Market Research Analyst
vigating the World of Market Research Analysis
Market Research Analysts play a pivotal role in helping businesses understand their customers, identify market trends, and make informed decisions. They delve into consumer behavior, assess competitive landscapes, and translate complex data into actionable strategies. This career path is ideal for individuals who are curious, analytical, and possess a knack for uncovering the stories hidden within data. In essence, Market Research Analysts are the detectives of the business world, piecing together clues to solve marketing mysteries and guide companies toward success.
Working as a Market Research Analyst can be an engaging and exciting endeavor. One thrilling aspect is the constant learning and discovery; every project brings new questions and challenges, requiring analysts to explore different industries, consumer segments, and market dynamics. Furthermore, the ability to directly influence business strategy and see the tangible impact of one's research on a company's performance can be incredibly rewarding. Imagine the satisfaction of knowing your insights helped launch a successful product or refine a marketing campaign to better connect with its audience.
What Exactly Does a Market Research Analyst Do?
At its core, the role of a Market Research Analyst revolves around gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data to provide businesses with a clear understanding of their market, customers, and competitors. This involves a blend of research methodologies, analytical rigor, and strategic thinking. These professionals are instrumental in shaping how companies approach product development, marketing campaigns, and overall business growth.
The insights generated by Market Research Analysts help companies make data-backed decisions, reducing risks and optimizing opportunities. They essentially act as a bridge between raw data and strategic action, ensuring that business choices are grounded in evidence rather than intuition alone.
Unpacking the Day-to-Day: Core Responsibilities
The daily life of a Market Research Analyst is dynamic and multifaceted, often involving a variety of tasks aimed at uncovering market intelligence. These professionals are responsible for monitoring and forecasting market trends, which helps businesses anticipate shifts in consumer preferences and industry landscapes. A significant part of their role involves measuring the effectiveness of ongoing marketing programs and strategies, allowing companies to understand what's working and where improvements are needed.
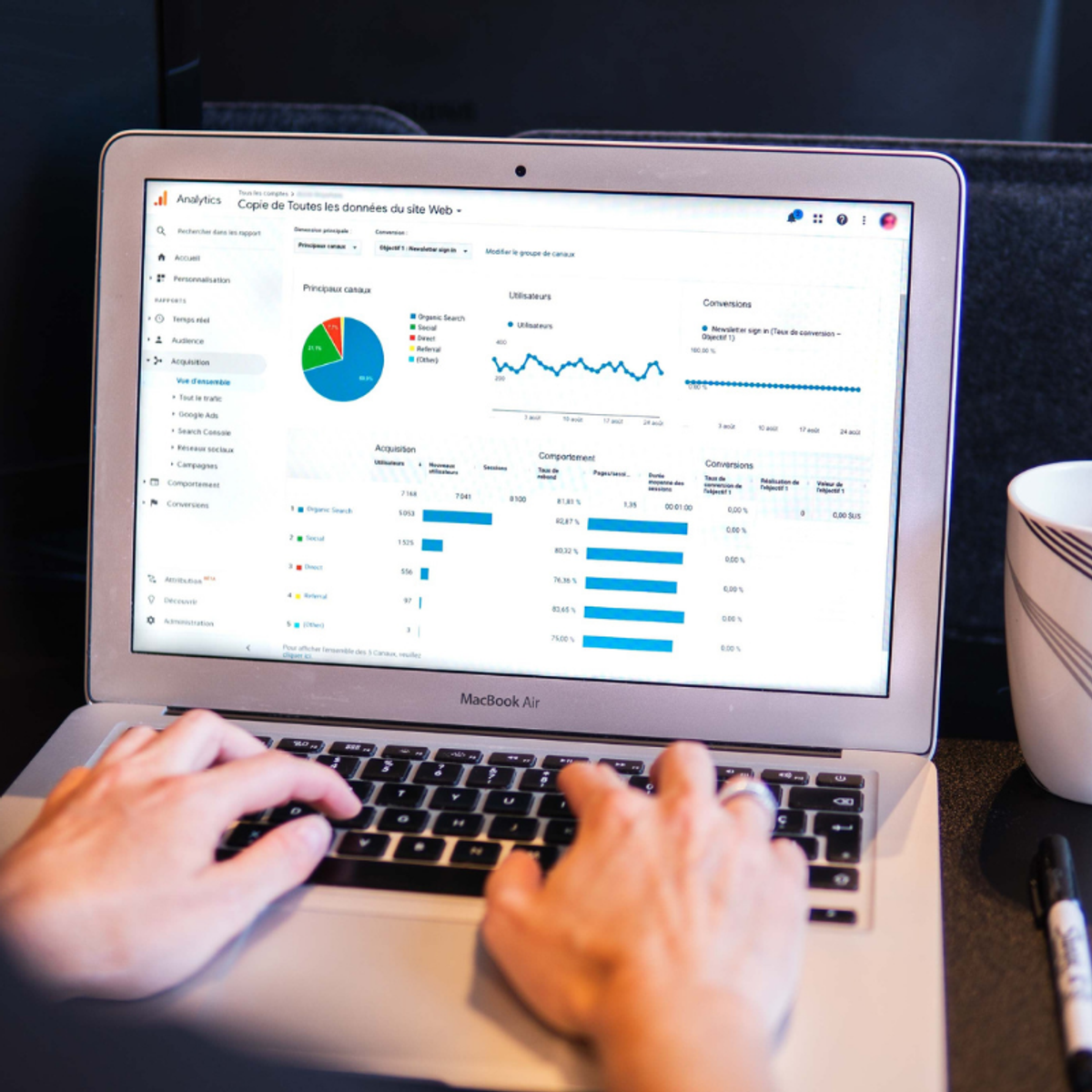
To gather the necessary information, analysts devise and evaluate methods for data collection, such as surveys, questionnaires, and opinion polls. They collect data not only on consumers but also on competitors and broader market conditions to provide a holistic view. Once data is gathered, a crucial step is to analyze it using statistical software, transforming raw numbers into meaningful patterns and insights. Finally, analysts are tasked with converting these complex findings into understandable formats like tables, graphs, and written reports, and presenting these results to clients and management to inform strategic decisions.
For those interested in gaining foundational knowledge in market research, online courses can be a great starting point. These courses often cover the basics of research design, data collection, and introductory analysis.
The Analyst's Role in Guiding Business Strategy
Market Research Analysts are pivotal in steering a company's strategic direction by providing a deep understanding of the marketplace. They identify who the target customers are, what products and services these customers desire, and what price points are viable. This knowledge empowers businesses to tailor their offerings and marketing messages effectively, ensuring they resonate with the intended audience.
By conducting thorough competitor analysis, analysts help businesses understand their position relative to other players in the market. They examine competitors' marketing strategies, pricing models, and sales performance to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This competitive intelligence is crucial for developing strategies that differentiate the company and capitalize on market openings. For instance, understanding how competitors are perceived by consumers can inform a company's own branding and messaging efforts.
Ultimately, the work of a Market Research Analyst culminates in providing actionable recommendations that guide everything from product development to advertising campaigns. Their insights help businesses decide which new markets to enter, what features to prioritize in new products, and how to best communicate their value proposition to potential customers. The ability to translate raw data into strategic imperatives is what makes this role so valuable.
Developing a strong marketing mix is fundamental to executing these strategies. Courses that delve into product policy, distribution channels, communication, and pricing can provide a comprehensive understanding of how to bring a product or service to market successfully.
For a deeper dive into the foundational economic principles that underpin market dynamics, consider exploring these books.
Where Do Market Research Analysts Work? A Look at Industries
Market Research Analysts are employed across a diverse spectrum of industries because most sectors benefit from a deeper understanding of their market and consumers. Their skills are highly transferable, making this a versatile career path. You'll find them in finance and insurance, management and consulting firms, and companies involved in publishing and information services. Manufacturing companies, retail businesses, and wholesale trade operations also rely heavily on market research to stay competitive.
The technology sector, with its rapid innovation cycles and evolving consumer preferences, is a significant employer of Market Research Analysts. Healthcare organizations use market research to understand patient needs and assess the viability of new services or treatments. Even government agencies and non-profit organizations utilize market research to inform public policy and program development. The breadth of industries means that analysts can often find roles that align with their personal interests, whether that's in fashion, entertainment, automotive, or sustainable energy.
The adaptability of market research skills also means that analysts can work for market research agencies that serve multiple clients across different industries, or they can be part of an in-house marketing team dedicated to a single company. This flexibility offers varied work environments and opportunities for specialization.
Understanding the economic landscape of different markets is crucial. These resources provide insights into various economic contexts.
Key Responsibilities of a Market Research Analyst
The role of a Market Research Analyst is multifaceted, encompassing a range of critical duties that drive informed business decisions. These professionals are tasked with a systematic approach to understanding market dynamics, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes.
Designing and Executing Research Initiatives
A primary responsibility of a Market Research Analyst is to design and conduct comprehensive research studies. This often begins with clearly defining the research problem and objectives in collaboration with stakeholders. [13slb2] Analysts then devise appropriate methodologies, which can include quantitative approaches like surveys and questionnaires, or qualitative methods such as focus groups and in-depth interviews.
They are responsible for developing data collection instruments, ensuring questions are unbiased and designed to elicit the required information. For instance, when designing a survey, an analyst must carefully consider the target audience, sample size, and question wording to maximize response rates and data quality. Managing the logistics of data collection, whether it's an online survey distributed to thousands or intimate focus group sessions, also falls under their purview.
The ability to create effective surveys is a core skill. Online courses can help aspiring analysts learn the intricacies of survey design and implementation using various tools.
Analyzing Consumer Behavior and Market Dynamics
Once data is collected, Market Research Analysts dive deep into analyzing consumer behavior and prevailing market trends. This involves sifting through datasets to identify patterns, correlations, and anomalies that can shed light on why consumers make certain purchasing decisions. They might explore demographic data, purchasing habits, lifestyle choices, and psychographic profiles to build a comprehensive picture of different consumer segments.
Understanding market trends involves monitoring industry shifts, technological advancements, economic indicators, and even cultural changes that could impact consumer preferences and demand. For example, an analyst might track the rise of sustainable products in a particular market or the growing preference for online shopping over brick-and-mortar stores. This analysis helps companies anticipate future market needs and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Leveraging customer insights is key to this process. Courses focused on customer analytics and behavior can provide the tools and frameworks needed for this type of analysis.
To further explore the intricacies of consumer behavior and market analysis, consider these insightful books.
Translating Data into Actionable Insights for Stakeholders
A critical function of a Market Research Analyst is not just to analyze data, but to translate those findings into clear, actionable insights that stakeholders can understand and use to make decisions. This requires strong communication and presentation skills, as analysts often need to explain complex statistical concepts and research results to non-technical audiences.
Analysts prepare comprehensive reports, dashboards, and presentations that summarize key findings, highlight important trends, and provide data-driven recommendations. For example, if research indicates a growing demand for a specific product feature, the analyst will present this finding along with an assessment of the market opportunity and potential ROI. They might use charts, graphs, and other visual aids to make the information more accessible and impactful.
The ultimate goal is to empower stakeholders – whether they are marketing managers, product developers, or senior executives – to make strategic choices that are grounded in solid market evidence. This could involve decisions about new product launches, marketing campaign adjustments, pricing strategies, or market entry plans.
Effectively communicating findings often involves data visualization. Learning tools like Power BI or Tableau can be invaluable for creating compelling reports and dashboards.
Monitoring Competitors and Broader Industry Developments
Keeping a close watch on competitors and broader industry shifts is another vital responsibility for Market Research Analysts. This involves systematically gathering intelligence on competing products, services, marketing tactics, pricing, and market positioning. By understanding what competitors are doing, businesses can identify opportunities to differentiate themselves, anticipate competitive threats, and refine their own strategies.
Analysts also monitor wider industry developments, such as emerging technologies, regulatory changes, economic fluctuations, and evolving consumer expectations that could impact the market. For instance, the rise of e-commerce has fundamentally changed the retail landscape, and analysts would track this trend to advise businesses on how to adapt their sales and distribution strategies. Staying informed about these macro-level changes helps companies remain agile and proactive rather than reactive.
This continuous monitoring ensures that the business has an up-to-date understanding of its operating environment, enabling it to make timely adjustments and maintain a competitive edge.
Analyzing competitive landscapes and market opportunities requires a strategic mindset. Courses on competitive analysis and market opportunity assessment can enhance these skills.
Essential Skills and Competencies for Success
To thrive as a Market Research Analyst, a specific blend of technical prowess and soft skills is necessary. These competencies enable analysts to not only perform the analytical aspects of the job but also to effectively communicate their findings and contribute to strategic decision-making. Excelling in this field means being comfortable with numbers, adept at critical thinking, and skilled in conveying complex information in an accessible manner.
Many of these skills can be honed through dedicated study and practice. For individuals looking to transition into this field, focusing on developing these core competencies can significantly enhance their preparedness and attractiveness to potential employers. Even for seasoned professionals, continuous skill development is key to staying relevant in a rapidly evolving industry.
Mastering Data: Statistical Analysis and Visualization
A cornerstone of a Market Research Analyst's skillset is proficiency in statistical analysis and data visualization. Analysts must be adept at using statistical software packages such as R, SPSS, or even advanced Excel functions to dissect data, identify significant patterns, and test hypotheses. This includes understanding concepts like regression analysis, sampling techniques, and significance testing to ensure the validity and reliability of their findings.
Equally important is the ability to visualize data effectively. Tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Python libraries (e.g., Matplotlib, Seaborn) allow analysts to transform complex datasets into intuitive charts, graphs, and dashboards. These visual representations are crucial for communicating insights to stakeholders who may not have a statistical background, making it easier for them to grasp key trends and make informed decisions. Strong data visualization skills turn numbers into compelling narratives.
For those looking to build or strengthen their analytical and visualization capabilities, numerous online courses offer comprehensive training in these areas.
Developing a strong foundation in statistical methods is critical. These books offer in-depth knowledge of statistical learning and its applications.
Thinking Critically and Solving Complex Problems
Beyond crunching numbers, Market Research Analysts must possess strong critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. They are often faced with ambiguous business questions or complex market challenges that require careful deconstruction and analysis. Critical thinking enables them to evaluate information from various sources, identify underlying assumptions, and assess the validity of different arguments or interpretations.
Problem-solving skills come into play when designing research methodologies to address specific business objectives, troubleshooting issues during data collection, or interpreting unexpected findings. Analysts need to be resourceful and creative in finding ways to gather the right data and extract meaningful insights, even when faced with limitations or incomplete information. This involves not just identifying problems, but also proposing viable solutions and recommendations based on their research.
These skills are often developed through experience but can also be sharpened through targeted training. Courses that focus on analytical reasoning and strategic problem-solving can be highly beneficial.
Bridging the Gap: Communicating Complex Findings Effectively
The ability to communicate complex research findings to diverse audiences, especially those without a technical background, is a crucial skill for Market Research Analysts. It's not enough to have brilliant insights; analysts must be able to convey them in a clear, concise, and compelling manner to drive action. This involves both written and verbal communication skills, from crafting well-structured reports to delivering engaging presentations.
Analysts often act as storytellers, using data to weave narratives that explain market dynamics, consumer behavior, or competitive threats. They need to tailor their communication style to the specific audience, avoiding jargon where possible and focusing on the implications of their findings for the business. Strong presentation skills, including the effective use of visual aids, are essential for making a lasting impact and ensuring that research results are understood and acted upon.
Improving communication abilities can significantly enhance an analyst's effectiveness. Consider courses that focus on business reporting and presentation skills.
Navigating the Tech Landscape: CRM Tools and Databases
Familiarity with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools and databases is increasingly important for Market Research Analysts. CRM systems, such as Salesforce or HubSpot, house vast amounts of customer data, including purchase history, interactions, and demographic information. Analysts often tap into these databases to segment customers, analyze buying patterns, and understand customer lifetime value.
Proficiency in querying databases using languages like SQL is a valuable asset, allowing analysts to extract and manipulate data efficiently. Understanding database structures and data management principles also helps ensure data quality and integrity. As businesses collect more and more data, the ability to navigate and leverage these data repositories effectively is becoming a core competency for market research professionals.
Online courses can provide practical training in SQL and database management, as well as an introduction to popular CRM platforms.
Understanding how to work with large datasets is crucial. This book provides a helpful overview of data sources.
Formal Education Pathways to Becoming a Market Research Analyst
Embarking on a career as a Market Research Analyst typically begins with a solid educational foundation. While specific requirements can vary by employer and role complexity, a bachelor's degree is generally considered the entry-level standard. For those aspiring to more specialized or leadership positions, an advanced degree can provide a significant advantage.
The educational journey often emphasizes a blend of analytical skills, research methodologies, and business acumen. Prospective analysts should seek out programs and coursework that provide both theoretical knowledge and practical application, ideally culminating in projects or theses that involve real-world data and industry-relevant questions.
Laying the Groundwork: Relevant Undergraduate Degrees
Several undergraduate degree paths can pave the way for a career as a Market Research Analyst. Degrees in Marketing are a common choice, as they provide a strong understanding of consumer behavior, branding, and promotional strategies. Psychology degrees can also be highly relevant, offering insights into human cognition, motivation, and decision-making processes, which are crucial for understanding consumer choices.
Economics degrees equip students with analytical frameworks for understanding market dynamics, supply and demand, and economic trends – all vital for market assessment. Statistics or Mathematics degrees provide the rigorous quantitative skills necessary for data analysis and modeling. Increasingly, degrees in Data Science or Business Analytics are also becoming popular entry points, as they directly teach the technical skills required for handling and interpreting large datasets. Communications or Social Sciences degrees, when supplemented with analytical coursework, can also offer a good foundation, particularly for qualitative research roles.
Regardless of the specific major, aspiring analysts should seek out courses that cover research methods, statistics, data analysis, and business principles. Gaining experience with relevant software tools during undergraduate studies is also highly beneficial.
These courses offer a glimpse into the economic principles and analytical skills that are foundational for market research.
Reaching Higher: Advanced Degrees for Specialized Roles
For those aiming for more specialized roles, research leadership positions, or a deeper dive into complex analytical techniques, pursuing an advanced degree is often a valuable step. A Master of Business Administration (MBA) with a concentration in marketing or business analytics is a popular choice, as it combines advanced business strategy with specialized market research skills. A Master of Science (MS) in Marketing Research, Market Research and Consumer Insights, Business Analytics, Data Science, or Statistics can provide more focused, technical expertise.
These advanced programs typically offer coursework in areas like advanced statistical modeling, qualitative research methods, consumer psychology, data mining, and marketing strategy. Many also include opportunities for hands-on projects, internships, or thesis work, allowing students to apply their learning to real-world problems and build a professional portfolio. [v7loof] An advanced degree can not only enhance technical capabilities but also signal a higher level of commitment and expertise to potential employers, often leading to higher starting salaries and more significant career advancement opportunities.
For individuals considering a deeper academic pursuit, courses that provide an introduction to research methodologies at a graduate level can be beneficial.
For those interested in the strategic application of market research, these books offer valuable insights into innovation and market dynamics.
The Building Blocks: Coursework in Research Methods and Analytics
Regardless of the specific degree, coursework that emphasizes research methods and analytics is fundamental for aspiring Market Research Analysts. Core subjects typically include statistics, covering topics from basic descriptive statistics to more advanced inferential techniques like regression analysis and hypothesis testing. [clwx8x, 2] Understanding these statistical principles is essential for designing sound research, analyzing data accurately, and drawing valid conclusions. [clwx8x]
Courses in research methodology are also critical. These teach students how to formulate research questions, design studies (both qualitative and quantitative), develop sampling plans, create effective survey instruments, and conduct interviews or focus groups. [1uq4eb, 42paf3] Exposure to data analysis software, such as Excel, SPSS, R, or Python, is often integrated into this coursework, providing students with hands-on experience in data manipulation and analysis. [p6d8mr, pfqo74]
Furthermore, courses in Marketing principles, consumer behavior, and business strategy provide the contextual understanding needed to apply research findings effectively in a business setting. The goal is to produce well-rounded analysts who not only possess technical skills but also understand the business implications of their work.
Online learning platforms offer a wealth of courses to build these essential skills, from foundational statistics to applied marketing research techniques.
Bridging Theory and Practice: Capstone Projects and Industry Partnerships
Capstone projects and theses provide invaluable opportunities for students to apply their accumulated knowledge and skills to a significant research question or business problem. These projects often require students to go through the entire research process, from defining the problem and designing the methodology to collecting and analyzing data, and finally, presenting their findings and recommendations. [go1zir] This hands-on experience is highly valued by employers as it demonstrates practical application of theoretical concepts.
Industry partnerships can further enhance the educational experience. Some academic programs collaborate with businesses to offer students real-world projects, internships, or case studies. These partnerships allow students to work on actual market research challenges faced by companies, gain exposure to industry practices, and network with professionals in the field. Such experiences not only enrich learning but also make graduates more competitive in the job market by providing tangible evidence of their abilities.
Engaging in a capstone project that aligns with industry needs can be a significant resume builder. Look for courses that offer such practical, culminating experiences.
Online and Self-Directed Learning: Forging Your Own Path
The rise of online learning has opened up numerous avenues for individuals to acquire the skills needed for a career as a Market Research Analyst, regardless of their current profession or geographical location. Whether you are looking to build foundational knowledge, upskill in specific analytical techniques, or earn a certification, online courses offer flexibility and accessibility. This path is particularly appealing for career pivoters, working professionals seeking to enhance their skillset, and international learners who may not have access to traditional academic programs in this field.
Self-directed learning, often supplemented by online resources, empowers individuals to take control of their educational journey. It allows for a personalized approach, where learners can focus on areas most relevant to their career goals and learn at their own pace. However, this path also requires discipline, motivation, and a proactive approach to building a comprehensive skillset and demonstrating proficiency to potential employers.
OpenCourser is a valuable resource for navigating the vast landscape of online courses. With its extensive catalog of courses from various providers, learners can easily search for specific skills or topics related to market research analysis, compare course content, and read reviews. Features like the "Save to list" button help organize potential courses, while the "Learner's Guide" offers tips on how to effectively learn online and structure a self-directed curriculum.
Building Foundational Analytics Skills Remotely
For those new to the field or looking to transition into a Market Research Analyst role, online courses provide an excellent way to build foundational analytics skills from anywhere in the world. Many platforms offer introductory courses in statistics, data analysis, and research methodologies, often taught by instructors from reputable universities or industry experts. [t9v98x] These courses typically cover essential concepts such as understanding data types, basic probability, descriptive statistics, and an introduction to data visualization.
Online learning allows individuals to grasp the fundamentals of Excel for data analysis, learn the basics of SQL for database querying, or even get started with programming languages like Python or R, which are increasingly used in market research. [p6d8mr, pfqo74] Project-based courses are particularly valuable, as they provide hands-on experience in applying analytical techniques to real or simulated datasets, helping to solidify understanding and build practical skills. [r62svb] The flexibility of remote learning means you can fit your studies around existing commitments, making it a viable option for those already in the workforce.
Consider these online courses to start building your core analytical capabilities:
To supplement your online learning, foundational books on data analysis and statistical methods can provide deeper understanding and alternative explanations of key concepts.
Certifications vs. Degree Equivalency in Hiring
A common question for self-directed learners and career changers is how online certifications compare to traditional degrees in the eyes of employers. While a formal degree, particularly from a reputable institution, often carries significant weight, industry-recognized certifications can also be valuable, especially when they demonstrate proficiency in specific, in-demand skills. Certifications in tools like Google Analytics, Tableau, Power BI, or in methodologies like survey design or data analysis with Python, can enhance a resume. [hn6eev]
For individuals without a directly relevant degree, a portfolio of projects (discussed in the next subsection) combined with relevant certifications can showcase practical abilities and dedication to the field. Some employers may prioritize demonstrated skills and real-world problem-solving capabilities over formal academic credentials, particularly for entry-level or junior analyst roles. However, for more senior or specialized positions, a relevant bachelor's or master's degree often remains a strong preference or requirement.
Ultimately, the "equivalency" is not always direct. Certifications are excellent for skill demonstration and specialization, while degrees often signify a broader and deeper foundational knowledge. A combination of relevant education (even if in an adjacent field), targeted certifications, and a strong portfolio often presents the most compelling case to hiring managers. OpenCourser's Learner's Guide offers articles on how to effectively earn and leverage online course certificates, including tips on adding them to your LinkedIn profile or resume.
These courses offer certifications that can be valuable additions to your professional profile:
Creating Portfolio Projects with Publicly Available Datasets
For aspiring Market Research Analysts, especially those taking a self-directed learning path, creating a portfolio of projects is crucial for demonstrating practical skills to potential employers. Publicly available datasets offer a wealth of opportunities to practice analytical techniques and showcase your abilities. Government agencies (like the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics or census bureaus of various countries), academic institutions, and platforms like Kaggle provide diverse datasets on topics ranging from consumer spending and economic indicators to social trends and public opinion.
A portfolio project could involve analyzing a dataset to identify market segments for a hypothetical product, forecasting sales trends based on historical data, or conducting a sentiment analysis of publicly available customer reviews. The key is to define a clear research question, apply appropriate analytical methods, visualize the findings effectively, and write a concise report summarizing the insights and recommendations, just as you would in a professional setting. Documenting your process, including the tools and techniques used (e.g., Excel for initial cleaning, Python for statistical modeling, Tableau for visualization), adds further credibility.
These projects not only provide tangible evidence of your skills but also give you talking points for interviews, allowing you to discuss your problem-solving approach and analytical thinking in concrete terms. Sharing these projects on platforms like GitHub or LinkedIn can further enhance your visibility to recruiters.
Many online courses include capstone projects or guided projects that can serve as excellent additions to your portfolio. Look for opportunities to work with real-world data and solve practical business problems.
Blending Online Learning with Networking Opportunities
While online learning offers incredible flexibility and access to knowledge, it can sometimes feel isolating. To maximize the benefits of a self-directed learning path, it's highly beneficial to blend online coursework with networking opportunities. Engaging with online communities, forums, or social media groups dedicated to market research, data analysis, or specific tools (like R or Python user groups) can provide support, allow you to ask questions, and help you learn from others' experiences.
Consider attending virtual conferences, webinars, or local meetups (if available) related to market research or data analytics. These events offer chances to learn about the latest industry trends, hear from experienced professionals, and make connections that could lead to mentorship or job opportunities. Some online courses also have active student forums or communities where you can interact with peers and instructors.
Networking is not just about finding job leads; it's also about continuous learning and staying motivated. Sharing your learning journey and portfolio projects with your network can also lead to valuable feedback and encouragement. Remember, building a career is not just about acquiring skills, but also about building relationships and becoming part of a professional community.
For those looking to make a career change, a supportive network can provide emotional support and practical advice during the transition. Ground yourself in the reality that breaking into a new field takes time and persistence, but with dedicated effort and a proactive approach to learning and networking, achieving your goals is certainly possible.
Career Progression and Advancement for Market Research Analysts
The career trajectory for a Market Research Analyst typically offers various avenues for growth and specialization. Starting from entry-level positions, analysts can advance to more senior roles with increased responsibilities, move into management, or transition into related fields that leverage their analytical and strategic thinking skills. Salary and responsibilities generally increase with experience, demonstrated expertise, and the ability to deliver impactful insights.
For those committed to this path, continuous learning and adaptation are key, as the tools, techniques, and market dynamics are always evolving. Building a strong track record of successful projects and developing leadership qualities can open doors to more significant opportunities.
Stepping In: Entry-Level Roles and What to Expect
Entry-level positions in market research often carry titles such as Research Assistant, Junior Analyst, Market Research Coordinator, or Data Analyst. [2oeaj8] In these roles, individuals typically support senior analysts and managers in various aspects of the research process. Responsibilities might include assisting with survey design, collecting and cleaning data, performing basic statistical analysis, preparing charts and tables for reports, and conducting background research on industries or competitors.
This stage is crucial for building foundational skills, gaining practical experience with research tools and methodologies, and understanding the day-to-day realities of the profession. It's a period of learning and development, where new analysts hone their analytical abilities, attention to detail, and communication skills under the guidance of more experienced colleagues. While a bachelor's degree in a relevant field like marketing, statistics, economics, or psychology is often the minimum requirement, internships or relevant project work can be a significant advantage.
Individuals starting in these roles should focus on being meticulous, asking questions, and demonstrating a strong work ethic. Building a solid understanding of different research techniques and software will set a strong foundation for future advancement.
These courses can provide a good starting point for those looking to enter the field and understand the initial phases of research work.
Moving Up: Mid-Career Transitions to Managerial or Specialized Positions
After gaining a few years of experience and demonstrating strong analytical and project management skills, Market Research Analysts can progress to mid-career roles. These might include titles like Senior Market Research Analyst, Market Research Manager, or specialized roles such as Consumer Insights Manager or Competitive Intelligence Analyst. [asu8hg] At this stage, responsibilities often expand to include leading research projects, managing junior analysts, developing research strategies, and presenting findings to higher-level management or clients.
Specialization is common at this stage. An analyst might focus on a particular industry (e.g., healthcare, technology, finance), a specific research methodology (e.g., qualitative research, advanced quantitative modeling), or a particular type of analysis (e.g., brand research, new product development research). Pursuing an advanced degree, such as an MBA or a Master's in Market Research, can be beneficial for those aiming for managerial or highly specialized roles, as it often provides deeper strategic insights and leadership skills.
Strong communication, leadership, and strategic thinking skills become increasingly important as analysts move into these more senior positions. The ability to not only conduct research but also to translate it into impactful business strategies is key to success.
For those looking to enhance their strategic marketing and analytical capabilities for mid-career advancement, these courses can be valuable.
Understanding marketing management and strategy is crucial for these roles. These books offer in-depth perspectives.
Expanding Horizons: Cross-Functional Moves into Product Management or Consulting
The skills and experience gained as a Market Research Analyst can open doors to various cross-functional roles. One common path is a transition into Product Management. Product Managers are responsible for guiding the success of a product and leading the cross-functional team that is responsible for improving it. The market understanding, consumer empathy, and data-driven decision-making skills honed by research analysts are highly valuable in this role, as product managers need to identify market needs, define product vision, and prioritize features based on customer feedback and market opportunities.
Another potential avenue is a move into Management Consulting. Consultants help organizations solve complex business problems and improve performance. Market research skills – such as problem definition, data collection and analysis, and the ability to synthesize information and present recommendations – are directly transferable to consulting. [tmo05v] Analysts with strong industry knowledge and strategic thinking capabilities can thrive in consulting environments, advising diverse clients on market entry, competitive strategy, or operational improvements.
These transitions often leverage the analyst's ability to understand market dynamics, interpret data, and communicate insights effectively. Such moves can offer new challenges, broader responsibilities, and often, further career and salary growth.
For those considering a move into related fields, these courses can provide relevant skills and insights.
Understanding Your Worth: Salary Benchmarks at Different Career Stages
Salaries for Market Research Analysts vary based on factors such as experience, education, industry, geographic location, and the size and type of the employing organization. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for market research analysts was $74,680 in May 2023. However, this is a median, and actual salaries can range significantly.
Entry-level analysts with a bachelor's degree might start in the $50,000 to $60,000 range, though this can be higher in high-cost-of-living areas or in high-demand industries. With a few years of experience (one to four years), salaries can increase to the $50,000s and $60,000s. Mid-career professionals (five to nine years of experience) often earn in the $60,000s to $80,000s or higher, particularly if they have specialized skills or managerial responsibilities. Senior analysts, managers, and those with advanced degrees (like an MBA or a specialized Master's) or extensive experience (10+ years) can command salaries well over $100,000, with the top 10 percent earning more than $137,040.
Industries such as publishing, finance and insurance, and management of companies and enterprises tend to offer higher median salaries for market research analysts. It's advisable to research salary benchmarks specific to your location and industry using resources like the BLS, Payscale.com, or Glassdoor.com to get a more precise understanding of potential earnings. The BLS also projects an 8% job growth for market research analysts from 2023 to 2033, which is faster than the average for all occupations, indicating continued demand in the field.
Industry-Specific Applications of Market Research
The principles and practices of market research are highly adaptable, finding critical applications across a multitude of industries. While the core objective – to understand markets and consumers – remains consistent, the specific focus, methodologies, and regulatory considerations can vary significantly depending on the sector. Understanding these nuances is crucial for analysts looking to specialize or work within particular industries.
From the fast-paced world of technology to the heavily regulated healthcare sphere, market research provides the insights necessary for innovation, compliance, and strategic growth. The versatility of market research skills means analysts can often find niches that align with their interests and expertise.
Navigating the Nuances: B2B vs. B2C Market Research
A fundamental distinction in market research lies between Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Consumer (B2C) contexts. B2C research focuses on individual consumers, their purchasing habits, motivations, and preferences for products and services like electronics, apparel, food, or entertainment. [fhajkm] Methodologies often involve large-scale surveys, focus groups with end-users, and analysis of retail data or social media trends. The goal is to understand individual decision-making processes, brand perceptions, and lifestyle trends. [fhajkm]
B2B research, on the other hand, targets organizations as the customer. This could involve understanding the needs of businesses for software solutions, industrial equipment, consulting services, or raw materials. [abried] The decision-making unit in B2B is often more complex, involving multiple stakeholders (e.g., procurement departments, technical experts, executives). Research methodologies might lean more towards in-depth interviews with key decision-makers, case studies of client organizations, and analysis of industry-specific data or trade publications. The sales cycles are typically longer, and purchasing decisions are often based on factors like ROI, efficiency gains, and long-term partnerships rather than purely emotional drivers. [abried]
While both B2B and B2C research aim to understand customer needs, the approach, sample sizes, data sources, and key influencing factors can differ substantially. Analysts often specialize in one area or adapt their skills to navigate both.
These courses provide insights into B2C marketing and consumer understanding, which are foundational for B2C market research.
For understanding B2B dynamics, this course offers valuable perspectives.
Specialized Fields: Regulatory Considerations in Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Market research in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries operates within a highly regulated environment, which significantly shapes research practices. [njzzxx] Analysts in this sector must have a keen understanding of regulations governing drug promotion, medical device marketing, patient data privacy (like HIPAA in the U.S.), and clinical trial reporting. Ethical considerations are paramount, especially when dealing with sensitive health information and vulnerable patient populations.
Research often focuses on understanding the needs of physicians, patients, and payers (insurance companies, government health programs). This can involve assessing the market potential for new drugs or medical devices, understanding treatment pathways, evaluating the effectiveness of patient support programs, or gauging physician prescribing behavior. [njzzxx, ohmj08] Methodologies might include surveys and interviews with healthcare professionals, patient journey mapping, and analysis of anonymized health data or clinical trial results.
The long development cycles and high costs associated with bringing new healthcare products to market mean that market research plays a critical role in informing investment decisions and ensuring that products meet genuine unmet medical needs. Analysts must be adept at navigating complex stakeholder environments and communicating findings in a way that is both insightful and compliant with regulatory standards. [y40v5c]
Courses focusing on the pharmaceutical industry and healthcare innovations can provide context for market research in this specialized area.
Expanding Reach: Global Market Entry Strategies for Tech Firms
For technology firms looking to expand into new international markets, market research is indispensable for developing effective entry strategies. [0owq7p] Analysts play a crucial role in assessing the attractiveness and viability of foreign markets, considering factors like market size and growth potential, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, cultural nuances, and consumer technology adoption rates. [s3ajfn] Understanding local consumer preferences, language differences, and purchasing behaviors is key to tailoring products and marketing messages effectively. [kdty3n]
Research might involve analyzing economic data, consumer surveys in target countries, competitor analysis of local and international players, and understanding local distribution channels and payment preferences. [kdty3n, altkid] For example, a tech firm considering launching a new app in Southeast Asia would need to research smartphone penetration, preferred mobile operating systems, local social media habits, and e-commerce trends in that region. [4su2de]
The insights from this research inform critical decisions about which markets to enter, how to adapt products for local needs (localization), what pricing strategies to adopt, and how to build brand awareness in a new cultural context. Global market research helps tech firms mitigate risks and maximize their chances of success when venturing abroad. [s3ajfn, v9yxgq]
Understanding international markets and consumer behavior in different cultural contexts is vital for global expansion.
For deeper insights into global marketing and economic factors, these resources are recommended.
Keeping Pace: Sustainability Trends Influencing Consumer Research
The growing global emphasis on sustainability is significantly influencing consumer behavior and, consequently, market research practices. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental and social impact of their purchasing decisions, leading to demand for more sustainable products, ethical sourcing, and transparent business practices. Market Research Analysts are tasked with understanding these evolving consumer attitudes and preferences related to sustainability. [fz08gq]
Research in this area might involve exploring consumer willingness to pay more for eco-friendly products, identifying key sustainability concerns (e.g., plastic waste, carbon footprint, fair labor practices), segmenting consumers based on their environmental consciousness, and assessing the credibility of corporate sustainability claims. [fz08gq] Analysts may use surveys, focus groups, and analysis of social media conversations to gauge public sentiment and identify emerging sustainability trends.
These insights help businesses develop and market products that align with consumer values, improve their environmental and social performance, and build brand reputation as responsible corporate citizens. As sustainability continues to be a major driver of consumer choice, market research in this domain will only grow in importance.
Understanding the intersection of consumer behavior and sustainability is becoming crucial for market researchers.
Ethical Challenges in the Realm of Market Research
The field of market research, while providing invaluable insights, is not without its ethical challenges. As analysts delve into consumer behavior, preferences, and personal data, they bear a significant responsibility to conduct their work with integrity, ensuring the privacy and well-being of research participants. Adherence to ethical guidelines and data protection regulations is paramount to maintaining public trust and the credibility of the research profession. [k6g3bu]
Navigating these ethical complexities requires a strong moral compass, a thorough understanding of relevant laws, and a commitment to transparency. From safeguarding data to avoiding manipulative practices, ethical considerations are woven into every stage of the market research process.
Guarding the Gates: Data Privacy Regulations (GDPR, CCPA)
Data privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States have profoundly impacted how Market Research Analysts collect, store, and process personal data. These regulations grant individuals greater control over their personal information, including the right to know what data is being collected, the right to access it, the right to have it deleted, and the right to opt-out of its sale or sharing.
For market researchers, compliance means implementing robust data protection measures, obtaining explicit and informed consent for data collection, and being transparent about how data will be used and for how long it will be retained. Anonymizing data wherever possible is a key strategy, as GDPR, for example, does not apply to truly anonymized data. Analysts must be meticulous in their data handling practices, ensuring data security and adhering to the principles of data minimization (collecting only necessary data) and purpose limitation (using data only for the stated research purposes). Understanding and navigating the specific requirements of regulations like GDPR and CCPA is crucial to avoid significant penalties and maintain ethical standards.
Many organizations offer resources to help understand these complex regulations. For instance, ESOMAR provides guidelines and checklists for GDPR compliance in the research sector.
The Pitfalls of Perception: Bias in Survey Design and Sampling
Bias in survey design and sampling methods can significantly compromise the validity and reliability of market research findings. Survey design bias can arise from poorly worded questions, leading questions that suggest a desired answer, or response scales that don't adequately capture the range of opinions. For example, if a question is framed in a way that makes one option seem more socially desirable, respondents might be swayed, leading to skewed results.
Sampling bias occurs when the sample of individuals selected for the research is not representative of the broader target population. This can happen if certain demographic groups are overrepresented or underrepresented due to the sampling method used (e.g., relying solely on online panels might exclude individuals with limited internet access). [07duje] If the sample is biased, the research findings cannot be accurately generalized to the entire population, leading to flawed conclusions and potentially misguided business decisions.
Market Research Analysts have an ethical responsibility to strive for objectivity and minimize bias in their research. This involves careful attention to questionnaire design, rigorous sampling techniques, and transparency about any potential limitations in the data or methodology. Recognizing and mitigating these biases is crucial for producing credible and trustworthy research. [07duje]
Understanding how to design unbiased research and select representative samples is a core skill. These resources can provide a solid foundation.
The Balancing Act: Corporate Interests and Consumer Protection
Market Research Analysts often find themselves navigating the delicate balance between serving their corporate clients' interests and protecting the rights and welfare of consumers. Businesses fund market research with the aim of improving their products, increasing sales, and gaining a competitive advantage. While these are legitimate business goals, the pursuit of these goals must not come at the expense of ethical treatment of consumers.
Ethical dilemmas can arise when there's pressure to produce certain findings or when research methodologies could be perceived as intrusive or manipulative. For example, using deceptive practices to recruit participants or misrepresenting research findings to fit a desired narrative would be clear ethical violations. Analysts must uphold their professional integrity, ensuring that research is conducted honestly and that findings are reported accurately, even if they are not what the client hoped to hear.
Consumer protection involves ensuring informed consent, safeguarding privacy, avoiding harm (psychological or otherwise), and being transparent about how research data will be used. Maintaining this balance is crucial for the long-term credibility of both the individual analyst and the market research industry as a whole. Ethical guidelines from professional organizations can provide valuable frameworks for navigating these situations.
Exploring case studies in marketing ethics can provide real-world examples of these challenges and how they can be addressed.
record:31
record:32
record:41
Exploring the Boundaries: Case Studies of Ethical Dilemmas
Examining case studies of ethical dilemmas in market research can provide valuable learning opportunities and highlight the complexities involved in making ethical decisions. These real-world or hypothetical scenarios can illustrate the potential consequences of unethical practices and showcase best practices for navigating challenging situations. For example, a case study might explore a situation where a company is tempted to use data collected for one purpose for an entirely different marketing campaign without obtaining further consent, raising issues of transparency and purpose limitation.
Another case might involve a research firm facing pressure from a client to alter research findings to present a more favorable picture. Such cases underscore the importance of researcher integrity and the ethical obligation to report data accurately. Case studies can also delve into dilemmas related to researching vulnerable populations (e.g., children, individuals with cognitive impairments), where extra care must be taken to ensure informed consent and avoid exploitation.
Discussing these cases helps analysts develop their ethical reasoning skills and prepare for potential challenges they might encounter in their careers. Many academic programs and professional development resources use case studies as a tool for ethics education. Analyzing these scenarios helps to internalize ethical principles and understand their practical application in the day-to-day work of a Market Research Analyst.
You can explore various collections of business ethics case studies online to deepen your understanding. Resources from universities like the University of Texas at Austin's Ethics Unwrapped program or the Markkula Center for Applied Ethics at Santa Clara University offer a wide range of examples.
The Evolving Landscape: Future of Market Research Analysis
The field of market research analysis is in a constant state of evolution, driven significantly by technological advancements and changing economic landscapes. Professionals in this area must be adaptable and continuously update their skills to remain effective and relevant. The future promises both exciting opportunities and new challenges as data becomes more abundant and analytical tools grow more sophisticated.
Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for anyone considering a career as a Market Research Analyst, as well as for current practitioners looking to future-proof their expertise. The ability to embrace new technologies while upholding ethical standards will be a defining characteristic of successful analysts in the years to come.
The Rise of Machines: AI/ML Automation of Routine Tasks
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are increasingly being integrated into market research, automating many routine and time-consuming tasks. This includes automating aspects of data collection, data cleaning, and even initial data analysis. For example, AI-powered tools can sift through vast amounts of text data from social media or online reviews to identify key themes and sentiment much faster than manual methods. Survey programming and the generation of basic reports can also be streamlined through AI, freeing up analysts' time.
While some may view automation as a threat to job security, many experts believe that AI and ML will augment the role of Market Research Analysts rather than replace them entirely. By handling repetitive tasks, these technologies allow analysts to focus on more strategic activities, such as interpreting complex findings, developing nuanced insights, understanding context, and providing strategic recommendations that require human judgment and creativity. The key will be for analysts to learn how to effectively leverage these AI tools to enhance their work and deliver greater value.
Online courses are emerging that focus on the application of AI in market research and data analysis, which can help professionals adapt to these changes.
Seeing into Tomorrow: Increasing Demand for Predictive Analytics
There is a growing demand for Market Research Analysts who can move beyond descriptive analysis (what happened) and diagnostic analysis (why it happened) to predictive analytics (what is likely to happen next). Businesses are increasingly looking for forward-looking insights that can help them anticipate market shifts, forecast consumer demand, and proactively identify opportunities and threats. Predictive modeling techniques, often powered by machine learning algorithms, are used to analyze historical data and identify patterns that can be used to make forecasts about future behavior or trends.
For example, an analyst might use predictive analytics to forecast the sales of a new product based on pre-launch interest and historical data from similar products, or to predict which customers are most likely to churn based on their past behavior. This capability allows companies to make more informed strategic decisions, optimize marketing spend, and manage inventory more effectively. As data sources become richer and analytical tools more sophisticated, the ability to provide accurate and actionable predictions will be a highly valued skill for Market Research Analysts.
Courses focusing on predictive modeling and forecasting are essential for analysts looking to develop these in-demand skills.
The Mind's Frontier: Ethical Implications of Neuromarketing Technologies
Neuromarketing, which uses neuroscientific methods to study consumer responses to marketing stimuli, presents a new frontier with significant ethical implications. Techniques such as EEG (electroencephalography), fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging), eye-tracking, and facial coding aim to uncover subconscious reactions to advertisements, product designs, or brand messaging that traditional surveys might not capture. While these technologies can offer deeper insights into consumer preferences and emotional engagement, they also raise concerns about manipulation, privacy, and informed consent.
Ethical questions abound: To what extent is it permissible to tap into consumers' subconscious to influence their purchasing decisions? How can informed consent be truly obtained when the techniques probe non-conscious responses? What are the safeguards against using these insights to exploit vulnerable consumers or create overly persuasive (and potentially misleading) marketing? As these technologies become more accessible, the market research industry, regulators, and ethicists will need to establish clear guidelines and ethical frameworks to ensure responsible use.
Market Research Analysts working with or encountering neuromarketing data will need to be acutely aware of these ethical considerations and advocate for practices that respect consumer autonomy and privacy.
Understanding the ethical dimensions of these advanced techniques is crucial. This course touches upon neuromarketing and its principles.
Riding the Waves: Impact of Global Economic Shifts on Research Priorities
Global economic shifts, such as recessions, inflation, changes in international trade policies, or the rise of new economic powers, significantly impact market research priorities. During economic downturns, for example, businesses may become more cost-conscious, leading to increased demand for research that identifies ways to optimize marketing spend, understand changing consumer spending habits (e.g., a shift towards value brands), or assess the risk of market contraction. [altkid]
Conversely, periods of economic growth or the emergence of new markets might spur demand for research focused on market entry strategies, understanding new consumer segments, or assessing opportunities for product innovation. [altkid, 75zt5z] Geopolitical events and changes in international relations can also influence research agendas, particularly for companies with global operations, requiring analysts to assess political risk, changes in consumer sentiment towards foreign brands, or shifts in supply chain dynamics. [75zt5z]
Market Research Analysts need to stay attuned to these macroeconomic trends and understand how they might affect consumer behavior and business strategies in the industries they cover. The ability to interpret economic indicators and incorporate them into market analysis will be increasingly important for providing relevant and timely insights to clients and stakeholders. [3fgj1e, ysgjxh]
Courses that explore the global economy and international business can provide valuable context for understanding these shifts.
Frequently Asked Questions (Career Focus)
Embarking on or navigating a career path often comes with many practical questions. This section aims to address some of the common queries aspiring and current Market Research Analysts might have regarding salary, career advancement, industry demand, work environment, and transitioning from related fields.
What are the typical entry-level salary ranges for Market Research Analysts?
Entry-level salary ranges for Market Research Analysts can vary based on several factors including geographic location, the size and type of the company, the specific industry, and the candidate's educational background and relevant internships or experience. In the United States, those starting in the field with a bachelor's degree might expect salaries generally ranging from $50,000 to $60,000 annually. However, in high-cost-of-living metropolitan areas or in industries with high demand for analysts, starting salaries could be higher. Conversely, in smaller markets or less data-intensive sectors, they might be slightly lower. It's always a good idea to research salary data specific to your region and target industry using resources like the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics or online salary aggregators.
Is it possible to advance in a market research career without an advanced degree?
Yes, it is certainly possible to advance in a market research career without an advanced degree, though an advanced degree can sometimes accelerate progression or open doors to more specialized or senior leadership roles. Many successful Market Research Analysts build their careers through a combination of a bachelor's degree, continuous on-the-job learning, professional certifications, and a strong track record of delivering impactful insights. Advancement often depends on demonstrated skills in data analysis, critical thinking, communication, project management, and the ability to translate research findings into actionable business strategies.
As analysts gain experience, they can take on more complex projects, mentor junior team members, and move into senior analyst or project manager positions. Specializing in a particular industry or research methodology can also create pathways for advancement. While a master's degree (like an MBA or an MS in Market Research/Analytics) can be an asset, particularly for higher-level management or highly technical roles, strong performance and a commitment to ongoing professional development are key drivers of career growth regardless of academic qualifications.
Which industries currently show the highest demand growth for Market Research Analysts?
The demand for Market Research Analysts is robust across many sectors, as businesses increasingly rely on data to make informed decisions. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, overall employment for market research analysts is projected to grow 8 percent from 2023 to 2033, which is faster than the average for all occupations. While specific high-growth industries can fluctuate with economic trends, sectors that heavily utilize data and analytics consistently show strong demand. These often include technology companies, consulting services, marketing and advertising agencies, finance and insurance, and healthcare.
The rise of "big data" and digital transformation means that industries involved in e-commerce, digital media, and online services also have a growing need for analysts who can interpret vast amounts of online consumer data. Furthermore, as sustainability and social responsibility become more prominent, there's an emerging demand for market research related to consumer attitudes towards ethical products and sustainable practices. [fz08gq]
What are the typical remote work opportunities available in the market research field?
Remote work opportunities for Market Research Analysts have become increasingly common, particularly as companies have adopted more flexible work arrangements and as the tools for remote collaboration and data analysis have improved. Many tasks involved in market research, such as data analysis, report writing, survey design, and online data collection, can be performed effectively from a remote location.
Job boards and company career pages frequently list remote or hybrid positions for Market Research Analysts, ranging from entry-level to senior roles. Companies that are fully remote or have a distributed workforce are natural fits for such opportunities. Even traditional office-based companies may offer remote work options for experienced analysts or for specific project-based work. However, some aspects of the role, like conducting in-person focus groups or client presentations, might still require some physical presence, depending on the specific job and company culture. It's important to clarify remote work policies during the job application and interview process.
How common is it for individuals to transition from academic research into a Market Research Analyst role?
Transitioning from academic research into a Market Research Analyst role is a viable and increasingly common career path. Academic researchers, particularly those in fields like psychology, sociology, economics, statistics, and other social sciences, develop many transferable skills that are highly valued in market research. These include expertise in research design, quantitative and qualitative data collection methods, statistical analysis, critical thinking, and the ability to synthesize complex information and write detailed reports. [tmo05v]
To make a successful transition, academic researchers may need to reframe their experience to highlight its relevance to business problems and demonstrate an understanding of marketing principles and commercial objectives. Networking with professionals in the market research industry, tailoring resumes to emphasize business-oriented skills, and potentially undertaking short courses or certifications in marketing or specific analytical tools can be beneficial. Highlighting experience with data analysis software (e.g., SPSS, R, Python) and any projects involving survey design or large dataset analysis will also strengthen their candidacy. The key is to bridge the gap between academic rigor and the practical, fast-paced, and business-driven nature of market research.
This course can help bridge the gap between academic problem-solving approaches and those used in a business consulting context, which shares similarities with market research.
What is the likely impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on job security for Market Research Analysts?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to significantly transform the market research field, automating many routine tasks, but it is more likely to augment the role of Market Research Analysts rather than lead to widespread job displacement. AI can enhance efficiency in areas like data collection, basic data processing, sentiment analysis from large text volumes, and even initial pattern identification. This automation can free up analysts to focus on higher-value activities that require human critical thinking, creativity, contextual understanding, and strategic insight – skills that AI currently cannot replicate.
The demand for analysts who can interpret AI-generated outputs, ask the right strategic questions, design research that addresses complex human behavior, and communicate nuanced insights to stakeholders will likely remain strong, and may even increase. However, job roles will evolve. Analysts will need to develop skills in working alongside AI tools, understanding their capabilities and limitations, and integrating AI-driven insights into their broader analysis. Those who embrace these changes and continuously upskill will be best positioned for job security and career growth in an AI-influenced landscape. The focus may shift from manual data wrangling to more strategic interpretation and advisory functions.
Learning how AI is being applied in market research can be a proactive step. Consider exploring these resources:
Helpful Resources
For those looking to delve deeper into the field of Market Research Analysis or explore related educational opportunities, several resources can provide valuable information and guidance. Professional organizations, government labor statistics agencies, and comprehensive course catalogs are excellent starting points.
Professional Organizations
- ESOMAR: As a global community for data, research and insights professionals, ESOMAR offers a wealth of resources, including industry reports, ethical guidelines (like those for GDPR compliance), and professional development opportunities.
- Insights Association: This U.S.-based organization provides advocacy, resources, and certifications for market research and data analytics professionals. Their website includes information on legal and ethical standards, such as those related to the CCPA.
- American Marketing Association (AMA): The AMA offers resources, publications, and events for marketing professionals, including those specializing in market research.
Government Labor Statistics
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS): The BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook provides detailed information on Market Research Analysts, including job duties, education requirements, salary expectations, and job outlook. This is an excellent resource for career planning.
- CareerOneStop: Sponsored by the U.S. Department of Labor, CareerOneStop offers career exploration tools, training information, and local job data, including profiles for Market Research Analysts and Marketing Specialists.
- Statistics Canada / Emploi et Développement social Canada: For those in Canada, these government resources offer insights into the Canadian labor market, including job descriptions and outlooks for roles related to market research and business development.
Online Learning Platforms and Course Catalogs
- OpenCourser: As a comprehensive catalog of online courses and books, OpenCourser allows you to search for and compare educational resources related to market research, data analysis, statistics, and specific software tools from a wide array of providers. You can explore courses in Marketing, Data Science, and Business to find relevant learning paths.
- Coursera, edX, Udemy, and other MOOC Platforms: These platforms host a vast number of courses, from university-level programs to skill-specific bootcamps, covering many of the essential competencies for Market Research Analysts. Many of the courses referenced in this article are available through such platforms.
Industry Publications and Blogs
- GreenBook: Offers articles, webinars, and reports on trends and innovations in the market research industry.
- Quirk's Marketing Research Review: A leading publication featuring articles, case studies, and directories for marketing research professionals.
- Various Market Research Company Blogs: Many market research firms and analytics software providers publish blogs with valuable insights, tips, and discussions on current trends and best practices in the field.
Exploring a career as a Market Research Analyst is a journey into a dynamic and impactful field. By understanding the core responsibilities, developing essential skills, and staying attuned to industry trends, individuals can forge a rewarding path. Whether you are just starting, considering a career pivot, or looking to advance, the resources and information available can help guide your decisions. Remember that continuous learning and a proactive approach are key to navigating the exciting and ever-evolving world of market research. We hope this comprehensive overview has provided you with the clarity and encouragement to explore your potential in this exciting career.