences. Many companies, like Duolingo and Patagonia, have famously leveraged innovative social media strategies to win over new fans and customers.
Social media has become a primary channel for marketing and customer service. It allows brands to publish relevant content and communicate directly with customers, identifying opportunities to improve products and services. Increasingly, social media permeates various aspects of a business, with social media managers engaging directly with customers, maintaining brand reputation, collecting valuable customer insights in real-time, and providing customer support.
The importance of social media management is underscored by user behavior. For example, a significant percentage of consumers rely on social media to guide their purchasing decisions. Platforms like Instagram have become top choices for brands, with a high percentage of users following businesses and making purchases after seeing products or services promoted.
Key objectives and benefits for organizations
Organizations invest in social media management to achieve a variety of key objectives. A primary goal is to increase brand awareness and visibility. A consistent and engaging presence across social platforms helps businesses reach a larger audience and become more familiar and accessible. This, in turn, can lead to increased trust and loyalty among customers.
Another crucial objective is improved customer engagement and communication. Social media provides a direct line to customers, allowing for real-time interaction, feedback collection, and the fostering of a sense of community. This active engagement helps in handling complaints quickly and building stronger customer relationships.
Furthermore, social media management aims to drive website traffic and conversions. By sharing valuable content and targeted advertisements, businesses can lead users to their websites and encourage desired actions, ultimately contributing to sales and revenue growth. Social media is also a cost-effective marketing initiative compared to many traditional advertising methods. Aligning marketing initiatives with user behavior on these platforms is a significant benefit.
These courses offer a solid foundation in understanding the objectives and benefits of social media management.
Core Strategies in Social Media Management
Effective social media management hinges on a set of core strategies that guide content, engagement, and overall platform presence. These strategies are designed to not only capture attention but also to build meaningful connections with the target audience and achieve specific business outcomes. Mastering these strategies is crucial for any social media professional looking to make a significant impact.
Content creation and curation techniques
Content is the cornerstone of any social media strategy. Effective content creation involves developing original, high-quality, and engaging material that resonates with the target audience. This can range from compelling visuals like photos and videos to informative blog posts and interactive polls. The key is to understand what your audience is looking for and to provide value, whether it's information, entertainment, or inspiration. When creating content, it's important to ensure clarity in your message and to maintain consistency in your posting schedule to keep your audience engaged.
Visuals play a critical role in grabbing attention on social media. Posts with images or videos consistently receive more engagement than text-only posts. This includes using a mix of photos, graphics with text overlay, and videos. High-quality, eye-catching graphics and making posts actionable (e.g., asking a question or sharing a link) are effective tactics. Furthermore, content should be optimized for mobile devices, as a majority of social media consumption happens on these devices.
Content curation, on the other hand, involves sharing relevant content from other sources. This can help position your brand as a valuable resource and thought leader within your industry. A common guideline is the "rule of thirds": one-third of your content promotes your business, one-third shares personal stories or brand insights, and one-third shares insights from experts or influencers. It's also beneficial to use keyword research to generate content ideas that address what your audience is searching for.
These courses can help you master content creation and curation for social media.
For those looking to delve deeper into the principles of content strategy, these books offer valuable insights.
You might also find these topics on OpenCourser relevant to developing your content creation skills.
Audience engagement and community building
Social media is fundamentally about connection and interaction. Effective audience engagement goes beyond simply broadcasting messages; it involves fostering a two-way dialogue and building a vibrant online community. This means actively responding to comments and messages, participating in relevant conversations, and encouraging user-generated content (UGC). When brands engage authentically, they build trust and loyalty.
Understanding your audience is the first step to meaningful engagement. This involves researching their interests, needs, pain points, and online behaviors. Once you know who you're talking to, you can tailor your content and interactions to resonate with them. Interactive content formats, such as polls, Q&As, and contests, are excellent ways to boost engagement and make your audience feel involved.
Community building involves creating a space where your audience feels connected to your brand and to each other. This can be achieved by consistently interacting with followers, showcasing UGC, and even creating private or niche communities for more focused discussions. Actively listening to your audience and incorporating their feedback not only improves engagement but also provides valuable insights for product and service development.
These online courses can equip you with strategies for effective audience engagement and community building.
Consider exploring these related topics on OpenCourser to deepen your understanding.
Cross-platform strategy integration
Most businesses maintain a presence on multiple social media platforms to reach diverse audiences. A cross-platform strategy ensures that these efforts are coordinated and work harmoniously towards common goals. This doesn't mean posting the exact same content everywhere; rather, it involves adapting your message and format to suit the unique characteristics and user expectations of each platform. For instance, content that performs well on LinkedIn, a professional networking site, will likely differ significantly from content suited for TikTok, known for its short-form, entertaining videos.
Effective cross-platform integration involves understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each channel and how they can complement each other. For example, you might use Instagram for visually driven brand storytelling, Twitter for real-time updates and customer service, and LinkedIn for industry insights and B2B engagement. The goal is to create a cohesive brand experience across all touchpoints, reinforcing your core message while tailoring the delivery for optimal impact on each platform.
This also means ensuring that your social media efforts are aligned with your broader marketing objectives. Social media should not operate in a silo but rather as an integral part of your overall marketing mix. Analyzing data across platforms can provide a holistic view of your audience and campaign performance, allowing for more informed strategic decisions.
To learn more about integrating your strategies across different platforms, consider these resources.
This book provides further insights into integrating various marketing channels.
Explore this related topic on OpenCourser.
Tools and Technologies
The landscape of social media management is greatly enhanced by a variety of tools and technologies. These platforms and software solutions help professionals streamline workflows, gain deeper insights from data, and ultimately manage their social media presence more efficiently and effectively. From scheduling posts to analyzing campaign performance, these tools are indispensable for the modern social media manager.
Overview of social media management software
Social media management software encompasses a range of tools designed to help individuals and businesses manage their social media activities from a centralized dashboard. These platforms typically offer features for content scheduling, publishing across multiple networks, monitoring mentions and engagement, and collaborating with team members. Popular examples include Hootsuite, Buffer, Sprout Social, Agora Pulse, and Sendible. Each tool often has its own unique set of features and pricing plans, catering to different needs and budgets.
The primary benefit of using such software is efficiency. Instead of logging into multiple social media accounts individually, managers can oversee all their channels in one place. This saves significant time and allows for a more coordinated approach to content distribution and engagement. Many of these tools also offer features to help discover relevant content to share and to identify key influencers in a particular industry.
When selecting social media management software, it's important to consider factors such as the number of social profiles you need to manage, the specific features you require (e.g., advanced analytics, team collaboration tools, approval workflows), the user-friendliness of the interface, and the overall cost. Many platforms offer free trials or basic free plans, allowing users to test the software before committing to a paid subscription. You can explore OpenCourser for courses on specific social media management tools.
These courses provide an introduction to popular social media management platforms.
This topic on OpenCourser provides a broader overview of available tools.
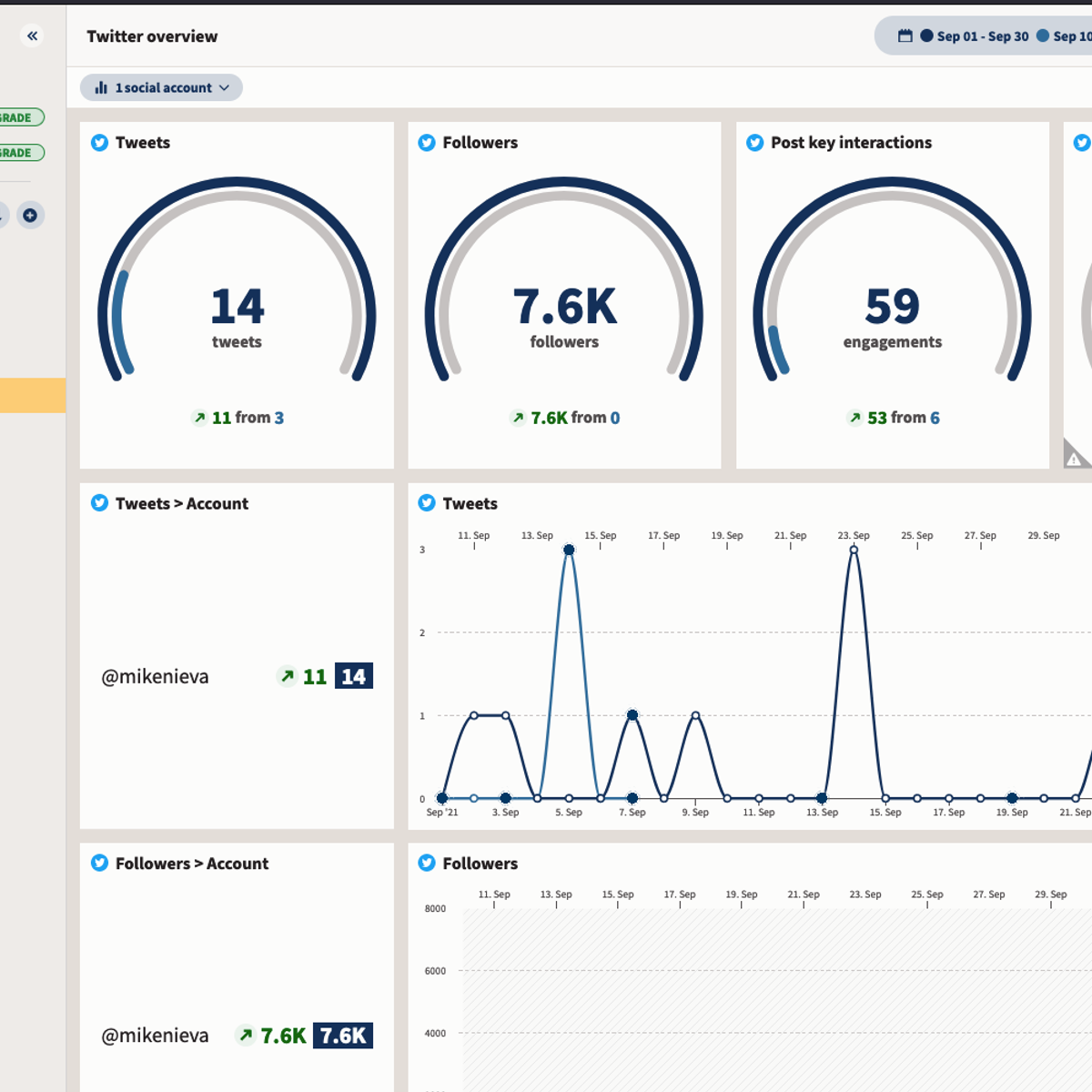
Analytics and performance tracking tools
Understanding how your social media content is performing is crucial for refining your strategy and demonstrating ROI. Analytics and performance tracking tools provide the data needed to measure key metrics, identify trends, and gain insights into audience behavior. Most social media platforms offer their own native analytics (e.g., Facebook Audience Insights, Instagram Insights, Twitter Analytics), which provide valuable information about reach, engagement, follower demographics, and post performance.
Beyond native analytics, many third-party tools offer more advanced reporting capabilities and the ability to track performance across multiple platforms in a consolidated view. Tools like Google Analytics can be used to track website traffic originating from social media, helping to measure the impact of social efforts on broader business goals. Social media management platforms like Hootsuite, Sprout Social, and Buffer also include robust analytics features.
Key metrics commonly tracked include engagement rates (likes, comments, shares), reach and impressions, follower growth, click-through rates (CTR), and conversion rates. Analyzing this data helps social media managers understand what content resonates most with their audience, the best times to post, and how different campaigns are performing against their objectives. This data-driven approach allows for continuous optimization and more effective social media strategies.
These courses can help you get started with social media analytics.
For further reading on leveraging social media data, consider this book.
Explore these related topics on OpenCourser.
Automation and scheduling platforms
Automation and scheduling platforms are essential for maintaining a consistent and strategic social media presence without requiring constant manual intervention. These tools allow social media managers to plan and schedule posts in advance, ensuring a steady flow of content even during busy periods or outside of working hours. This frees up time for managers to focus on other critical tasks like engagement, strategy development, and performance analysis.
Most comprehensive social media management software, such as Hootsuite, Buffer, and Sprout Social, offer robust scheduling capabilities. These platforms often allow users to create a content calendar, visually plan their posts, and automatically publish them at optimal times for audience engagement. Some tools also offer features for "evergreen" content recycling, automatically re-sharing successful past posts to maximize their reach.
While automation is a powerful tool for efficiency, it's important to use it wisely. Over-automating can lead to a robotic or impersonal presence. The best approach is to balance scheduled content with real-time engagement and spontaneous posts that react to current events or trending topics. AI is increasingly being integrated into these platforms to help with tasks like optimizing posting schedules based on audience activity, generating content ideas, and even automating responses to common inquiries.
These courses explore how to effectively use scheduling and automation tools.
For more on automating social media tasks, you might find this topic helpful.
Trends Shaping Social Media Management
The field of social media management is in a constant state of flux, driven by technological advancements, evolving user behaviors, and the emergence of new platforms. Staying ahead of these trends is crucial for professionals who want to maintain relevance and effectiveness in their strategies. Understanding these shifts allows for proactive adaptation and the leveraging of new opportunities.
Emerging platforms and user behavior shifts
The social media landscape is continuously expanding, with new platforms gaining traction and existing ones evolving. While established giants like Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube remain dominant, platforms like TikTok have seen explosive growth, particularly among younger audiences, reshaping content consumption habits towards short-form video. We are also seeing a rise in nostalgia-inspired networks and platforms prioritizing simplicity, authenticity, and more personal connections, suggesting a potential shift away from passive content consumption towards more meaningful engagement.
User behavior is also undergoing significant changes. There's a growing demand for authentic and transparent content, with users increasingly valuing genuine interactions over overly polished corporate messaging. User-generated content (UGC) continues to be a powerful force, often seen as more trustworthy and relatable. Furthermore, social fatigue and selective engagement are becoming more prevalent, meaning brands need to work harder to capture and retain audience attention. The rise of private communities and niche platforms also indicates a desire for more focused and intimate online interactions.
Social media managers must keep a pulse on these emerging platforms and shifts in user behavior to adapt their strategies effectively. This includes experimenting with new formats, understanding the nuances of different demographics, and prioritizing content that fosters genuine connection and provides real value. The ability to quickly identify and leverage trends, or "trendjacking," when done strategically, can lead to significant engagement boosts.
These courses offer insights into the evolving social media landscape and user behaviors.
This book explores how social media is disrupting various aspects of our lives.
Stay updated on these related topics on OpenCourser.
Impact of AI and machine learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are rapidly transforming social media management, moving beyond basic task automation to become integral strategic partners. Generative AI tools like ChatGPT are now widely used for content creation, helping marketers brainstorm ideas, draft posts, and even generate images and videos. This allows for content creation at scale and helps combat creative burnout.
AI is also enhancing social listening and analytics capabilities. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify trends, gauge audience sentiment, and provide predictive insights into content performance. This enables social media teams to make more data-driven decisions and optimize their strategies in real-time. Furthermore, AI is being used to personalize user experiences, delivering tailored content and recommendations. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are also becoming more sophisticated, handling customer inquiries and providing 24/7 support.
The integration of AI is leading to more efficient workflows and more effective campaigns. As AI technology continues to evolve, social media managers who embrace these tools and develop AI literacy will be better equipped to drive efficiency, gain deeper insights, and enhance overall marketing effectiveness. According to Hootsuite's 2025 Social Media Trends report, organizations that prioritize agility in their strategies also prioritize AI use across their social teams.
Explore the impact of AI on social media with these courses.
This book delves into the intersection of big data and social media.
For more on AI's role, check out these topics on OpenCourser.
Influence of video content and live streaming
Video content, particularly short-form video, continues to dominate the social media landscape and is a key driver of engagement. Platforms like TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts have conditioned users to consume and create brief, often entertaining or informative, video clips. This trend shows no signs of slowing down, with even platforms traditionally focused on other formats, like LinkedIn, incorporating more video features.
Live streaming has also carved out a significant niche, offering an unscripted and immediate way to connect with audiences. Facebook Live, Instagram Live, and other platforms enable brands to host Q&A sessions, behind-the-scenes tours, product demonstrations, and live events, fostering a sense of presence and direct interaction. Live video often receives higher engagement and is prioritized by platform algorithms.
For social media managers, this means that a strong video strategy is essential. This includes creating high-quality, visually appealing videos that are optimized for each platform and experimenting with different formats, from quick, "snackable" clips to longer-form storytelling. Leveraging video effectively can lead to increased reach, higher engagement rates, and a more dynamic brand presence. As noted by Forbes, the landscape is shifting as platforms like Instagram and TikTok lean into high-production, algorithm-driven video content.
These courses can help you develop your skills in creating video content for social media.
Explore these related topics on OpenCourser for more information.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Navigating the ethical and legal landscape is a critical aspect of social media management. As platforms and regulations evolve, professionals in this field must stay informed and vigilant to ensure their practices are responsible, compliant, and respectful of user rights. Failure to do so can lead to significant reputational damage and legal repercussions.
Data privacy and user consent issues
Data privacy is a paramount concern in social media management. With regulations like GDPR in Europe and various state-level laws in the U.S., how organizations collect, store, and use personal data from social media users is under strict scrutiny. Social media managers must be knowledgeable about these regulations and ensure their practices are compliant. This includes obtaining proper consent before collecting user data, being transparent about how data is used, and providing users with options to control their information.
The use of tracking technologies, such as cookies and pixels, for advertising and analytics also falls under these privacy considerations. It's crucial to inform users about these practices and obtain their consent where required. Data breaches are another significant risk, and organizations must implement robust security measures to protect user data collected through social media channels.
Ethical data handling goes beyond mere compliance. It involves respecting user privacy even when not explicitly mandated by law and being mindful of the potential impact of data collection and usage on individuals. Building trust with your audience means being responsible stewards of their personal information. According to Forbes, data privacy and compliance are emerging trends that social media managers need to highlight on their resumes.
This course touches upon ethical considerations in the digital space.
These books explore the broader societal and ethical implications of social media.
Explore these related topics on OpenCourser for more detailed information.
Content moderation challenges
Content moderation presents a significant and ongoing challenge for social media managers and platforms alike. This involves monitoring user-generated content and online discussions to identify and address problematic material, such as hate speech, harassment, misinformation, and illegal content. While platforms have their own community standards and moderation systems, brands are also responsible for the content and conversations happening on their own channels.
The sheer volume of content generated on social media makes manual moderation an immense task. Automated tools and AI can assist in flagging potentially problematic content, but human oversight is often still necessary to handle nuanced cases and avoid errors. Striking a balance between fostering open discussion and maintaining a safe and respectful online environment is a delicate act. Overly aggressive moderation can be perceived as censorship, while insufficient moderation can lead to a toxic community.
Developing clear community guidelines for your brand's social media channels and consistently enforcing them is crucial. Social media managers need to be prepared to handle negative feedback, trolls, and potentially harmful content in a professional and timely manner. This often involves having clear protocols for escalating issues and, in some cases, involving legal or law enforcement agencies.
This course offers insights into managing online reputation, which is closely tied to content moderation.
This book discusses regulatory aspects of social media content.
Consider these topics on OpenCourser for further exploration.
Regulatory compliance across regions
For organizations with a global or multi-regional presence, navigating the complex web of regulatory compliance across different jurisdictions is a significant challenge. Social media laws and regulations can vary widely from one country or region to another, covering areas such as data privacy, advertising standards, content restrictions, and consumer protection.
For example, advertising disclosure requirements for sponsored content or influencer marketing can differ significantly. What might be an acceptable advertising practice in one country could be illegal in another. Similarly, rules around contests and promotions on social media can vary. Social media managers operating internationally must be aware of these diverse legal landscapes and ensure their campaigns and content comply with all applicable local laws.
This often requires working closely with legal counsel to understand the specific requirements in each target market. It may also involve tailoring social media strategies and content for different regions to ensure compliance. Staying updated on changes in international regulations is an ongoing responsibility, as laws in this area are continually evolving. Ignorance of local laws is not a defense, and non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and legal disputes. According to Forbes, data privacy and compliance are key areas for social media professionals to be aware of.
While specific courses on regional regulatory compliance are niche, understanding general marketing law is a good start.
This book offers guidance on the legal aspects of social media for businesses.
Explore these OpenCourser topics for more context.
Career Pathways in Social Media Management
A career in social media management offers diverse opportunities for growth and specialization. As businesses increasingly recognize the importance of a strong online presence, the demand for skilled social media professionals continues to rise. Whether you're just starting or looking to advance, understanding the various roles, required skills, and potential career trajectories can help you navigate this dynamic field.
If you're considering a career transition into social media management, or are new to the field, it's natural to feel a mix of excitement and perhaps some apprehension. This is a field that values creativity, communication, and adaptability – skills that are often transferable from other professions. While the digital landscape is ever-changing, the core principles of connecting with people and telling compelling stories remain constant. Be encouraged that with dedication to learning and a willingness to experiment, you can build a rewarding career. Ground yourself in the fundamentals, stay curious, and don't be afraid to start small and build your experience. Many successful social media managers began by managing accounts for small businesses, non-profits, or even their own passion projects.
Entry-level roles and required skills
Entry-level positions in social media management often include titles like Social Media Coordinator, Social Media Assistant, or Digital Content Creator. These roles typically involve tasks such as drafting and scheduling posts, monitoring social media channels for mentions and comments, assisting with content creation (graphics, basic video editing), and compiling performance reports. It's a great way to gain hands-on experience and learn the fundamentals of social media operations.
Key skills for entry-level roles include strong written and verbal communication abilities, as crafting engaging copy and interacting with audiences is paramount. A good understanding of major social media platforms (Facebook, Instagram, X, LinkedIn, TikTok, etc.) and their respective best practices is essential. Basic design skills, familiarity with content creation tools (like Canva or Adobe Creative Cloud basics), and an analytical mindset to understand basic metrics are also highly valued. Soft skills like creativity, attention to detail, organization, time management, and the ability to work well in a team are equally important.
Many employers look for candidates with a bachelor's degree in marketing, communications, journalism, or a related field, although this is not always a strict requirement, especially if you have a strong portfolio and demonstrable skills. Gaining experience through internships, volunteer work (e.g., managing social media for a local charity or club), or building your own successful social media presence can significantly boost your chances of landing an entry-level job. OpenCourser's Marketing and Communication Studies categories offer a wealth of foundational courses.
These courses are excellent starting points for aspiring social media professionals.
For those starting out, these books can provide a comprehensive overview.
Career progression and specialization options
As social media professionals gain experience, their career paths can diverge in several directions. A common progression involves moving from coordinator or specialist roles to Social Media Manager, then potentially to Senior Social Media Manager, Social Media Strategist, or Head of Social Media. At higher levels, responsibilities shift towards developing overarching strategies, managing teams, overseeing budgets, and working more closely with other marketing and communications departments to ensure alignment with broader business objectives.
Specialization is another popular route. Social media managers might choose to focus on a particular area such as:
- Social Media Advertising Specialist: Concentrating on creating and managing paid advertising campaigns.
- Social Media Analyst: Specializing in data analysis, reporting, and deriving actionable insights from social media metrics.
- Content Marketing Manager: Focusing on the strategy and creation of compelling content across various platforms.
- Community Manager: Dedicated to building, nurturing, and engaging with online communities.
- Influencer Marketing Manager: Managing relationships and campaigns with social media influencers.
With further experience, some social media managers transition into broader digital marketing roles like Digital Marketing Manager or Marketing Director, or even into consultancy. The skills developed in social media management – strategic thinking, content creation, data analysis, and audience engagement – are highly transferable to many other areas of marketing and communications. The field is constantly evolving, so continuous learning and adaptation are key to long-term career growth.
These courses can help experienced professionals specialize or move into strategic roles.
Consider these careers if you're looking at specialization.
Freelancing and entrepreneurial opportunities
Social media management lends itself well to freelancing and entrepreneurial ventures. Many businesses, particularly small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups, may not have the resources or need for a full-time, in-house social media manager. This creates a significant market for freelance social media managers or consultants who can offer their services on a project basis or retainer.
As a freelance social media manager, you can work with a variety of clients across different industries, offering services such as strategy development, content creation, account management, and advertising campaigns. This path offers flexibility in terms of work hours and location, but also requires strong self-discipline, business acumen (client acquisition, invoicing, contract negotiation), and the ability to manage multiple projects simultaneously. Building a strong personal brand and a portfolio of successful projects is crucial for attracting clients.
Entrepreneurial opportunities also exist, such as starting your own social media marketing agency. This involves scaling your operations, potentially hiring other specialists, and managing the business aspects of an agency. Another avenue is to leverage social media expertise to build and monetize your own online presence as an influencer or content creator, or to launch and promote your own products or services. The skills acquired in social media management are directly applicable to building and growing any online business. OpenCourser's Entrepreneurship section has resources for those looking to start their own ventures.
These courses may be particularly useful for those considering freelancing or starting their own social media business.
If you're interested in the entrepreneurial side, these careers might appeal to you.
Educational and Training Resources
Developing the skills and knowledge required for a successful career in social media management can be achieved through various educational and training pathways. From formal academic programs to flexible online courses and industry events, there are numerous resources available for aspiring and established professionals to learn, grow, and stay current in this rapidly evolving field.
Online courses, in particular, offer a highly accessible and flexible way to build a strong foundation in social media management. They are suitable for individuals at all stages of their career, whether you're looking to enter the field, supplement existing education, or upskill as a working professional. Many online courses provide practical, hands-on learning experiences, allowing you to develop job-ready skills. Furthermore, OpenCourser makes it easy to search and compare thousands of online courses, read reviews, and even find deals to make your learning journey more affordable.
Academic programs and certifications
Many universities and colleges now offer academic programs directly related to social media management, often as part of broader degrees in marketing, communications, digital media, or business. These programs typically provide a comprehensive theoretical foundation combined with practical skills development. A bachelor's degree in one of these fields is often cited as a typical educational background for social media managers. Some institutions also offer master's degrees or specialized graduate certificates for those seeking more advanced knowledge.
Professional certifications are another valuable way to validate your skills and enhance your credibility in the field. Several organizations and platforms offer certifications in social media marketing and management. For instance, platforms like Meta (Facebook), Google, and HubSpot Academy offer their own certification programs that cover their specific tools and general social media marketing principles. Industry bodies like the Digital Marketing Institute also provide recognized certifications. These certifications can be particularly beneficial for those looking to demonstrate proficiency in specific areas or to potential employers. When pursuing certifications, check the deals page on OpenCourser as sometimes discounts are available for certification programs or their preparatory courses.
These programs can provide structured learning and recognized credentials.
Many reputable books also cover the material needed for certification or academic programs.
Online courses and self-paced learning
Online courses have become an incredibly popular and effective way to learn social media management skills. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, edX, and others host a vast array of courses, ranging from introductory overviews to deep dives into specific platforms, strategies, and tools. These courses are often self-paced, allowing learners to study at their convenience, which is ideal for those balancing studies with work or other commitments. Many courses are taught by industry experts or affiliated with reputable universities, offering high-quality instruction.
Online learning is suitable for various individuals. Students can use online courses to supplement their formal education, gaining practical skills that may not be covered in depth in traditional curricula. Professionals already working in marketing or other fields can use them to pivot into social media management or to update their existing skill sets with the latest trends and tools. Aspiring social media managers can build a foundational understanding and a portfolio of work through project-based online courses. OpenCourser's Learner's Guide offers valuable tips on how to make the most of online learning, including how to create a structured curriculum for yourself and stay disciplined.
To supplement online coursework, learners can engage in practical projects. This could involve creating a mock social media campaign for a fictional brand, managing the social media for a small local business or non-profit on a volunteer basis, or even building and growing their own personal brand on social media. These hands-on experiences are invaluable for applying learned concepts and for building a portfolio to showcase to potential employers.
Here are some highly-rated online courses available for self-paced learning:
These books are also excellent resources for self-study.
Workshops and industry conferences
Workshops and industry conferences offer valuable opportunities for learning, networking, and staying abreast of the latest developments in social media management. Workshops, whether online or in-person, often provide intensive, hands-on training in specific skills or tools. They can be a great way to quickly get up to speed on a new platform, learn advanced techniques, or focus on a niche area like social media analytics or advertising.
Industry conferences bring together experts, thought leaders, practitioners, and vendors from across the social media and digital marketing landscape. Attending these events allows you to hear about cutting-edge trends, best practices, and case studies directly from those shaping the field. Keynote presentations, panel discussions, and breakout sessions can provide a wealth of knowledge and inspiration. Furthermore, conferences are excellent networking venues, offering chances to connect with peers, potential mentors, collaborators, and employers.
While the cost of attending conferences can sometimes be a barrier, many events offer virtual attendance options or make recordings of sessions available afterward. Some organizations also provide scholarships or discounts for students or professionals early in their careers. Following industry publications, thought leaders on social media, and professional organizations can help you identify relevant workshops and conferences. These experiences can be particularly beneficial for understanding emerging trends like AI in social media or new platform functionalities before they become mainstream.
While OpenCourser primarily focuses on online courses and books, keeping an eye on industry event calendars from organizations like Social Media Examiner or Content Marketing Institute can be beneficial. For now, consider these broad courses that cover strategic elements often discussed at conferences.
Challenges and Risk Management
While social media offers immense opportunities, it also comes with its share of challenges and risks. Effective social media management involves not only leveraging the positive aspects but also being prepared to navigate and mitigate potential downsides. From handling crises to managing online reputation and combating misinformation, a proactive and strategic approach to risk management is essential.
Crisis communication strategies
A social media crisis can erupt quickly and cause significant damage to a brand's reputation if not handled effectively. Crises can stem from various sources, such as negative customer experiences going viral, product recalls, controversial company statements, employee misconduct, or external events impacting the brand. A well-defined crisis communication strategy is crucial for navigating these situations calmly and effectively.
Key components of a social media crisis communication plan include:
- Monitoring: Continuously monitoring social media channels for mentions, sentiment shifts, and potential emerging issues. Social listening tools can be invaluable here.
- Assessment: Quickly assessing the severity and potential impact of a situation to determine if it constitutes a crisis.
- Response Team: Designating a clear response team with defined roles and responsibilities.
- Communication Protocols: Establishing clear protocols for internal communication and for external messaging, including who is authorized to speak on behalf of the company and what key messages should be conveyed.
- Timeliness: Responding promptly is critical. Silence or delayed responses can often exacerbate a crisis.
- Transparency and Honesty: Addressing the issue openly and honestly, acknowledging mistakes if they occurred, and outlining steps being taken to rectify the situation.
- Platform-Specific Responses: Tailoring responses to the specific platform where the crisis is unfolding.
- Post-Crisis Analysis: After the immediate crisis has subsided, conducting a thorough review to understand what happened, how it was handled, and what lessons can be learned to prevent future occurrences or improve future responses.
Having a plan in place before a crisis hits allows for a more measured and effective response, rather than reacting in an ad-hoc manner under pressure. Regular training and simulations can also help prepare the team.
These courses can help build foundational knowledge relevant to crisis communication.
This book specifically addresses crisis management in the digital age.
Explore this related topic on OpenCourser.
Reputation management techniques
Online reputation management (ORM) is an ongoing process of monitoring, influencing, and protecting a brand's image on the internet, particularly on social media. A positive online reputation is a valuable asset, while a negative one can deter customers and damage credibility. Social media managers play a key role in ORM by actively managing the brand's presence and interactions.
Key techniques for social media reputation management include:
- Proactive Content Strategy: Consistently publishing positive and valuable content that showcases the brand's values, expertise, and positive customer experiences.
- Engagement: Actively engaging with the audience, responding to comments and messages (both positive and negative) in a timely and professional manner. Addressing complaints constructively can often turn a negative situation into a positive one.
- Monitoring Mentions: Using social listening tools to track brand mentions, keywords, and industry conversations to stay informed about what is being said about the brand and its competitors.
- Encouraging Positive Reviews: Ethically encouraging satisfied customers to leave positive reviews and testimonials on relevant platforms.
- Addressing Negative Feedback: Developing a strategy for handling negative reviews and comments. This often involves acknowledging the feedback, taking the conversation offline if necessary, and working towards a resolution.
- SEO for Reputation: Ensuring that positive content about the brand ranks prominently in search engine results.
Building a strong, positive reputation takes time and consistent effort. It's about fostering genuine relationships with your audience and demonstrating that you value their feedback and are committed to providing a good experience.
This course is highly relevant to understanding and implementing reputation management.
This book offers insights into maintaining a positive online image.
Mitigating misinformation and fake accounts
The spread of misinformation and the proliferation of fake accounts are significant challenges on social media platforms, and brands are not immune to their impact. Misinformation about a company, its products, or its services can spread rapidly, causing reputational damage and confusing customers. Fake accounts can be used to impersonate brands, spread false narratives, or engage in fraudulent activities.
Strategies for mitigating these risks include:
- Vigilant Monitoring: Actively monitoring social media for mentions of the brand and for accounts that may be impersonating it.
- Fact-Checking: Quickly addressing and correcting any misinformation about the brand with factual, verifiable information.
- Reporting Fake Accounts: Promptly reporting fake or impersonator accounts to the respective social media platforms for removal. Most platforms have established procedures for this.
- Educating Your Audience: Making your audience aware of your official social media channels and advising them to be cautious of unofficial sources or suspicious accounts.
- Building Trust through Transparency: Consistently providing accurate and transparent information to build credibility with your audience, making them less susceptible to misinformation.
- Verification: Where possible, getting official accounts verified (e.g., the blue checkmark on X or Instagram) can help users distinguish authentic accounts from fakes.
Combating misinformation is an ongoing battle that requires diligence and a proactive stance. By being a reliable source of information and actively working to debunk falsehoods, brands can help protect their reputation and their audience.
This course touches upon identifying and handling false information.
Consider this book for a broader understanding of online authenticity.
Global Perspectives and Market Dynamics
As businesses expand their reach across borders, social media management takes on new layers of complexity. Understanding global perspectives and market dynamics is crucial for tailoring strategies that resonate with diverse cultural audiences and navigate varying competitive landscapes. A one-size-fits-all approach rarely succeeds in the international arena.
Cultural adaptation in content strategy
When managing social media for a global audience, cultural adaptation in content strategy is paramount. What resonates with one culture might be ineffective or even offensive in another. This goes beyond simple language translation and involves understanding cultural nuances, values, beliefs, humor, and social etiquette. Content, including visuals, copy, and even the choice of social media platforms, needs to be localized to ensure it is relevant and respectful to each target market.
Effective cultural adaptation requires thorough research into the target audience's cultural background. This might involve working with local teams or consultants who have an intimate understanding of the local culture. It also means being mindful of imagery, symbols, colors, and references that might have different connotations in different cultures. For example, a hand gesture that is positive in one culture could be offensive in another. Similarly, humor often does not translate well across cultures.
A successful global social media strategy balances brand consistency with local relevance. While the core brand message might remain the same, the execution and an_article_about_how_to_learn_social_media_management_in_html_format should be adapted to reflect local cultural preferences and sensitivities. This demonstrates respect for the local audience and can significantly improve engagement and brand perception.
While specific courses on cultural adaptation for every region are rare, foundational courses in international marketing can provide a good starting point.
This book offers broader perspectives on social media's global impact.
You may find this topic on OpenCourser helpful.
Market entry challenges and localization
Entering new international markets with a social media presence presents unique challenges. Beyond cultural adaptation, businesses must consider practical aspects such as language barriers, preferred social media platforms (which can vary significantly by region), local internet penetration rates, and device usage habits. For instance, while Facebook is dominant in many Western countries, platforms like WeChat are essential in China, and VKontakte is popular in Russia.
Localization is the process of adapting a product or content to a specific locale or market. In social media, this involves not just translating content accurately but also ensuring it is culturally appropriate and relevant. This might mean creating entirely new content for specific markets rather than just translating existing materials. It also involves understanding local trends, holidays, and current events that can be incorporated into the content strategy to make it more engaging for the local audience.
Other market entry challenges can include navigating local regulations related to advertising and data privacy, understanding the competitive landscape in the new market, and building relationships with local influencers or partners. A thorough market research phase is essential before launching social media activities in a new country or region. This helps in identifying potential challenges and developing strategies to overcome them.
Courses on international business or global marketing strategies often cover market entry and localization.
This book discusses broader market optimization, which includes localization aspects.
Competitive landscape analysis
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for effective social media management, both domestically and internationally. A competitive analysis involves identifying key competitors, analyzing their social media strategies, and assessing their strengths and weaknesses. This information can help you identify opportunities, differentiate your brand, and refine your own social media approach.
Key areas to examine in a competitive analysis include:
- Platform Presence: Which social media platforms are your competitors active on?
- Audience Size and Engagement: How large is their following, and how engaged is their audience (likes, comments, shares)?
- Content Strategy: What types of content are they posting? What is their tone and voice? How frequently do they post?
- Strengths: What are they doing particularly well? What seems to resonate with their audience?
- Weaknesses: Where are their gaps or areas for improvement? Are there audience needs they are not addressing?
- Key Differentiators: What makes their brand and social media presence unique?
Tools for social listening and social media analytics can be helpful in gathering data on competitors. The goal of competitive analysis is not to simply copy what others are doing, but to gain insights that can inform your own unique strategy. By understanding what works well in your industry and where there are unmet needs, you can position your brand more effectively and create a more compelling social media presence.
These courses can provide frameworks for analyzing market dynamics.
This topic is directly relevant to understanding your market position.
Frequently Asked Questions (Career Focus)
Embarking on or advancing a career in social media management often brings up many questions. This section aims to address some of the most common queries from job seekers and career changers, providing clarity and guidance to help you navigate your professional journey in this exciting field.
What qualifications are needed for entry-level roles?
For entry-level social media roles, such as Social Media Coordinator or Assistant, employers typically look for a blend of education, skills, and practical experience. A bachelor's degree in fields like marketing, communications, journalism, or public relations is often preferred, but not always mandatory. Demonstrable skills and a strong portfolio can sometimes outweigh formal education.
Essential skills include excellent written and verbal communication, a solid understanding of major social media platforms (Facebook, Instagram, X, LinkedIn, TikTok, etc.), creativity, and attention to detail. Basic graphic design skills (e.g., using Canva) and familiarity with social media management tools are also advantageous. Perhaps most importantly, showcasing a genuine passion for social media and an eagerness to learn is key. Experience gained through internships, volunteer work, or managing personal/club social media accounts can be very valuable.
Building a portfolio, even with personal projects or mock campaigns, can help you demonstrate your abilities to potential employers. Many find that completing online courses or certifications in social media marketing can also strengthen their applications. You can find many such resources on OpenCourser's marketing section.
How to transition from traditional marketing to social media management?
Transitioning from traditional marketing to social media management can be a smooth process, as many core marketing principles apply to both fields. Your understanding of target audiences, branding, campaign development, and communication strategies provides a strong foundation. The key is to build upon this foundation with social media-specific knowledge and skills.
Start by immersing yourself in the world of social media. Actively use various platforms to understand their nuances, user behaviors, and content formats. Follow industry blogs, thought leaders, and attend webinars to stay updated on current trends and best practices. Consider taking online courses or workshops specifically focused on social media strategy, content creation for social platforms, social media advertising, and analytics. Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer a wide range of relevant courses.
Tailor your resume and portfolio to highlight transferable skills and any social media projects you've undertaken, even if they were part of broader traditional marketing campaigns. Emphasize your adaptability and willingness to learn new digital tools and techniques. Networking with professionals already in the social media field can also provide valuable insights and potential opportunities.
These courses can help bridge the gap between traditional and social media marketing.
What are the salary expectations in this field?
Salary expectations in social media management can vary significantly based on factors such as experience level, geographic location, company size and industry, and specific job responsibilities. According to Glassdoor data from January 2025, social media managers in the US earn an average base salary of $60,881. Payscale, as of May 2023, reported an average salary of around $54,600 per year for social media managers.
Entry-level positions like Social Media Coordinator will typically command lower salaries, while senior roles like Social Media Director or Head of Social Media can earn significantly more. For instance, Payscale indicated that Social Media Directors earn around $80,700 annually. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups social media managers under the broader category of advertising, promotions, and marketing managers. For this group, the BLS reported a median annual wage of $127,830 in May 2022, though this figure encompasses a wider range of marketing management roles and experience levels. It is important to research salary benchmarks specific to your location and desired role using resources like Glassdoor, Payscale, LinkedIn Salary, and the BLS.
The job outlook for roles related to social media management is generally positive. The BLS projects an 8% growth for advertising, promotions, and marketing manager roles between 2023 and 2033 in the US, which is faster than the average for all occupations. Zippia reports a projected 10% job growth for marketing/social media managers from 2018-2028. This demand reflects the increasing importance businesses place on social media marketing.
How to build a portfolio without prior experience?
Building a compelling portfolio is crucial for landing a social media management job, especially if you lack formal prior experience. A portfolio demonstrates your skills, creativity, and understanding of social media in a tangible way. Fortunately, there are several ways to create portfolio pieces even without paid client work.
One approach is to create mock campaigns for fictional businesses or brands you admire. Develop a complete social media strategy, create sample content (posts, visuals, short videos), design a content calendar, and outline how you would measure success. Document this process thoroughly. Another option is to volunteer your services to a small local business, non-profit organization, or a friend's startup. This provides real-world experience and tangible results you can showcase. Even managing and significantly growing your own professional social media presence or a passion project's accounts can serve as a powerful case study.
Take screenshots of your best work, including examples of engaging posts, successful campaigns (even small ones), and any analytics that demonstrate growth or positive results. Write brief case studies explaining the objectives, your strategy, the actions you took, and the outcomes. Include any positive feedback or testimonials if available. Online courses often include projects that can be adapted for your portfolio. Remember, quality over quantity is key; showcase your best, most strategic work. Tools like Canva can be used to create professional-looking presentations of your portfolio pieces.
These courses often include projects that can contribute to a portfolio.
What industries hire social media managers most frequently?
Social media managers are in demand across a vast range of industries because virtually every type of organization can benefit from a strong online presence. However, some sectors tend to hire social media professionals more frequently or have a greater reliance on social media for their marketing and communication efforts.
Industries such as retail and e-commerce heavily rely on social media for product promotion, customer engagement, and driving sales. The media and entertainment industries use social media extensively to promote content, engage with fans, and build communities around their shows, movies, or publications. Technology companies, from startups to large corporations, often have robust social media teams to announce products, provide support, and engage with tech-savvy audiences. The travel and hospitality sectors use social media to showcase destinations, share user experiences, and manage bookings and customer service. Non-profit organizations also utilize social media for awareness campaigns, fundraising, and volunteer recruitment.
Furthermore, marketing and advertising agencies frequently hire social media managers to handle the social media accounts of their various clients. The rise of influencer marketing has also created opportunities in almost every consumer-facing industry. Essentially, any organization that needs to connect with an audience, build a brand, or drive engagement online is a potential employer for a social media manager.
Is certification necessary for career advancement?
While not always strictly necessary, certifications can be a valuable asset for career advancement in social media management. They can help you stand out to potential employers, demonstrate specialized knowledge, and show a commitment to professional development in a rapidly changing field. For individuals transitioning into social media or those in the early stages of their careers, certifications can help validate their skills and bridge any experience gaps.
Several types of certifications are available, ranging from platform-specific credentials (e.g., Meta Blueprint, Google Digital Garage) to broader social media marketing certifications from industry organizations or educational institutions. Choosing which certifications to pursue depends on your career goals and the specific areas you wish to specialize in. For example, if you aim to become a social media advertising expert, a certification in Facebook Ads or Google Ads could be highly beneficial.
However, it's important to remember that certifications are just one piece of the puzzle. Practical experience, a strong portfolio showcasing real results, and a deep understanding of social media strategy and execution are equally, if not more, important for career progression. Certifications are best viewed as a supplement to, rather than a replacement for, hands-on experience and continuous learning. Many learners find success by combining online courses that prepare for certifications with practical application of the learned skills. You can explore a variety of professional development courses on OpenCourser to find relevant certifications.
Consider these certification-focused programs:
Conclusion
Social Media Management is a vibrant, essential, and constantly evolving field that sits at the intersection of communication, marketing, technology, and creativity. It offers a dynamic career path for individuals who are passionate about connecting with audiences, crafting compelling narratives, and leveraging the power of online platforms to achieve tangible results. From understanding the core strategies of content creation and audience engagement to navigating the latest technological trends and ethical considerations, the journey of a social media professional is one of continuous learning and adaptation. Whether you are just starting, seeking to transition into this field, or aiming to advance your existing career, the opportunities are plentiful for those willing to dedicate themselves to mastering this craft. With a strong foundation of skills, a commitment to staying current, and a proactive approach to building experience, a fulfilling and impactful career in social media management is well within reach. Remember that resources like OpenCourser are here to support your learning journey every step of the way, offering access to a vast catalog of courses and educational materials to help you succeed.